Contents
- Myth 1. Pneumonia is a benign disease.
- Myth 2. Pneumonia is a disease of the elderly and children
- Myth 3. Pneumonia is always treated with antibiotics.
- Myth 4. Temperature is a mandatory symptom of pneumonia.
- Myth 5. With pneumonia, there is always a cough.
- Myth 6. With pneumonia, you need to warm your chest.
- Myth 7. There is no vaccine for pneumonia.
- Conclusion

Pneumonia is not always an independent disease, sometimes it acts as a complication of the flu. Inflammation of the lungs is life-threatening, so it needs to be detected and treated in time. However, many do not take the disease seriously, as they believe that they are not at risk. There are those who think that you can cope with pneumonia on your own, without going to the doctor. But is it?
In the Russian Federation, its frequency is 3,9 cases per 1000 adults, and in Europe from 2 to 15 cases per 1000 people. Women get sick less often, but die with the same frequency as men.
Pneumonia can be community-acquired and nosocomial. Separately, consider aspiration pneumonia, which develops when foreign substances enter the lungs, for example, vomit.
A severe form of the disease is always treated in a hospital. Her signs:
Severe shortness of breath with a respiratory rate of more than 30 per minute.
Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia).
Sudden hypotension (less than 90/60 mm Hg).
Fever.
Myth 1. Pneumonia is a benign disease.
Not everyone knows that at the beginning of the last century, 85% of patients died from pneumonia. Since the discovery of antibiotics, the situation has changed, but it is a deep delusion to consider the disease to be harmless.
The chief pulmonologist of the Russian Federation, Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences A. G. Chuchalin lists pneumonia among the most deadly infections in the world. WHO claims it is the 4th leading cause of death. Even mild pneumonia leads to the death of 5% of patients, and with complicated pneumonia, 25-50% die! At the same time, mortality continues to grow, the reason for which is the resistance of bacteria to antibacterial drugs. Now this figure has increased by another 9%.
Timely diagnosed inflammation in 80% of cases can be treated at home, but only with strict adherence to all medical recommendations. However, every 5th sick person will end up in a hospital. Most often these are elderly people with chronic pathologies that significantly worsen the prognosis. In this regard, diabetes mellitus, kidney and liver damage, COPD, cardiovascular diseases, and alcoholism are especially dangerous.
Myth 2. Pneumonia is a disease of the elderly and children
In fact, people over 65 are at risk (80/1000 cases). This also includes children (10-12/1000 cases). However, any young and adult person can get pneumonia at any time, and a severe course of the disease cannot be ruled out.
The risk group includes almost the entire working-age population. This statement is especially true in relation to persons leading a sedentary lifestyle, often experiencing stress, forced to work in large teams, in a confined space.
Myth 3. Pneumonia is always treated with antibiotics.
Antibiotics are effective if the disease is caused by bacteria. Most often this is actually the case, but we must not forget about viral (5-15% of cases) and fungal pneumonia.
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the main culprit in pneumonia. It is sown in the sputum of every 3 patients, and in children under 5 years old – in 70-90% of cases.
About 10-20% of pneumonia cases are caused by the bacteria Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydophila pneumoniae.
In 5% of cases, the causative agents of the disease are legionella. These microbes live in air conditioners that have not been cleaned for a long time.
In addition, the following pathogenic flora can provoke inflammation of the lung tissue: Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc.
Antibiotics for pneumonia are indeed used, but an individual therapeutic regimen is made up for each patient.
Myth 4. Temperature is a mandatory symptom of pneumonia.
This myth is one of the most dangerous. The absence of temperature is the most common reason for misdiagnosis or late detection of the disease. This situation is observed in 30% of cases. As a result, the patient develops severe complications.
Latent asymptomatic pneumonia often affects the elderly, hiding for some time under the guise of other chronic diseases.
Pneumonia can occur without fever. At the same time, it is accompanied by symptoms such as: weakness, shortness of breath, cough, increased sweating.
Myth 5. With pneumonia, there is always a cough.

In children, cough may be absent, which is associated with taking antitussive drugs and weak immunity. Parents should not give their child any cough medicine unless recommended by a doctor. Although it is possible that the cough reflex may be absent even if the patient did not receive any pills.
Symptoms to be concerned about:
Dyspnea.
Pain in the chest that worsens when turning the body and when trying to take a deep breath.
Fatigue, weakness.
Paleness of the skin against the background of a bright blush on the cheeks.
The child should be immediately shown to the doctor in the following cases:
Inhalation is accompanied by a whistle.
The nasolabial triangle became blue.
For no apparent reason, drowsiness, tearfulness and irritability increase.
The skin loses elasticity.
Myth 6. With pneumonia, you need to warm your chest.
Chest warming is contraindicated. You can not go to the bath and sauna, it is forbidden to put jars or mustard plasters. Any of these procedures can lead to the progression of the disease and the involvement of healthy lung tissue in inflammation.
Myth 7. There is no vaccine for pneumonia.
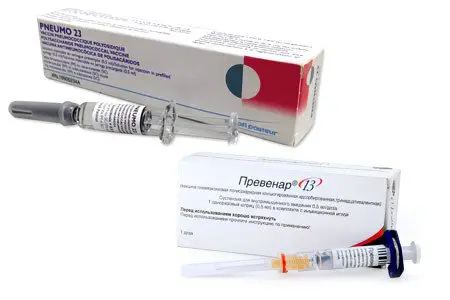
There is a vaccine against pneumonia, the pneumococcal vaccine. Today it is the most effective method of preventing bacterial pneumonia. More recently, up to 40% of recruits in the Russian army suffered from pneumonia. After the development and implementation of the vaccine, the incidence decreased by 3 times. Also, thanks to the vaccination campaign, the number of children under 5 who fell ill with community-acquired pneumonia has decreased.
Vaccines that have been registered in the Russian Federation:
Prevenar (America). It is given to children older than 3 months.
Pneumo 23 (France). Can be used to vaccinate children over 2 years of age.
In addition to vaccinating against pneumonia, it is important to protect yourself from the flu, since pneumonia often develops precisely against the background of this disease, acting as a complication. According to statistics, no more than 12% of vaccinated, but sick people die from pneumonia caused by influenza.
Persons suffering from chronic diseases must be vaccinated.
Conclusion
To make a diagnosis of pneumonia, it is necessary to undergo an examination. The first is an x-ray of the lungs.
Do not refuse vaccination (for pneumonia and influenza). Be sure to vaccinate children and the elderly.
Pneumonia does not go away on its own. It can be fatal, so you need to see a doctor when the first signs of the disease appear.
Self-treatment of pneumonia is dangerous. Therapy and selection of drugs should be handled by doctors.









