In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
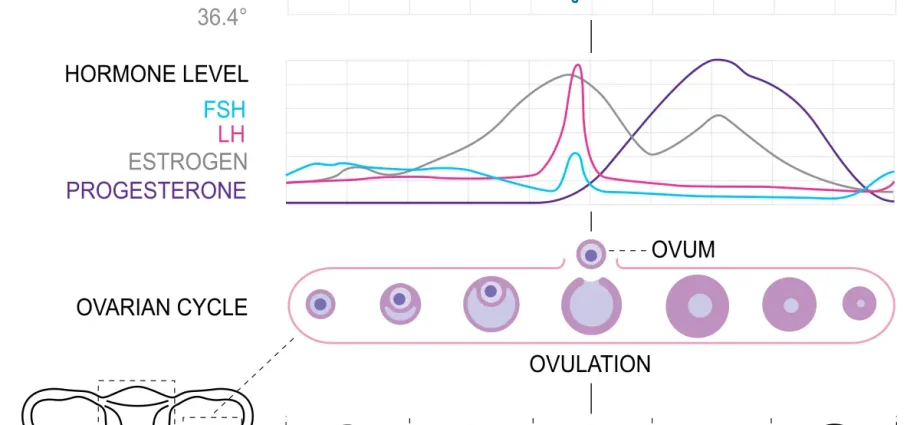
The luteal phase is one of the phases of a woman’s cycle. Simply calculating the day of the cycle does not guarantee that its start is correctly marked. This is the phase during which the woman’s body prepares to insert an egg into the uterus that has been fertilized. During this phase, an increase in progesterone concentration and symptoms of premenstrual tension are observed. The overwhelming majority of the luteal phase is infertile.
What is the luteal phase exactly?
The luteal phase is the last phase of the cycle and usually lasts 14 days. It begins when ovulation is completed. During the luteal phase, the ovary develops a yellow body. The cells in the woman’s body then store the nutrients to be used after the egg is fertilized. During the following days of the luteal phase, there is a high production of progesterone, which is to prevent fertilization. If fertilization does not occur, the amount of progesterone in her body decreases and her period begins. Determining the beginning of the luteal phase is extremely difficult, if only due to the fact that each woman may have a different length of the menstrual cycle.
One of the symptoms of starting the luteal phase is a change in the type of vaginal mucus. During ovulation, it is flexible, transparent, and its production is increased. During the luteal phase, the mucus changes its color and consistency to more watery, and there is less of it. Women who want to accurately mark the beginning of the luteal phase in their body are recommended to constantly and carefully observe it. It should be noted that the signals given by the body may change under the influence of climate change, diet, lifestyle or exposure to stress. Sometimes the symptoms of the luteal phase are confused with the early symptoms of pregnancy, especially if the length of the luteal phase is increased for some reason.
The determinant of the length of the luteal phase are individual hormonal tests checking the amount of progesterone. Too short a luteal phase in women may indicate fertility problems. Fortunately, proper nutrition has a large influence on the length of the luteal phase. Women who want to extend the length of the luteal phase in their cycle are advised to eat as much vegetables and fruit as possible while giving up products with high animal fat content. In addition, when trying to extend the luteal phase, the use of supplements with magnesium, calcium and B vitamins is proven.
Faza lutealna a progesterone
As mentioned earlier, during the luteal phase of a woman’s menstrual cycle, the concentration of progesterone, which is one of the most important female hormones, increases. In women, progesterone is produced in the adrenal glands. In men, this hormone is produced in the testes and adrenal glands. The increase in progesterone in women is manifested by a change in the color and consistency of the mucus, soreness and swelling of the breasts, as well as an increased temperature. Progesterone levels fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle. The lowest concentration of this hormone is observed in the first days of the cycle. It grows during ovulation, while the highest concentrations occur in the luteal phase. Progesterone is a hormone responsible for the maintenance of pregnancy – the higher its value during the “blessed state”, the greater the chances for its proper course and termination. Too high amounts of progesterone may indicate a multiple pregnancy.