Contents
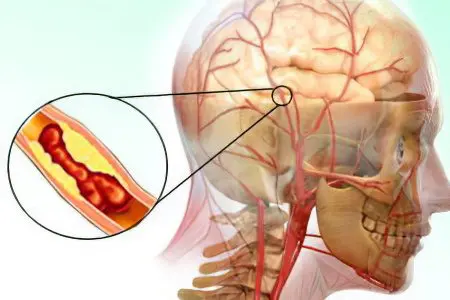
The vessels of the human body are subject to aging in the same way as other tissues. Metabolism slows down, due to age-related changes, blood clotting increases. The presence of somatic diseases exacerbates the situation. As a result, an elderly person develops thrombosis – the formation of blood clots in the vessels, completely or partially blocking the blood flow.
A blood clot can provoke a myocardial infarction, stroke or cerebral infarction, and other equally serious problems. To provide such a patient with effective assistance, a method of thrombolysis, or thrombolytic therapy (TLT), has been developed. The essence of the technique with which you can save a life and carry out a complete recovery is to remove a blood clot in the most radical way.
Types of thrombolytic therapy:
Selective thrombolysis. A drug that dissolves blood clots is injected into the pool of the damaged artery. The method can be applied no later than 6 hours from the moment of blockage of the vessel by a thrombus.
Non-selective (intravenous) thrombolysis. The method is applied no later than 3 hours after the vascular accident.
Thrombolysis in cerebral infarction
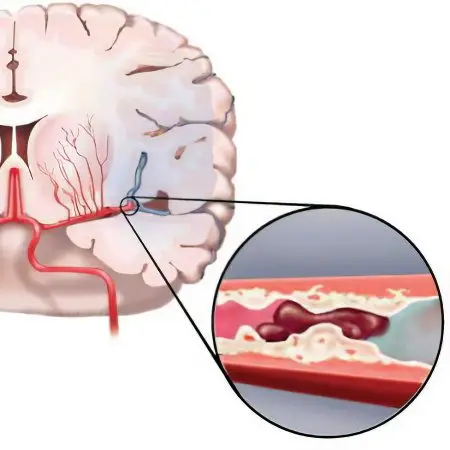
Stroke, or acute cerebrovascular accident, which causes major neurological complications, sounds like a death sentence for many patients. Until recently, in Russia during the first month, at least 50% of patients died, most of the survivors lost their ability to work and became disabled.
In countries where thrombolytic therapy is used, mortality from ischemic stroke does not reach 20%. The remaining patients restore the functioning of the central nervous system.
The thrombolysis procedure is not very difficult. It consists in introducing special enzymes into the vessel that dissolve the clot.
Contraindications for TLT:
Available at the time of thrombolysis, bleeding of any localization, since not only thrombi of a pathological nature are subject to dissolution, but also those that have formed to protect against blood loss during bleeding.
Aortic dissection.
Tumors of brain tissue of any etiology.
Arterial hypertension.
Diseases of the liver.
Pregnancy.
hemorrhagic stroke.
History of brain surgery.
Thrombolytic therapy is carried out in patients of any age. Some contraindications are relative, the most important among them is bleeding. If there is bleeding, thrombolysis is not performed.
To carry out this important event, it is important to meet the time allotted for TLT – 3-6 hours from the onset of a stroke. It is important to pay attention to its signs in a timely manner:
Numbness of a limb on one side of the body;
Articulation disorders;
The inability to make the simplest facial movements with the muscles of one half of the face.
The simplest test for determining the onset of a stroke is to ask the patient to stretch their arms and say something. If he cannot do this, urgent medical assistance is required, because there is not much time left to save a person!
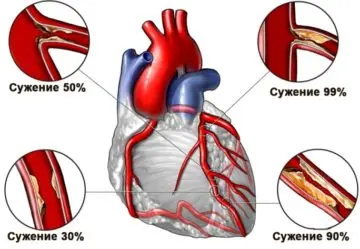
Heart and thrombolysis

As a result of blockage of a coronary vessel by a thrombus, a patient develops a myocardial infarction.
This process does not occur spontaneously, it is preceded by general disturbances:
Slowing down of blood flow;
Reduction in the blood content of heparin and fibrinolysin, which have an anticoagulant effect;
Increase in the content of blood coagulation components;
Ulceration of atherosclerotic plaques;
Roughness of the inner wall of the vessel;
Slowing down the flow of blood, thickening it.
In case of myocardial infarction, to restore the blood supply to the heart muscle, it is necessary to remove the blood clot that clogged the coronary vessel in a timely manner. If you do not first conduct a thorough examination of the patient, the procedure is fraught with complications.
Necessary studies to determine the localization of the thrombus and clarify the site for drug administration:
duplex scanning;
Angiography;
CT (computed tomography);
Doppler ultrasound.
A comprehensive study helps to reduce the risk of complications many times over.
For urgent indications, the cardiology ambulance team can perform thrombolysis on an emergency basis to save the patient’s life. The duration of the procedure takes from 10 minutes to 2 hours. Just as in the relief of the effects of a stroke, bleeding is the most important contraindication.
The cost of a complex of drugs for thrombolytic therapy can reach up to 50-60 thousand rubles, but these costs are included in the health insurance rates.
Thrombolysis Methods
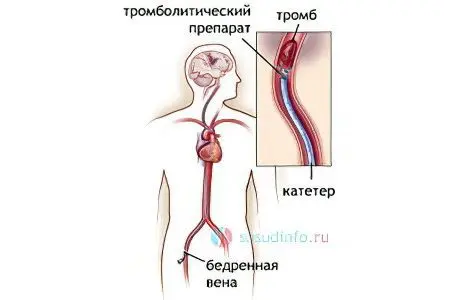
There are two main ways to carry out thrombolytic therapy:
System method – drugs are injected into a vein without taking into account the localization of the thrombus, they reach the blood clot and begin to dissolve it. To increase the effectiveness of the systemic method, a high concentration of the drug is required, which negatively affects the circulatory system.
local method – drugs are injected much more accurately than in the previous method, directly into the area of blockage of the vessel. For this, a catheter is used that moves through the vein, so the method is called catheter thrombolysis. This minimally invasive procedure is controlled by x-rays. It is used even with relative contraindications.
What is used in thrombolysis?
Preparations for thrombolytic therapy:
Streptokinase. One of the cheap thrombolytics, not very compatible with the human body, often causes allergic reactions. For effective action, slow administration of Streptokinase is required, the drug can cause hemorrhagic complications.
Urokinase. A protein found in small amounts in urine, tissues and organs of the human body. It has a higher cost compared to Streptokinase. When using Urokniase, simultaneous intravenous administration of Heparin is required.
Anistreplase. It has a high cost, it is injected in a stream, intravenous administration of Heparin is not required.
Alteplase. It has a high cost, provokes cerebral hemorrhages. The use of Alteplase improves patient survival.
Complications after thrombolytic therapy
The most common complication of thrombolysis is the occurrence of bleeding of varying intensity, from minor to massive and voluminous. May cause a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Other complications:
Heart failure, manifested by a violation of myocardial contraction;
Hemorrhagic stroke that occurs in elderly patients, as a side effect of streptokinase;
rash, fever, chills;
Various manifestations of allergy to the components of the drugs;
Reperfusion arrhythmia – occurs in 50% of patients;
Coronary artery reocclusion – occurs in 20% of patients.
Thrombolysis before hospitalization
Even a healthy person may show signs of impaired cerebral blood supply:
Headache;
Decreased vision, cognitive functions;
Dizziness.
These symptoms are a sign of the onset of the disease, especially if they occur in older people. In order not to miss fatal changes, you need to conduct the following studies:
Duplex scanning of the carotid arteries;
Ultrasound of the vessels of the brain;
Examination of coronary vessels;
MRI of the brain (indicated for patients with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, heart failure).
When the first signs of thrombosis appear, it is important to start thrombolysis in a timely manner, without waiting for the onset of a heart attack or stroke. This measure reduces in-hospital mortality by 17-19%, because “disease is easier to prevent than to cure.”
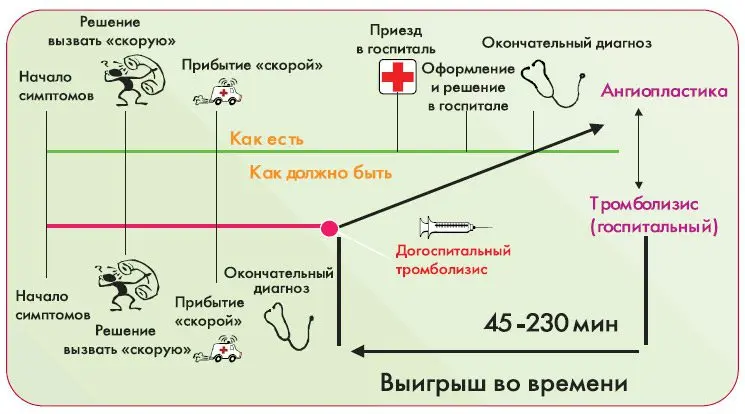
If thrombolytic therapy is available prior to hospitalization, it should be used. This requires qualified health workers, the ability to immediately conduct and decipher the cardiogram. Thrombolysis can be fully carried out within half an hour after examining the patient.
It is important to apply the method of thrombolytic therapy no later than 3-6 hours from the onset of the first symptoms. Delay in the use of TLT will lead to necrosis of myocardial cells and the cessation of the functioning of medulla cells.









