Contents
Prolonged alcohol abuse causes disruption of the work of all internal organs. First of all, the cardiovascular system suffers, and especially the liver, an organ that has a number of vital functions, including the neutralization of toxins and the removal of end products of metabolism. The destructive effect of alcohol on the liver is manifested in dangerous diseases that lead to a complete loss of health and even death.
Liver and alcohol
Ethanol is instantly absorbed into the blood through the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Alcohol then continues to enter the bloodstream through the walls of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine. Alcohol molecules cause erythrocytes to stick together. A kind of microthrombi is formed, which partially blocks the access of oxygen to the brain. As a result, the perception of the surrounding world changes, and the person experiences a state of euphoria.
The body perceives alcohol as a poison, therefore it seeks to neutralize it as quickly as possible. The excretory system is able to excrete no more than 10% of ethanol with breath, sweat and urine. The breakdown of most of the harmful substances takes place in the liver. The body produces enzymes that convert alcohol first into toxic acetaldehyde, and then into fairly harmless acetic acid.
But the liver cells are not able to quickly neutralize all the alcohol. It takes at least an hour to split one serving of strong drink with a volume of 50 ml. As a result, the concentration of acetaldehyde increases in the blood, which has a destructive effect on all internal organs, but primarily on the tissue of the liver itself.
With prolonged abuse of alcoholic beverages, the ability to self-heal is reduced, and the removal of toxic substances slows down. The liver ceases to cope with the processing of fatty acids, forming protein by-products. The reaction of acetaldehyde with proteins leads to a violation of the capacity of the cells of the organ, and they begin to break down. As a result, cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis and cellular mutations develop, which are fraught with the formation of cancerous tumors.
Stages of liver damage by alcohol
Serious liver damage occurs in 20% of those suffering from alcoholism. Several factors contribute to the development of diseases:
- genetic predisposition;
- metabolic diseases;
- malnutrition (lack of protein, excess fat);
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with a violation of the absorption capacity of the stomach and intestines.
Metabolic disorders in the liver tissues under prolonged exposure to alcohol lead to the development of steatosis or fatty degeneration. As a result of exposure to ethanol breakdown products, the liver can no longer cope with the breakdown of fats, which leads to their accumulation in cells. Moreover, the area of the lesion is directly proportional to the duration of alcohol intake and its amount regularly entering the body.
Pathology develops – fatty liver. The processes of accumulation of fats lead to the degeneration of cells, their structure changes and performance is impaired. The first stage of the disease is dangerous because it proceeds without pronounced symptoms and is often detected only on ultrasound or during a visit to the doctor about frequent nausea, vomiting, or loose stools.
Symptoms of steatosis:
- gastrointestinal disorders, intolerance to fried and fatty foods;
- lack of appetite;
- weakness and fatigue;
- pain in the right hypochondrium.
In connection with the violation of the protective function of the liver, immunity is weakened, which leads to frequent infectious and colds. One of the characteristic features is yellowed eye sclera and yellowish skin. Edema develops, body temperature may rise. A complication of steatosis is alcoholic hepatitis, an infectious disease that promotes the formation of fibrous tissue.
At the first stage, steatosis is completely reversible. The main condition for recovery is a complete rejection of alcohol. The patient is prescribed drug therapy in combination with a dietary diet. The course of treatment takes a long time and is selected taking into account the degree of cell damage and the individual characteristics of the organism. If all the recommendations of the attending physician are followed, a complete restoration of tissues and functions of the liver is possible.
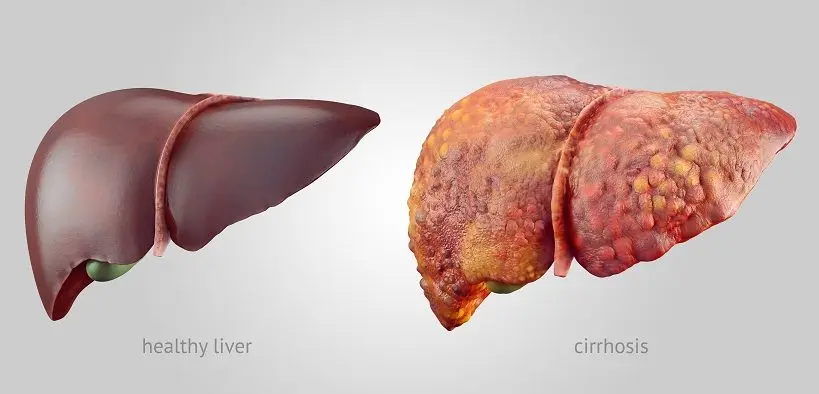
Cirrhosis
In the absence of proper treatment, steatosis passes into an already irreversible stage and cirrhosis of the liver develops. Healthy cells are replaced by fibrous tissue, leading to gradual organ failure.
The disease is classified according to the ability of the liver to function normally:
- compensation – the organ is functioning, diagnosis is carried out using a biopsy;
- subcompensation – partial dysfunction, determined using liver tests;
- decompensation – the body completely stops working.
Diagnosis of the disease at this stage is no longer difficult. Redness of the palms, the appearance of a pronounced vascular network on the face are added to the symptoms. Hepatic encephalopathy develops, which is characterized by mental disorders: loss in time and space, alternation of periods of excitement and apathy, inadequate assessment of reality. From the side of the cardiovascular system, pain in the region of the heart, tachycardia, arrhythmia attacks join.
With a partial loss of liver function, the patient’s condition can be stabilized with the help of drug therapy, provided that alcohol is completely abandoned. In a state of decompensation, the prognosis is usually unfavorable. The patient needs a liver transplant, which is not done with alcoholic cirrhosis. Life expectancy in this case does not exceed three to five years.
The most severe stage of alcoholic liver damage is cancer caused by cell degeneration under the influence of toxic acetaldehyde. The exact mechanism of its development has not been established. The disease is promoted by a genetic predisposition, the presence of endocrine disorders, a weak immune system. Tumor formation in most cases is accompanied by cirrhosis of the liver.
Protecting the liver from the effects of alcohol
A normally functioning liver does not need additional protection with a moderate intake of alcoholic beverages, as its cells are able to recover.
Keeping the body in a healthy state helps to follow several rules:
- a balanced diet with a restriction of fatty, fried and smoked foods;
- a sufficient amount of fluid – at least 1,5 liters of clean water per day;
- refusal of too salty and spicy food;
- introduction to the diet of cottage cheese, dairy products, fresh vegetables and fruits.
In the case of long-term use of antibiotics, it is necessary to choose the right hepatoprotectors and give preference to preparations based on herbal ingredients. With colds, it is not necessary to abuse antipyretics – paracetamol and aspirin, since these drugs adversely affect the protective functions of the liver. Periodically, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system with courses of vitamin therapy.
How to restore the liver after alcohol
During protracted holidays, the liver is under heavy stress and needs to be restored. It is necessary to plan a feast in such a way that the next day you will be able to relax and avoid excessive tension and stressful situations. Relaxing procedures will be useful – visiting a bath or sauna with the condition that the body has already cleared itself of excess alcohol and the state of a hangover no longer worries. Contribute to the removal of toxins and walks in the fresh air.
Complete cleansing of the liver from the decay products of ethanol takes an average of three days. During this period, a fractional diet is recommended with the inclusion of products that contribute to the removal of toxins: steamed vegetables, fresh salad, herbs and fruits. It is necessary to drink at least 2 liters of liquid daily, preferably pure or mineral water.
Fried and spicy foods are excluded, they are replaced with baked and steamed dishes. It is useful to replace black tea with herbal preparations based on chamomile or mint. Helps in restoring the work of the gastrointestinal tract oatmeal jelly: pour a glass of cereal with a liter of cold water, leave for 3 hours, then beat with a blender, strain and bring to a boil. The resulting product can be consumed for breakfast with honey or fresh berries.
The main condition for cleansing is the complete rejection of alcohol. Drinking beer or low-alcohol cocktails the day after drinking strong alcohol will cause an additional blow to liver cells, which may further adversely affect health.
Attention! Self-medication can be dangerous, consult your doctor.









