Contents
The heart murmur
How is a heart murmur characterized?
Heart murmurs or murmurs are characterized by “unusual” noises heard during auscultation with a stethoscope during the beating of the heart. They are produced by turbulence in the flow of blood to the heart and can be caused by various pathologies.
Heart murmurs can be congenital, that is, present from birth, or develop later in life. Everyone can be affected: children, adolescents, adults and the elderly.
Often, heart murmurs are harmless. Some of them do not require treatment, others must be monitored to ensure that they are not hiding a more serious illness. If other symptoms are associated, including shortness of breath, enlarged neck veins, lack of appetite, or chest pain, murmurs may indicate a serious heart problem.
There are generally two types of heart murmurs:
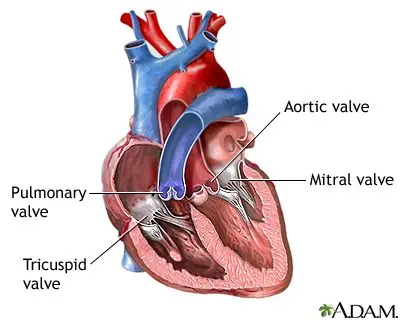
- systolic murmur, which appears when the heart contracts to expel blood to organs. It may be indicative of insufficient closure of the mitral valve, the heart valve that separates the left atrium from the left ventricle.
- diastolic murmur, which most often corresponds to a narrowing of the aorta. The aortic valves close poorly and this causes blood to flow back to the left ventricle.
What are the causes of a heart murmur?
In order to understand the origin of the heart murmur, the doctor will perform a heart ultrasound. This will allow him to quantify the extent of the damage to the heart valves and the consequences on the heart muscle.
If necessary, the doctor can also order other examinations such as a coronary angiography, which will allow him to visualize the coronary arteries.
The heart murmur can be functional (or innocent), that is to say that it does not result from any malformation and does not require special care or special treatment. In newborns and children, this type of heart murmur is very common and will most often go away during growth. It can also persist for life, but never cause health problems.
With a functioning heart murmur, the blood may be flowing faster than normal. In particular in question:
- the pregnancy
- la fièvre
- not having enough healthy red blood cells that can carry oxygen to the tissues (anemia)
- hyperthyroidism
- a phase of rapid growth, as is the case in adolescence
The heart murmur may also be abnormal. In children, an abnormal murmur is usually caused by congenital heart disease. In adults, it is most often a problem with the heart valves.
These include the following causes:
- congenital heart disease: interventricular communication (VIC), persistent ductus arteriosus, narrowing of the aorta, tetralogy of Fallot, etc.
- an abnormality of the heart valves, such as calcification (hardening or thickening) that makes it more difficult for blood to pass
- endocarditis: this is an infection of the lining of the heart that can seriously damage the heart valves
- rheumatic fever
What are the consequences of a heart murmur?
As we have seen, a heart murmur can have no impact on health. It can also be indicative of a heart problem, which can cause certain symptoms such as shortness of breath, lack of oxygenation of the blood, etc. When the doctor identifies a heart murmur, he will therefore carry out a thorough examination to better characterize the cause and ensure that there are no harmful consequences.
What are the solutions for treating a heart murmur?
Obviously, the treatment for a heart murmur depends on its origin. The doctor can prescribe, among other things:
- medications: anticoagulants, diuretics, or beta-blockers that reduce heart rate and blood pressure
- a surgical operation: repair or replacement of a heart valve, closure of an abnormal opening in the heart in the event of heart disease, etc.
- regular monitoring
Read also :Our fact sheet on hyperthyroidism What to know about the symptoms of pregnancy |