
Horseflies are a special kind of insects, the life cycle of which requires the blood of animals or humans, as well as their body. Reproduction of this species cannot be without these conditions. This is why all mammals and humans are so prone to being bitten by horseflies during the summer. Some species of these insects are popularly called horseflies.
Horsefly bite symptoms
Horseflies are a species of flies with a fairly large size. Therefore, it is very difficult not to notice his approach. But the tactics of these insects is very peculiar – while some individuals distract the prey, the second creep unnoticed or fly up to it, making a bite to suck blood and deposit larvae.
Due to the powerful sucking apparatus of gadflies and the aggressiveness of their saliva in relation to body tissues, it is impossible not to notice the very moment of the bite. It feels like a sharp burning pain at the site of the bite, accompanied by severe itching. In a short time, edema appears in the form of a nodule, which gradually spreads to the surrounding tissues. There is hyperemia (redness) of the skin, which causes burning and severe itching.
Allergic skin rashes can often occur, especially in people prone to allergies. With multiple bites, an increase in body temperature and general reactions in the form of general weakness and poor health are possible. Single bites never cause general reactions.
Edema from horsefly bite
One of the most important manifestations of a horsefly bite is edema. In its origin, the basic role belongs to the components of horsefly saliva, which enter the skin during a bite. The degree of development of edema depends on the specific type of insect and the immune activity of the organism.
The ingestion of antigens contained in saliva leads to a massive release of inflammatory factors by immunocompetent cells circulating in the intercellular space of the skin and its microvasculature. The severity of edema is determined by the initial number of responsible immune cells in the affected tissues (leukocytes, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes). All of them produce inflammatory mediators that disrupt vascular permeability, which causes the release of the liquid part of the blood into the tissues with the development of edema.
Clinically, edema after a horsefly bite in the first minutes of damage looks like a papule formed around a skin puncture. It spreads very quickly to the surrounding intact tissues. Usually swelling does not go beyond the affected segment. Edema after a horsefly bite persists for several days and is accompanied by reddening of the skin and severe itching. In rare cases, the papule does not turn into a widespread puffiness, but into a bump at the site of the bite.
Consequences of horsefly bites
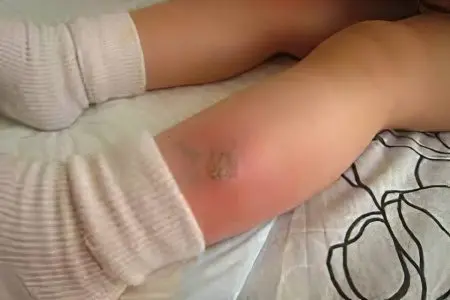
In typical cases, horsefly bites disappear without a trace after a few days. The only discomfort is the constant itching of the bitten place. But in some situations there are exceptions. The negative consequences of horsefly bites are:
Allergic reaction of a general type ( An allergic reaction can occur immediately after a bite, but cannot occur the next day. It manifests itself mainly as a skin rash. It disappears after a while on its own, and if you apply the appropriate treatment, then faster);
The formation of large and painful knots at the site of the bite (The formation of knots at the site of the bite is the result of bacteria entering the skin with infected horsefly saliva. Sometimes, horsefly larvae find themselves inside such knots, because in the classic version, bites are made by females to lay offspring.);
Infection and suppuration of the skin and soft tissues
Enlarged lymph nodes;
[Video] What to do if bitten by a gadfly / horsefly:









