Most often, tetanus in children occurs between the ages of three and seven years. Mostly this disease has a summer seasonality and covers rural residents more. The death rate for tetanus is over 40%.
The causative agent of tetanus enters the body through cuts and wounds on the skin, microtrauma can also cause illness. This usually happens with injuries and injuries to the feet. In newborns, the virus can enter through a wound in the navel or umbilical cord. After tetanus enters the child’s body, the virus begins to multiply rapidly. At the same time, tetanospasmin is produced, which can penetrate the child’s central nervous system and spread with the blood flow throughout the body.
Symptoms of tetanus in children
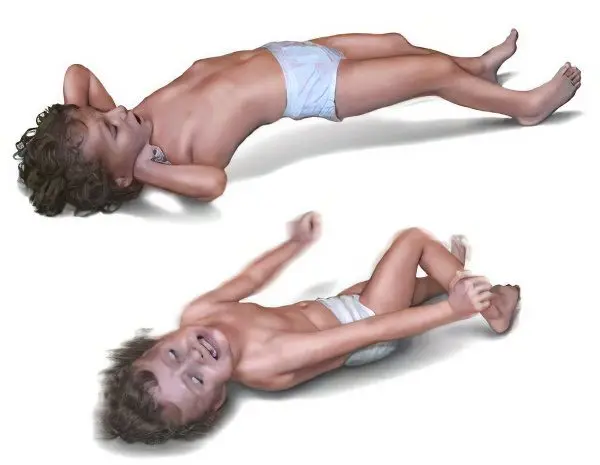
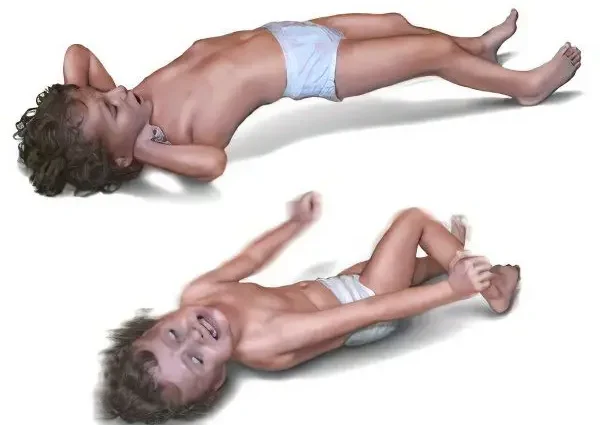
The onset of the disease is acute, the infected infant refuses to breastfeed and becomes anxious. The incubation picture usually lasts from 5 to 14 days. The main hallmark of tetanus is the involuntary contraction of the masticatory muscles, due to which the child cannot open his mouth. Due to the contraction of the swallowing muscles, swallowing is difficult. Crying and smiling can be expressed on the face at the same time, the mouth is stretched, the corners are slightly lowered, and the skin on the forehead is folded.
After a short period of time, other symptoms of tetanus are added: contraction of the long muscles of the ridge, arms and abdomen. Intercostal muscles and the diaphragm are also connected to the process. Seizures come on suddenly. At first, the nature of seizures is short-lived, but their duration and frequency gradually increase. The patient feels unbearable pain, while being fully conscious.
Tetanus can be aggravated by manifestations of tachycardia, arrhythmias, sweating, contractions of peripheral vessels and increased pressure. With frequent muscle contractions, acidosis can develop, disrupting the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The cause of death can be respiratory paralysis and asphyxia or cardiac paralysis.
Treatment of tetanus in children
If tetanus is detected in a child, he is immediately hospitalized, surgical treatment of damaged skin is performed with the removal of damaged tissue, the type of antibiotic therapy is determined, and an appropriate course is prescribed. Anti-tetanus serum is injected intramuscularly once in the amount of 1,5–2 thousand IU. With a difficult course of the disease, babies are transferred to intensive care, the lungs are artificially ventilated and the vaccine is administered intravenously.
To overcome convulsions, antipsychotics and sleeping pills are prescribed in combination with antihistamines and analgesic pharmaceuticals. As a preventive measure for tetanus infection, from the age of three months, infants are routinely vaccinated.