Contents
According to the WHO, the World Health Office, in France, 1 in 10 deaths is linked to the environment. Globally, a quarter of infant deaths would find their origins there.
There are multiple threats: air quality, soil quality, contaminated sites. In France, a recent scandal has affected some schools, singled out for their indoor pollution problems.
So what are the most affected places in our territory? Where does this pollution come from? Which are the most polluted cities in France in 2018?
This dossier offers you an overview of the threats hanging over our cities, and the means to protect ourselves and to take action.
Enter your text here…
The most polluted cities in France in 2019
What then are the most polluted cities in France? The classification will obviously be arbitrary: the quality of the air, water and soil is taken into account, but which is ultimately the most important?
The five cities which are at the top of this podium are subject to different types of pollution, but they are found on a recurring basis [1]
1 – Lyon Villeurbanne
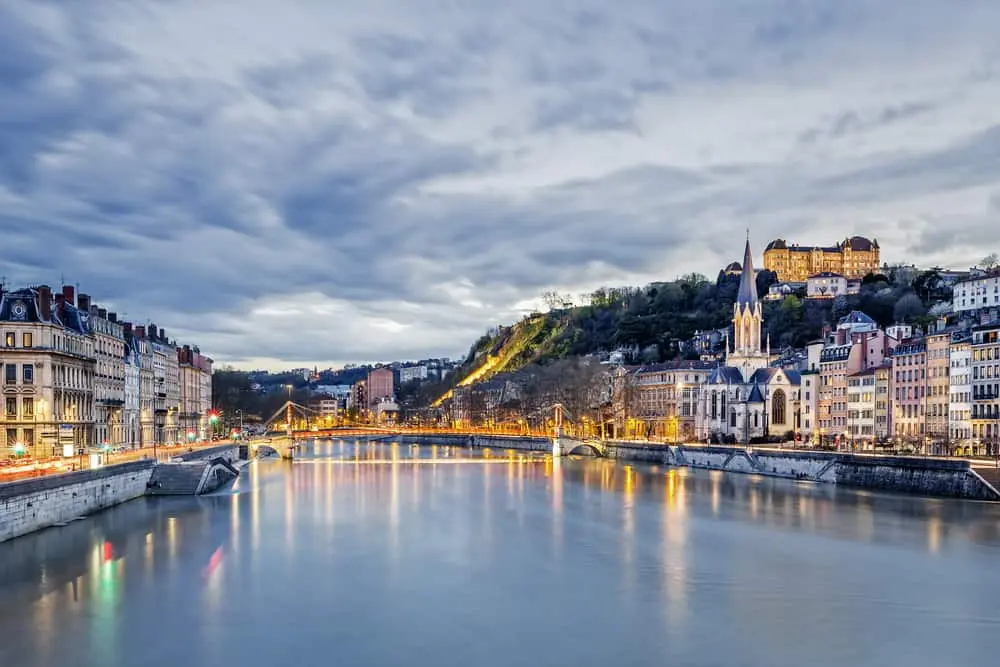

With an agglomeration of more than one million inhabitants, Lyon, prefecture of the Rhône, is at the top of the ranking. She’s there second French city where the most radioactive waste is stored.
With 2 million m2 of brownfields contaminated with lead, chromium or hydrocarbons, the soils are highly polluted: there are 66 sites classified as polluted, some of which are dangerous. Lyon is concerned by the recent lawsuits established by the European Union.
These target French cities where particle thresholds have reached critical limits. It experienced several episodes of pollution peaks in 2017 despite certain measures. In places, there are also traces of arsenic and high levels of nitrates in the water.
We can also cite, in the metropolis, the city of Villeurbanne which has 34 polluted sites. With 140 inhabitants, it has reached critical thresholds with regard to the levels of nitrogen dioxide and PM000 particles.
Not far from there, the Arve valley is known to be one of the most polluted places in France, partly because of its geographical location, and the wood heating which is widely used in winter which represents nearly 80%. particulate emissions.
2 – Marseilles
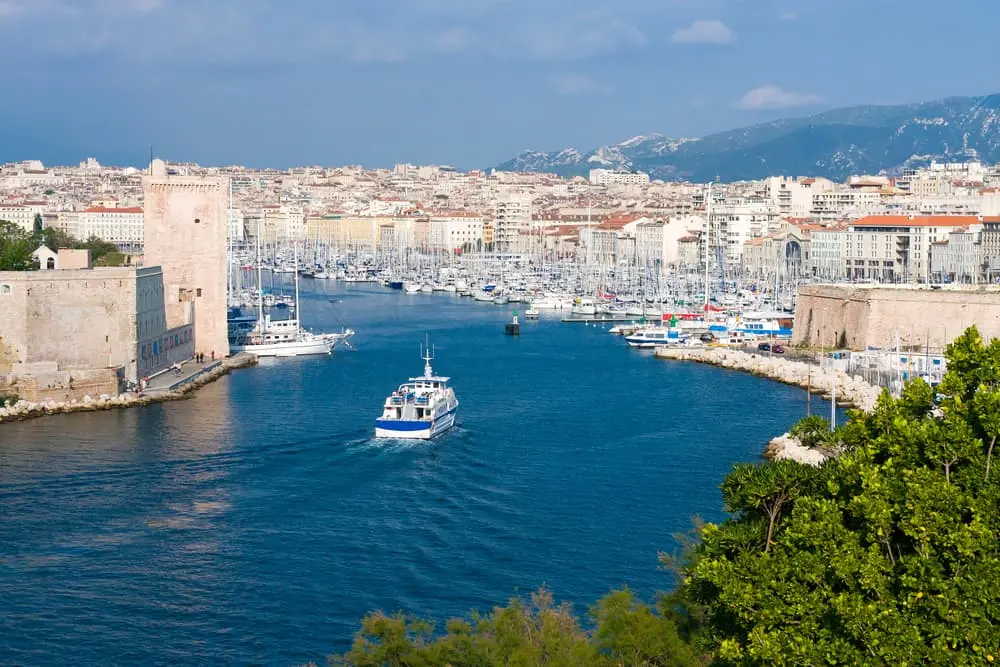

Photo credit: Cyrille Dutrulle (link)
Marseille and Paris often fight for the top of the ranking regarding air quality. With 50 sensitive sites, 2 sites classified Seveso, that is to say dangerous in the event of an accident, Marseille, in addition to conventional pollution linked to road transport, has high pollution rates linked to maritime transport, without count fuel incidents. It is this which records the highest rate of fine particles in the air.
One might think that Paris is ahead of it, but the climate is also involved: high temperatures tend to increase the level of pollution in the air. Without forgetting the sea breeze which sends pollution back inland.
Public transport is relatively underdeveloped in the Marseille capital: a single electric bus line, no incentive in the event of a proven pollution peak: no sticker or differentiated traffic.
It is true that some routes are difficult to divert, in particular to bring goods to the port.
However, Crit’air stickers should quickly appear.
3 – Paris
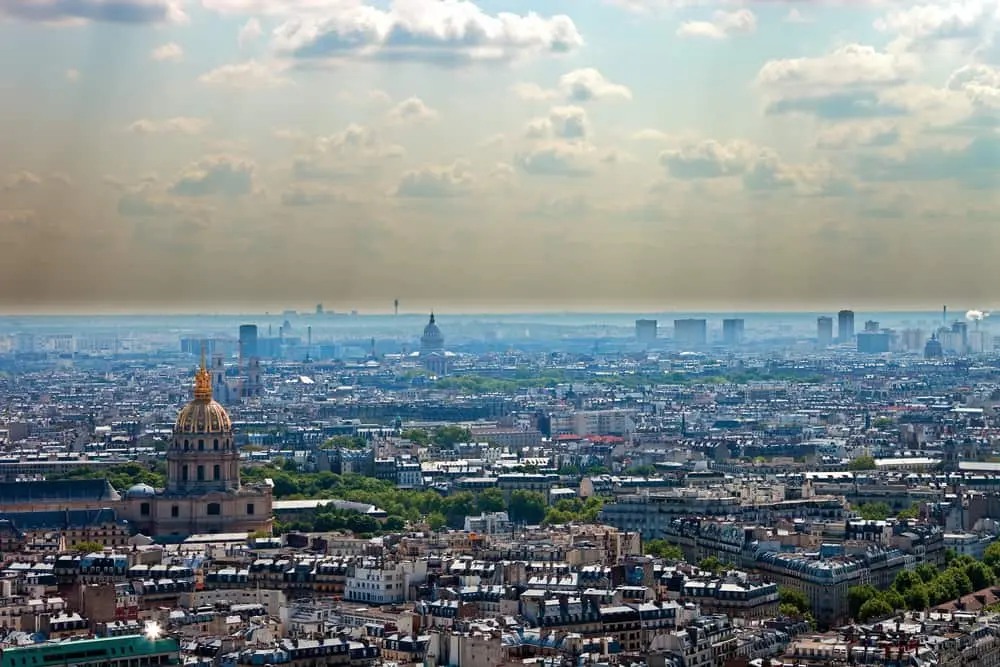

First French city in terms of radioactive waste sites, Paris is obviously in this ranking.
According to Air’Parif studies, the vast majority of air quality problems come from road traffic. 39% of particle pollution comes from elsewhere: particles are also carried by the wind.
The most recent WHO study ranks the first polluted French city in terms of air quality, and 17th largest city in the world.
While the regulatory threshold for PM10 in France is 20 μg / m3 – microgram per cubic meter – the concentration recorded in 2015 in the capital is 35 μg / m3
4 – Roubaix

Photo credit: GabianSpirit (link)
The pollution of certain sites in the city of Roubaix comes from its past linked to industrial textiles.
Beyond these 38 sites contaminated with lead and hydrocarbons, the levels of fine particles in the air are also above standard.
It is in Roubaix and in Hauts-de-France that recent scandals concerning contaminated schools have erupted.
There are also air quality problems in cities like Lens or Douai.
5- Strasbourg

Photo credit: ALexandre Prévot (link)
With 40 polluted sites, Strasbourg, located in the highly industrialized eastern part of the country, also records high levels of fine particles and carbon dioxide in the air.
These emissions are mainly due to diesel vehicles and road traffic.
Despite a general decline in air pollution, the city still experiences several pollution peaks each year.
A telephone alert has also been put in place to warn the population in time.
The pollution problems mainly concern the main roads.
Advice in the event of a pollution peak – according to the Ministry of Health
For vulnerable populations – infants, young children, the elderly, people suffering from cardiac or respiratory pathologies
✓ Avoid practicing sports activities, especially intensive, whether outdoors or outdoors (air circulates)
✓ If respiratory or heart discomfort appears, consult a doctor
✓ Go out a little less often if the symptoms are less marked indoors
✓ Avoid main roads, at the start and end of the day or during rush hour
✓ Postpone activities requiring too much effort
For the others
✓ Avoid intense physical effort
✓ The practice of moderate sports activities such as cycling is not a problem
✓ Ventilate your interior: avoid tobacco, cleaning products, scented candles, etc.
✓ Air your vehicle to limit the accumulation of pollutants
6- Small

Photo credit: Fred romero (link)
If the first 5 places in the ranking leave no room for doubt, it is then difficult to separate the cities according to whether we give more or less importance to air pollution or the presence of contaminated sites.
The Lille metropolis comes in our ranking: already for proven problems of air pollution, but also for the presence of polluted sites and soils.
About twenty schools and nurseries are potentially affected. Air pollution problems are also still present: at the time this article is being written, the city is experiencing an episode of peak pollution which leads, in particular, to speed limits and the limitation of certain activities.
This phenomenon is accentuated by relatively high summer temperatures
7- Nice

Photo credit: Hans Põldoja (link)
One might think that the cities of the south, further away from the historic industrial zones, are spared.
But the climate is playing against them, and there are many days when regulatory thresholds are exceeded.
The sun is strong, the traffic is intense, and although the mistral is responsible for cleaning the air, pollution problems persist.
The rates remain correct due to the absence of industry, but it is the city’s strengths that are working against it.
The weather favors the presence of particles, the absence of strong winds prevents their dispersion, and some pollution comes from afar. In addition to this phenomenon, all traffic remains concentrated on the coast, which concentrates the sources of pollution.
8- Grenoble

The city of Grenoble is known for its polluted air: it is not yet at the top of the ranking and remains far behind Paris or Marseille.
It is above all its geographical location that makes pollution stagnates in the valley, but the situation tends to improve over the years, in particular thanks to a policy of combating pollution.
With around thirty polluted sites, the issue of soil quality is at the heart of the city’s policy, which has implemented a mapping of its former industrial sites, in order to adapt and foresee risks.
9- Reims

Photo credit: Num (link)
It is also concerned by the European Court’s ruling against France for excessively high levels of air pollution: measures are starting to be put in place, in particular due to the appearance of episodes of pollution peaks. to PM10 particles.
There too, some schools are experiencing soil pollution problems : decontamination operations have already been launched.
PM10 levels in the air remain well above the national average. And the quality of the water is also reduced by the presence of nitrates.
10- The haven

Photo credit: daniel.stark (link)
The city of Le Havre completes this ranking. The air we breathe there is rather of good quality, but here the pollution problems mainly concern port areas and industrial areas, as well as contaminated sites.
In terms of air pollution, the thresholds are exceeded for nitrogen dioxide, fine particles, but also sulfur dioxide and ozone. Without forgetting, by the sea, recent illegal dumping issues.
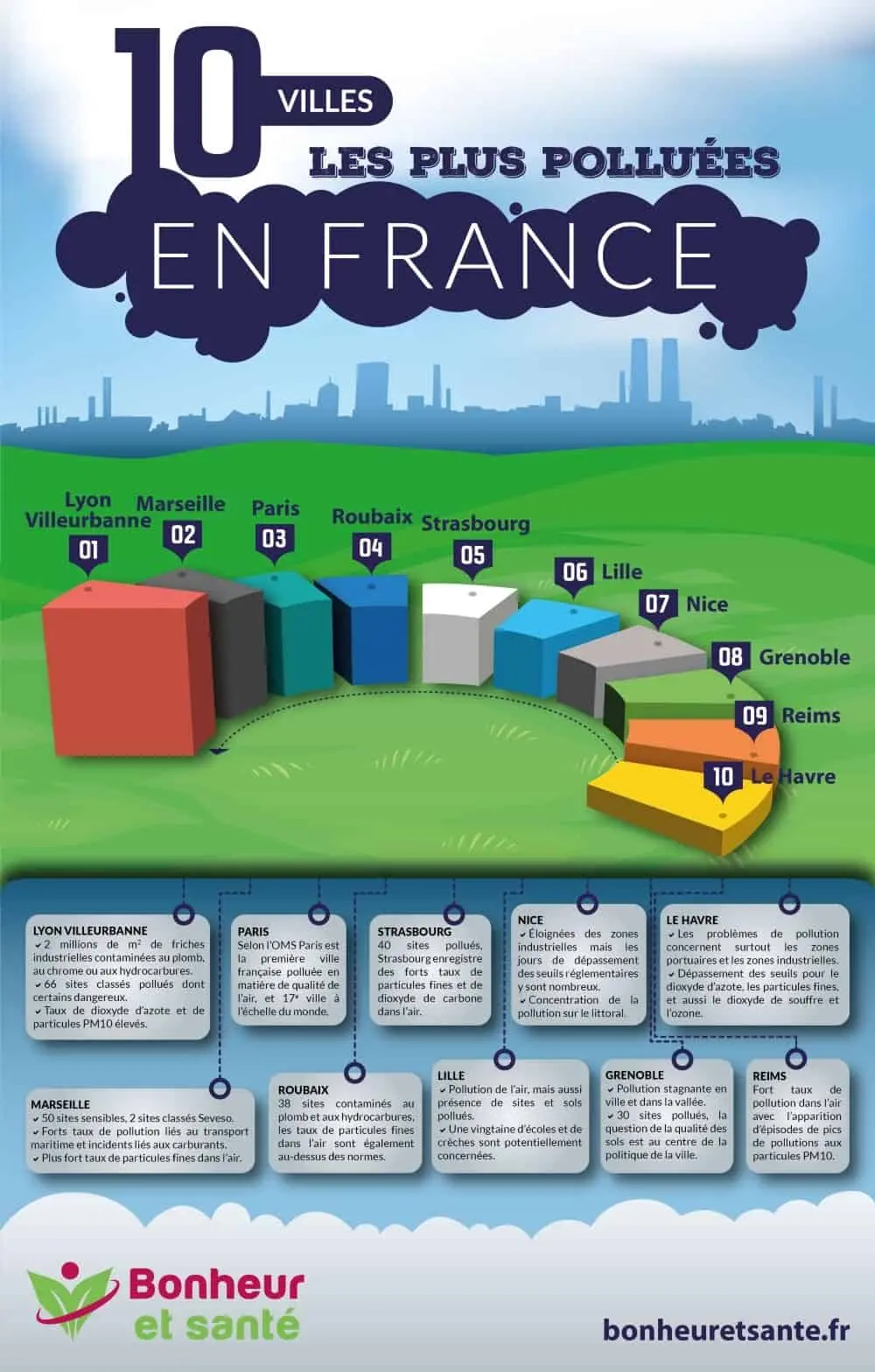
Cities with the lowest pollution rates in the country
We cannot guarantee that a city will be free from all pollution, but some cities are known for their air that is a little more breathable. Here are a few :
✓ Valves
It would be the least polluted city in France. We especially know that the levels of sulfur, nitrogen dioxide, and fine particles, are relatively low. Pollution peaks are rather rare there.
✓ Limoges
The air quality in Limoges is good for nearly three quarters of the year.
✓ Brest
There are only about twenty days when the air is considered bad, generally in winter.
✓ Pau (FR)
Apart from the summer when the geographical location of the city, at the bedside of the Pyrenees, generates peaks of pollution, you can fill up with fresh air all the rest of the year.
✓ Perpignan
Despite heavy traffic, especially in the city center, the absence of industrial pollution places Perpignan in the ranking.
A brief overview of our regions
In terms of soil quality, inequalities are great within the French metropolis. Before discovering the ranking of cities, here is a quick overview of the regions which have a large number of polluted soils and sites. On your mind :
➔ The North (59)
An agricultural region with more than 70%, with a strong industrial past, the North region has 497 proven polluted sites, the highest figure in the country. This is also where recent scandals broke out concerning polluted schools in the city of Roubaix.
➔ Seine-et-Marne (77)
There are 303 polluted sites in this department. This pollution is essentially industrial. We can also note poor water quality due to the nitrates, mercury and phosphates that can be found there.
➔ The Gironde (33)
Pollution in Gironde comes mainly from wine-growing activity and pesticides. There too, the proximity of certain schools to the vines is starting to raise questions.
On the contrary, certain departments are virtually devoid of any polluted site: Cantal, Creuse, Gers, or even Lozère.
These cities in France where we breathe badly
Are we better off in the country than in the city?

Even if cities concentrate industries and transport, and have high pollution rates, one should not neglect the pollution of agricultural areas either. The Arve valley, nestled in the heart of the French Alps, is said to be one of the most polluted places in France.
It is close to a very busy traffic axis, and in winter, the inhabitants heat with wood. The 500 heavy goods vehicles which circulate in the valley each year prevent the inhabitants from breathing. It sometimes happens, in this valley, that a pollution peak is spread over several months (2)
This situation is at the root of many health problems, from chronic respiratory failure to cancer.
In the middle of the countryside, you are less affected by traffic, but you may be exposed to pesticides and agricultural pollutants. Not to mention that the fine particles that cause air pollution move.
In our city / countryside distinction, let us not forget the case of industrial zones either. They are mainly located in the east of France, besides the prevailing winds come from the west.
The Rhône valley, as it played a big role in the industrialization of the country, is generally highly polluted, as is the lower valley of the Seine.
Urban air quality raises questions in France
Leading the podium? We can’t find the ones we would have imagined. It is not necessarily the big cities that record the highest levels of fine particles in the air.
A city of Seine-Saint-Denis, Puppet records a record in terms of concentration of fine particles in the air, with 36 μg / m3 for a city of 55 inhabitants (3)
The second municipality in this classification, located in Seine-et-Marne, has 15 inhabitants. Air pollution problems are added to recent scandals regarding unsafe water.
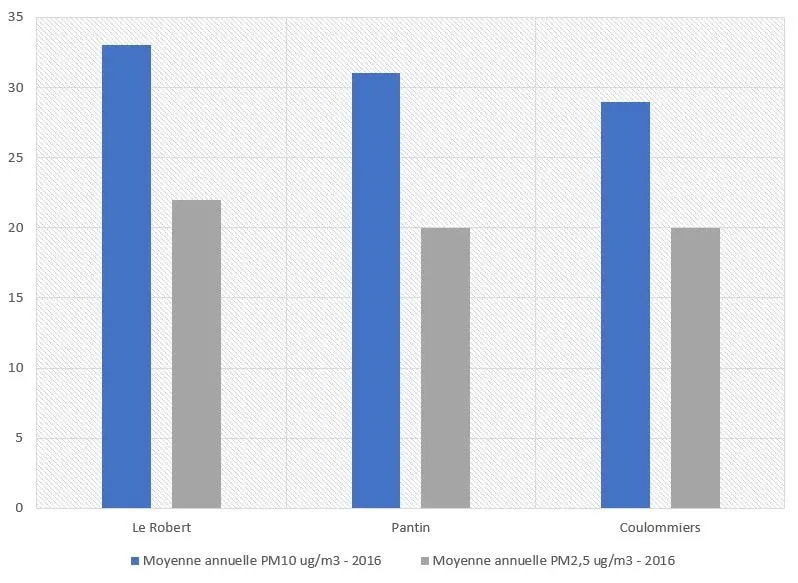
However, if we only retain the cities of more than 100 inhabitants, we can identify the large French cities which appear at the top of the ranking of the most unbreathable airs. Depending on whether we measure PM000 or PM10 particles, the ranking changes a little, but we find some cities on a recurring basis (4)
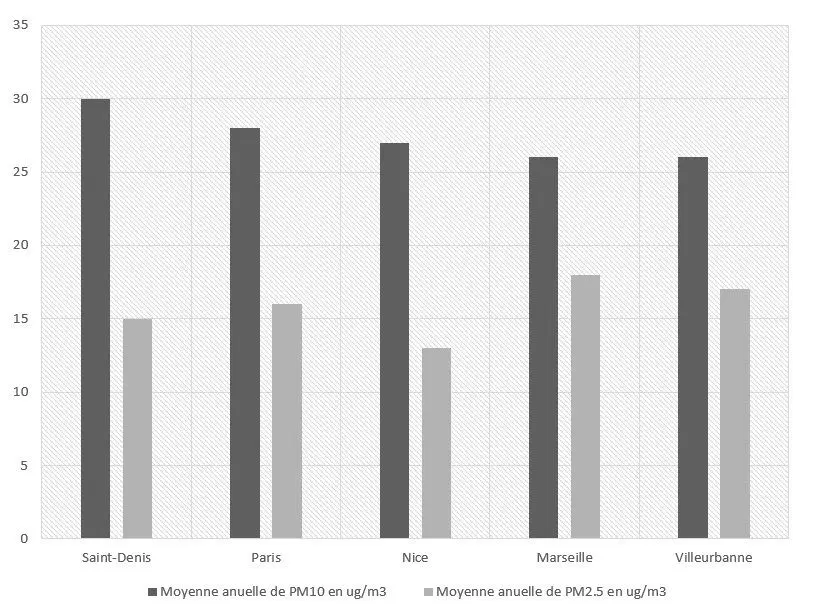
Let us also not forget that particle pollution is not the only air pollution that we can suffer from. The cities with the highest levels of carbon monoxide remain Paris in first place, Toulouse and the city of Saint-Denis.
It is therefore complex to make a definitive classification of the cities in the country whose air is the most polluted: it already depends initially on the type of pollution that is being measured. The situation may also vary from year to year.
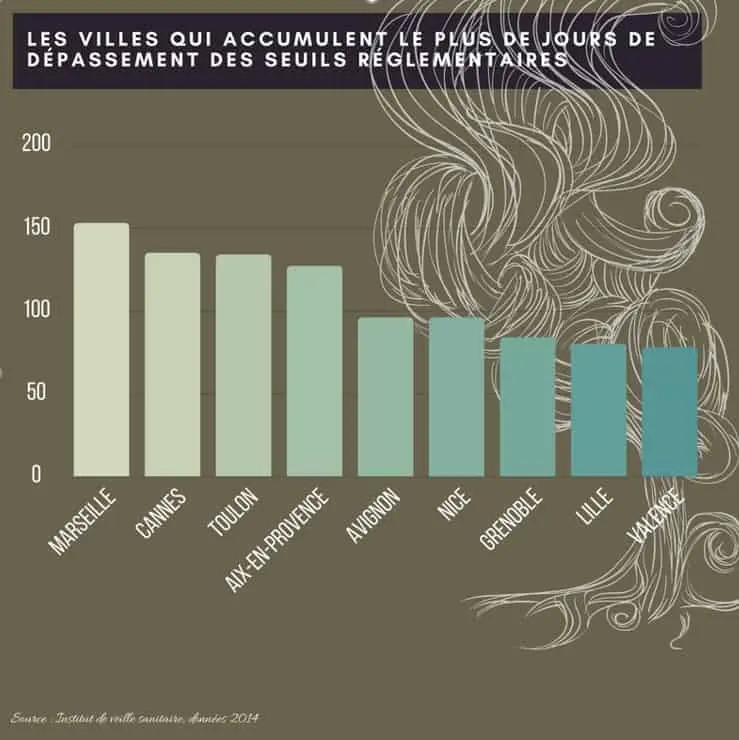
But the main variable remains the number of days concerned during the year: it is the data that matters the most. A city can be affected by passenger pollution peaks due to certain activities or weather conditions.
It can also be polluted on a regular and persistent basis. If we take this data into account, the cities that are at the top of the ranking, Marseille, Cannes, and Toulon, are mainly located in the south-east of France. (5)
Understanding pollution
What are we talking about exactly?
Air pollution is at the heart of the news and is the subject of a recent European Union lawsuit against France and frequent appeals by citizens. It is coupled with other pollution problems resulting from human activities which can affect water and soil.
Every day, approximately 14 liters of air pass through our respiratory tract. And in this air we find invisible threats. They come from industrial and agricultural activities, from the transport sector, but also from combustion plants, domestic activities, or even smoking.
According to the World Health Organization [1], nearly 500 French cities exceed the limits for the concentration of fine particles in the air. In the world, more than 9 people on 10 live with polluted air, at least loaded with fine particles PM10 and PM2,5.
Deaths caused by air pollution can be counted in the millions, due to both outdoor air pollution, mainly from industrial activities and traffic, and indoor air pollution. It is a large number of cerebrovascular accidents, respiratory pathologies, pulmonary diseases or even cancers.
What are the causes of pollution?
Fine particle pollution, the first responsible for many respiratory pathologies, comes mainly from the industrial, transport and agricultural sectors, and from the production of coal-fired power stations.
We often forget the quality of indoor air : at home, at the office, and even at school. This quality can be affected by the use of combustion appliances, human activities such as smoking or the use of household products, but can also come directly from construction materials and furniture.
PM, or airborne particles, are small particles that are carried through the air and enter the heart of the lungs and airways. They are believed to be the cause of more than 40 deaths per year in France [000].
They are classified according to their size: each particle thus has a regulatory threshold, beyond which the situation begins to be dangerous for human health.

Fine particles, and mainly PM10, accumulate on the territory. Poor air quality is the third cause of death in France, behind tobacco and alcohol.
According to the Court of Auditors[8], 60% of the population would be affected in France, particularly in winter when the weather is cold and dry. This is where the air is not renewed and the particles stagnate in the air and then infiltrate our lungs.
Apart from fine particles, regulatory bodies monitor other substances: nitrogen dioxide, from transport and combustion; sulfur dioxide, released by factories; and ozone, the results of various chemical reactions under the effect of ultraviolet rays.
Weather and climate change
At first glance, the consequences of climate change on pollution are imperceptible. But some proven links have already been established.
Already, rising temperatures mean more use of air conditioners, refrigerators, and other devices responsible for indoor pollution.
Fine particles and carbon monoxide suspended in the atmosphere can also be the cause of an increase in forest fires.
New plant migrations could cause allergies to pollen for populations that were not previously exposed to it. The air around us is still in danger of changing.
The weather outside also affects air quality: whether it is hot or cold, whether there is wind or not, precipitation or none.
Each weather condition will have a different effect on pollution: it will either disperse or concentrate on a space. If the wind is weak and the weather is calm, it will be difficult for the pollutants to disperse and remain at ground level, for example.

Water pollution, soil pollution: effects and consequences
Let us not forget also that the air is not the only one to be affected by human activities. Water, a vital asset, is particularly threatened by various chemical substances.
Nitrates, phosphates, heavy metals such as lead which come from agriculture or industry, or even hydrocarbons.
For some substances, including endocrine disruptors and traces of drugs, it is even difficult to assess the real effects on long-term health.
This, in the city, can be added to the poor maintenance of the pipes which aggravates the health risk. Some waters are no longer drinkable, in others, you can no longer bathe. The risks concerned are different according to the types of pollution.
Long-term symptoms depend mainly on the dose and the duration of exposure. Lead is the cause of lead poisoning. Hydrocarbons, nitrates, or arsenic are carcinogenic.
In the short term, the disorders are rather infectious. Benign disorders such as digestive disorders and mycoses; and more serious disorders such as legionellosis or hepatitis. Nitrates, for example, are found in concentrations above the regulatory thresholds in many parts of the territory due to agricultural activity and the use of fertilizers.
These cause two major concerns: they modify the biological balance of aquatic environments due to the phenomenon of eutrophication, and they are toxic to humans.
They become toxic beyond a certain threshold because they are converted into nitrites, via bacteria present in the body. With this phenomenon, the blood is no longer able to transport enough oxygen to the cells: it is a danger that particularly affects fragile populations such as infants.
For adults, they are dangerous because, together with certain pesticides, they form a real carcinogenic cocktail.
Act and protect yourself
Public transport and carpooling
For short or long journeys, I prefer collaborative solutions: too many cars crisscross the country with a single passenger on board. I therefore observe the solutions available to me: train, bus, carpooling …
Cycling, walking: 0 emissions for short distances
It is proven that in urban areas, the bicycle remains the fastest means of transport for a journey of less than 5 kilometers. One in two Europeans would take their vehicle to make journeys of less than 3 kilometers.
The problem is that these short trips made with the engine cold emit a lot of pollution.
Do I take the car anyway? But in eco-driving
Eco-driving is a way of driving that saves fuel and therefore reduces pollutant emissions. It is about driving smoothly, respecting speed limits.
In short, not to drive abruptly and aggressively. It is also imperative to have a vehicle tuned and maintained.

The golden rules for preventing pollution
To protect yourself you will inform yourself
In the same way that we consult the weather forecast in the morning, we can consult the pollution index of the day, whether on the web, on the radio, or on television.
Forecasts make it possible to limit excessively intense activities in the event of a pollution peak, especially for vulnerable people.
On the web, you can consult the Prév’air or Airparif site for each region. More and more applications such as Plume air Report also make it possible to know the air quality index in real time.
Adept of public transport you will be
In the event of a severe pollution episode, harmful particles accumulate in the passenger compartment of your vehicle. Not to mention that it is the very source of pollution.
We then favor the tram, the bus, the bicycle and other soft modes of urban transport for short journeys; carpooling and the train for long journeys.
And if you really want to take your vehicle, take other passengers by carpooling and don’t forget about eco-driving.
In the heart of sport you will do
As we said, it is advisable to avoid too intense physical activities in the event of peak pollution.
Indeed, when you make an effort, the bronchi are open and suck a lot more air: you are more vulnerable and more exposed. So, if you want to run or play sports, prefer to go to a natural area.
A vehicle that consumes little you will promote
When buying a vehicle, find out about its CO2 emissions using its label. A green label is less than 100 grams of CO2 per kilometer traveled.
A red label is more than 250 grams of CO2 per kilometer traveled. We can promote electric vehicles: without forgetting that the country’s electricity mix favors nuclear energy.
For short journeys, it remains ideal; a hybrid vehicle will be more suitable for long journeys.
You will be concerned about the quality of the air
Indoor air pollution is often overlooked, while the health impacts are the same. Ventilate your interior regularly to prevent CO2 and pollutants from cleaning products and coatings from accumulating. You can do this twice a day for at least ten minutes.
Polluting plants can also be a good solution: cacti, ivy, or succulents.
Also avoid toxic cleaning products, based on solvents and chlorinated compounds. More natural solutions exist: white vinegar, baking soda, or even black soap.
Of the antioxidants you will consume
Why is this important? The body transforms almost all of the oxygen we breathe, apart from a small amount of molecules called free radicals.
Pollution accentuates this phenomenon, and accelerates cellular aging. Eating antioxidant foods helps strengthen your immune system against this problem.
We think of small fruits such as blueberries, goji berries, prunes, or even strawberries and raspberries, but also vegetables such as peppers and broccoli.
In conclusion
What to conclude from this classification? We cannot point the finger at a city as being a bad student: particles are mobile, pollution is dispersed, and the problem is spreading on a global scale. There is also no need to panic about your data: the idea is to adopt responsible behavior and become aware of the problem.
Many policies and measures are in place, and already allow some improvements.
Let us add that even if our cities exceed the regulatory thresholds, and that France was the subject of a recent condemnation which will have to result in new efforts, we remain favored compared to other countries of the world where the air is absolutely unbreathable, in Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, or Pakistan.









