Contents
The earth’s crust has the deepest faults under the waters of the World Ocean, which are commonly called sea depressions or trenches. These places have not been thoroughly studied by science, due to their incredible depth.
Top 10 included the deepest trenches in the world’s oceansknown today.
10 Aleutian Trench
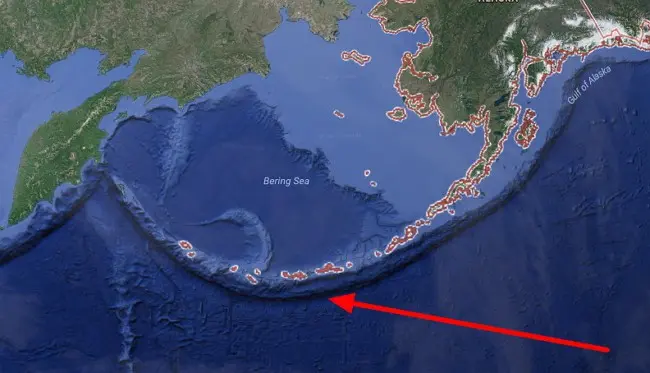
Aleutian Trench opens the top ten deepest trenches in the world’s oceans. Passes along the southern coast of Alaska and stretches to the coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula. Length – 3400 km, maximum depth – 7679 m. It is the boundary between lithospheric plates. The North American Plate, creeping onto the Pacific Plate, forms the island arc of the Aleutian Islands along the trench. In the west, in the Komandor region, the depression passes into the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench, which has a southwestern direction.
9. Javanese or Sunda depression
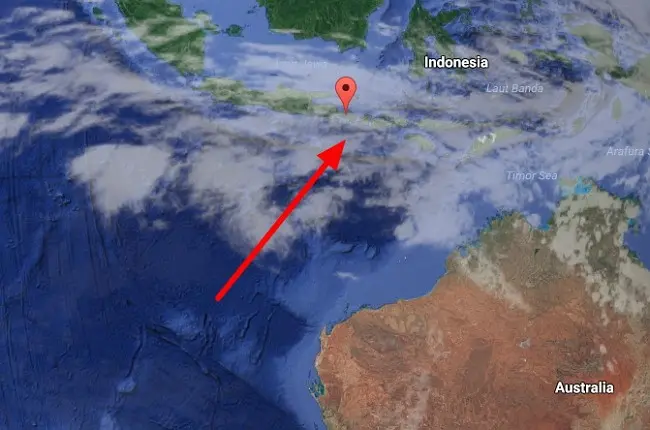
Javanese or Sunda depression – one of the deepest in the eastern Indian Ocean. It extends for 4-5 thousand km along the southern part of the Sunda island arc. The trench begins at the foot of the continental slope of Myanmar in the form of a shallow trough with a bottom width of up to 50 km. Then, towards the island of Java, it gradually deepens and its bottom narrows to 10 km. The maximum depth reaches 7730 meters, which makes it the deepest depression in the Indian Ocean. The bottom of the trough southeast of Java is a series of depressions separated by rapids. The slopes are steep, asymmetrical, insular higher and steeper than the oceanic and more dissected by canyons and complicated by steps and ledges. In the northern and central parts, the bottom, up to 35 km wide, is leveled by a layer of terrigenous sediments with a large admixture of volcanic material, whose thickness in the north reaches 3 km. In the Sunda Trench, the Australian Plate is subducting under the Sunda Plate, forming a subduction zone. It is seismically active and is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire.
8. Puerto-Rico
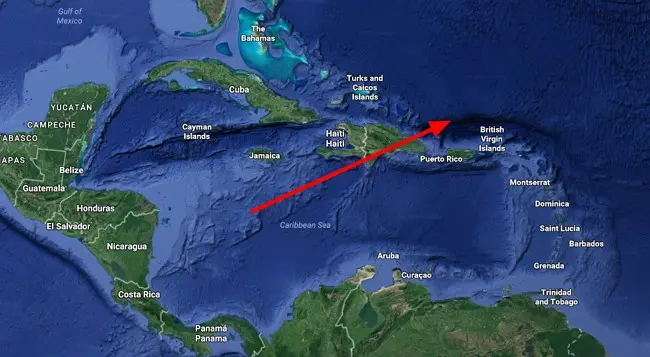
Puerto-Rico – a deep oceanic trench located on the border of the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The formation of the trench is associated with a complex transition between a subduction zone from the south along the island arc of the Lesser Antilles and a transform fault zone (plate boundary) extending eastward between Cuba and Haiti through the Cayman Trench to the coast of Central America. Studies have confirmed the possibility of significant tsunamis as a result of earthquakes in this area. The island of Puerto Rico lies immediately south of the depression. The length of the trench is 1754 km, the width is about 97 km, the maximum depth is 8380 m, which is the maximum depth of the Atlantic Ocean. Measurements made in 1955 from the American ship Vima showed the depth of Puerto Rico to be 8385 meters.
7. Izu-Bonin Trench
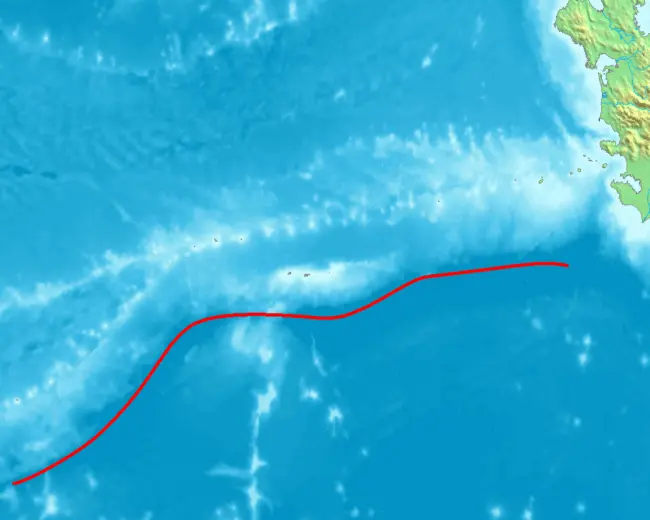
Izu-Bonin Trench or Izu-Ogasawara Trench – one of the deepest Pacific Ocean, located along the eastern foot of the ridge of the Nampo Islands, stretching from the island of Honshu to the Bonin Islands. In the north it connects with the Japan Trench, in the south it is separated from the Volkano Trench by a high narrow ridge. The length of the trench is 1030 km. The narrow, in some places flat bottom of the trench is divided by rapids into several closed depressions with depths of 7000-9000 m. The maximum depth – 9810 meters – was established in 1955 by the Soviet expedition on board the Vityaz ship.
6. Kermadek
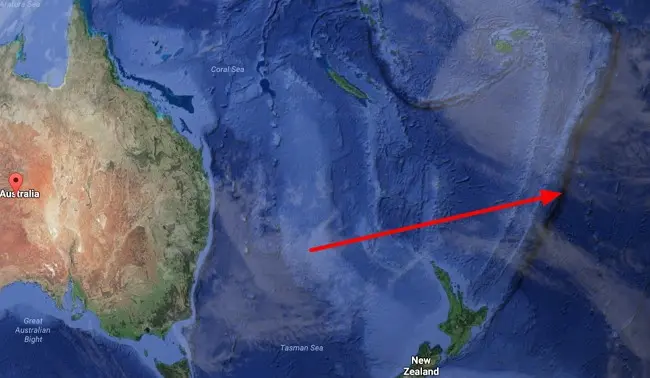
Kermadek – one of the deepest depressions, in the north connected to the Tonga trench. It is located at the eastern foot of the Kermadec Islands almost in the meridional direction. The length is about 1200 km. Kermadec was discovered in 1889 by the British ship Penguin. The maximum depth of 10 meters was measured in 047 during the voyage of the Soviet research vessel Vityaz. The depression is named after Huon de Kermadec
5. Japanese chute
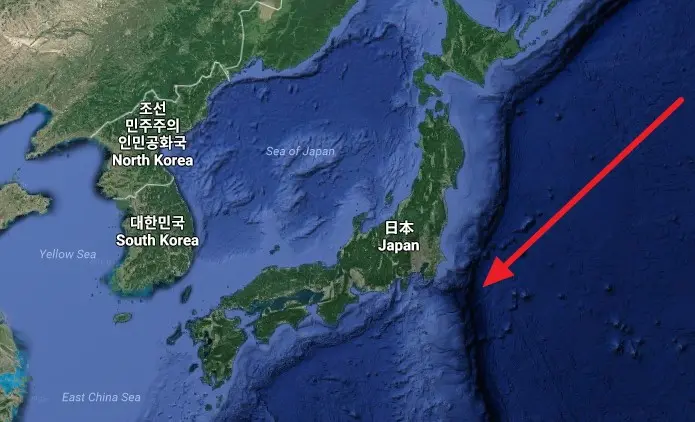
Japanese chute – a deep depression in the western Pacific Ocean, east of the island of Honshu, south of Hokkaido and north of the Bonin Islands. The length of the trench exceeds 1000 km. The transverse profile of the gutter is V-shaped. The maximum measured depth is 10504 m. The depression is the southern continuation of the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench. Three researchers on the Shinkai 6500 apparatus reached a depth of 11 m on August 1989, 6526. In October 2008, a Japanese-British expedition managed to photograph sea slugs, the deepest-sea fish, at a depth of 7700 m. The bottom and walls of the crack often become epicenters of earthquakes.
4. Smoked Kamchatka Trench
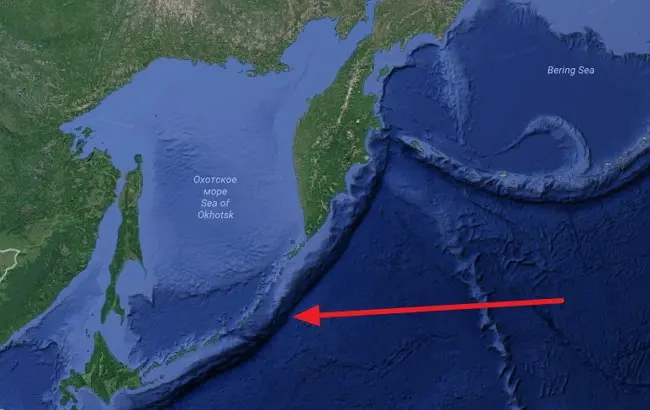
Smoked Kamchatka Trench ranks fourth in the top of the deepest trenches in the oceans. It is located on the eastern underwater slopes of the Kuril Islands and the southern part of the Kamchatka Peninsula. Length 2170 km, average width 59 km. The maximum depth is 10542 m. The boundaries of the depression approximately coincide with the 6000 m isobath. On the slopes there are numerous ledges, terraces, as well as valleys descending to the maximum depth. Investigated mainly in the 50s of the XX century by Soviet expeditions on the ship “Vityaz”.
3. Philippine Trench
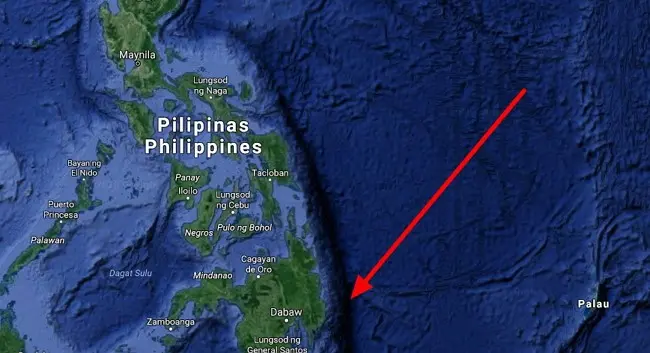
Philippine Trench opens the top three deepest trenches in the oceans. Located to the east of the Philippine Islands. Its length is 1320 km, from the northern part of the island of Luzon to the Molluk Islands. The deepest point is 10540 m. The Philippine Trench is the result of a collision of earth layers. Oceanic, with a 5 km wide, but with a characteristic specific gravity (basalt), the Philippine Sea Plate moves at a speed of 16 cm per year under the 60 km, with a lower specific gravity (granite), the Eurasian Plate, and melts due to the Earth’s mantle on depth from 50 to 100 km. This geophysical process is called subduction. The Philippine Trench is located in this zone.
2. Tonga
Tonga ranks second in the list of the deepest trenches in the oceans. Its total length is 860 km. It extends along the foot of the eastern slope of the underwater ridge of the same name from the Samoan Islands and the Kermadec Trench. The depth along the isobath is approximately 6000 m – about 80 km. The maximum depth is 10 m – the greatest depth of the World Ocean in the Southern Hemisphere.
Mariana Trench – the deepest trench in the oceans. The deepest point is the “Challenger Abyss”, which is 10 meters below sea level. recent studies conducted by the American Oceanographic Expedition from the University of New Hampshire (USA) have discovered real mountains on the surface of the bottom of the Mariana Trench. The studies took place from August to October 994, when a bottom area of 2010 square kilometers was studied in detail using a multibeam echo sounder. As a result, at least 400 oceanic mountain ranges 000 kilometers high were discovered, crossing the surface of the Mariana Trench at the point of contact of the Pacific and Philippine lithospheric plates.









