Contents
20-25% of women suffer from acute cystitis at least once in their lives. In 10%, due to improper treatment, the disease becomes chronic and then symptoms occur after every hypothermia, malnutrition and stress.
Timely treatment should be prescribed by a specialist individually, taking into account the symptoms, anamnesis, laboratory and instrumental data.
In 75% of women, the cause of cystitis is Escherichia coli, which requires antibiotic therapy.
In the article, we will consider the most effective and inexpensive antibiotics for cystitis for women, which are approved by clinical guidelines and are actively used by practitioners.
List of top 10 effective and inexpensive antibiotics for cystitis according to KP
1. Monural
An antibiotic, which is taken once for uncomplicated cystitis. The active substance is fosfomycin. According to clinical guidelines, Monural is a first-line drug. A single dose in combination with herbal preparations will be enough to stop an attack and get rid of bacteria. In chronic cystitis, there is a regimen for taking Monural, which is also effective. During pregnancy, it is often used to treat cystitis and asymptomatic bacteriuria.
Indications:
- uncomplicated urinary tract infections (cystitis).
Contraindicated in case of an allergic reaction to the components of the drug. Allowed during pregnancy and lactation after consulting a doctor. Allergic reactions and adverse reactions during the administration of the drug are not observed.
2. Furamag
The active substance is furazidin.
The advantage of the drug is that bacterial resistance to the nitrofuran group rarely appears, so Furamag is often prescribed for the treatment of cystitis, even without prescribing a microflora culture. Pain relief occurs within a couple of hours after taking the pill.
Indications:
- urinary tract infections;
- infectious diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- some diseases in gynecology.
The drug is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to nitrofurans, pregnancy, lactation, serious kidney disease.
3. McMirror
The active substance is nifuratel.
The drug belongs to the group of nitrofurans. It has antimicrobial, antiprotozoal and antifungal activity. The use of drugs in this group is recommended for the treatment of infections caused by Escherichia coli (the main causative agent of cystitis).
Indications:
- urinary tract infections;
- some gynecological infections;
- some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is not used for allergies to any of the components that make up the composition. During pregnancy, the appointment is highly undesirable. During lactation, when using the drug, breastfeeding should be temporarily discontinued, as the substances enter the milk and are transmitted to the child.
4. Furadonin
The active substance is nitrofurantoin.
The drug also belongs to the group of nitrofurans, but has a different active substance. When used, nausea, loss of appetite may occur. Taking the drug with food will significantly reduce the number of side effects.
Indications:
- urinary tract infections (cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis).
The antibiotic is contraindicated in case of allergy to the components of the drug. In case of serious diseases of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system, use only after consulting a doctor. During pregnancy and lactation, the use of the drug is possible only after assessing the possible risks for both the mother and the child.
5. Suprax Solutab
The active substance is cefixime.
The drug, according to clinical recommendations, is prescribed for an allergic reaction to nitrofurans. The convenient form of Solutab allows you to dissolve the tablet in a glass of water and drink the solution. The drug has practically no side effects, does not cause a feeling of bitterness.
Indications:
- urinary tract infections;
- infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract;
- some gynecological diseases.
The antibiotic is contraindicated in case of allergy to penicillins and cephalosporins. During pregnancy and lactation is allowed after consulting a specialist. It is prescribed with caution in case of serious diseases of the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, old age.
6. Nolicin
The active substance is norfloxacin.
It is a reserve drug for urinary tract infections, but its high efficiency allows it to be prescribed even for chronic cystitis. Belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones. Unpleasant symptoms disappear 2-3 hours after taking the pill.
Indications:
- urinary tract infections;
- some gynecological diseases;
- prostatitis.
Contraindicated in allergy to fluoroquinolones, pregnancy, lactation. The antibiotic negatively affects the connective tissue (tendons, joints), therefore, if there was a history of torn ligaments when using Nolicin, the drug should not be taken. During pregnancy, the drug also adversely affects the joints of the fetus, which can lead to serious illnesses of the child after birth.
7. Palin
The active substance is pipedimic acid.
The drug also belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones. It is often prescribed for resistance of microorganisms to other antibacterial drugs. Dosage and duration of administration must be selected individually by the doctor.
Indications:
- urinary tract infections.
Contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, with serious diseases of the liver and kidneys. In the first and third trimester of pregnancy, as well as during lactation, the drug is not used. In the second trimester, only after consulting a specialist and taking into account the risk to both the mother and the fetus.
8. Amoxiclav
The active substance is penicillin + clavulanic acid.
Refers to beta-lactam antibiotics and is an alternative drug for cystitis. Unfortunately, very often there is resistance to penicillins and then this drug will not be effective. However, in uncomplicated acute cystitis in the absence of serious comorbidities requiring the use of antibacterial drugs, Amoxiclav is very effective.
Indications:
- respiratory tract infections;
- urinary tract infections;
- infections of the skin, soft tissues, bones;
- gastrointestinal infections.
The drug is contraindicated in case of allergy to beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins), with serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, infectious mononucleosis, lymphocytic leukemia. During pregnancy and lactation, use only after consulting a specialist, taking into account all risks.
9. 5-nok
The active substance is nitroxoline.
The drug belongs to the group of oxyquinolines. Widely used to treat cystitis. The maximum concentration of the substance in the blood is reached 1,5-2 hours after ingestion. It is after this time that the unpleasant symptoms subside. Side effects may include nausea, vomiting.
Indications:
- urinary tract infections.
The drug is contraindicated in case of allergy to the components of the drug. Cataracts, hepatic and/or renal insufficiency are also contraindications for use. During pregnancy and lactation, the appointment of the drug is unacceptable.
10. Ciprofloxacin
The active substance is ciprofloxacin.
The drug belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones of the 2nd generation. It is prescribed for the treatment of both acute and chronic cystitis. Resistance to this group of drugs rarely occurs, which is an undoubted advantage.
Indications:
- urinary tract infections;
- infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue;
- some gynecological diseases;
- prostatitis.
The use of Ciprofloxacin is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Appointment during pregnancy and lactation only after consulting a doctor and assessing the possible risks to mother and child.
How to choose antibiotics for cystitis in women
Self-selection of antibiotic therapy can only aggravate the situation, so in any case, you should consult a doctor.
There are many antibiotics that are used to treat cystitis:
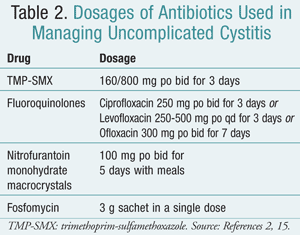
- fosfomycin – a modern drug that is recommended to be taken 1 time. It is effective at the very beginning of uncomplicated cystitis. Unfortunately, resistance often develops to it, so a single use is not enough or other drugs need to be added;
- nitrofurans – a group of drugs that has been actively used for the treatment of cystitis for 30 years. They have side effects (nausea, loss of appetite), but due to the lack of resistance, they are still actively used in practice;
- penicillins and cephalosporins – antibacterial drugs with a wide spectrum of action, but due to their active use in other diseases, resistance develops;
- fluoroquinolones – reserve drugs, but perfectly relieve cystitis in a short time, their use is possible only in extreme cases.
An effective selection of antibiotic therapy is possible only after urine culture for microflora with the obligatory determination of the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics.
Due to the huge choice of drugs, the selection of therapy should be entrusted to a specialist.
Popular questions and answers
We discussed important issues related to the prescription of antibiotics for cystitis with therapist Tatyana Pomerantseva.
Can cystitis be cured without antibiotics?
• If the cause of cystitis is a virus or fungus, then the use of antibacterial drugs will only adversely affect the normal microflora.
• At the very beginning, uncomplicated cystitis can be stopped with herbs and herbal preparations: cranberry, D – mannose, kanefron, phytolysin (this is true only in the case of Escherichia coli, all other pathogens require specific treatment).
Is it possible to buy antibiotics for cystitis without a doctor’s prescription?
Even if last time one antibiotic was prescribed for cystitis and it helped, this does not mean at all that this time the pathogen is the same.
Therefore, it is important to pass the culture on the microflora and consult a specialist.
What to do if antibiotics do not help with cystitis?
• the causative agent of cystitis is a virus or fungus;
• a microorganism resistant to this antibiotic;
• insufficient dosage of the drug.
If symptoms persist for more than 3 days, you should consult a specialist.
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations “Cystitis in women” 2021;
- 2000-2022. REGISTER OF DRUGS OF RUSSIA® RLS®