Contents

Male testicles are a very vulnerable part of the body. The female genital organs are located inside the body, they are protected not only by soft tissues, but also by bone structures, tendons, and muscles. While the testicles of a man do not have such protection. They are outside, permeated with a huge number of nerve fibers and blood vessels. Therefore, the testicles are so vulnerable to various factors of the external and internal environment. Pain in the testicles in men is the first signal that the organ has been damaged.
The testicles, or as they are also called, the testes, are an important organ of the male reproductive system. They produce testosterone and sperm, which are necessary for the fertilization of the female egg. Pain in the testicles can begin to bother a man at any age.
Damage to the organs leads to the fact that they stop producing testosterone and sperm, so you need to find out what is the cause of the pain as soon as possible. Only in this way will it be possible to prescribe a treatment that will be effective and effective. It will allow you to get rid of not only pathological symptoms, but also the most damaging factor that led to the dysfunction of the male genital glands.
Dangerous symptoms: pain in the testicles

The causes that lead to pain in the testicles can be very diverse. It can hurt either one or both organs.
Symptoms that should alert a man:
Pain in the testicles and their swelling.
Increased body temperature.
Local hyperthermic reaction. A dangerous symptom is a feeling of heat in the testicles.
Enlargement of the organ in size.
Scrotal tension.
Change in the shape of one testicle compared to the other.
The appearance of bulges or tubercles on the testicles, which are felt during palpation.
Nausea and vomiting.
Increased perspiration.
The pain tends to increase, becomes unbearable.
The pain is aggravated by walking or touching.
The pain is aching, dull, pulling, or cutting.
Increased irritability, depression, fear for one’s life.
If you experience pain in the testicles, you should seek the advice of a doctor. You should not hesitate with this, since painful sensations can indicate various pathologies or injuries of the organ.
Causes of pain in the testicles in men
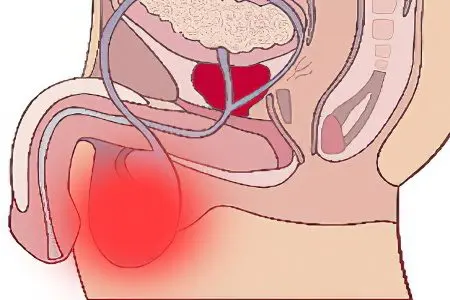
Pain in the testicles in men can occur for a variety of reasons.
All of them are grouped into 5 groups:
Physiological reasons. Drawing pain in the testicles may be due to abstinence. Every man noticed that if sexual arousal persists for an hour and there is no natural discharge, then this leads to discomfort in the genital area. This condition cannot be called pathological. It is the result of natural processes in the body.
Traumatic. The testicles are permeated with many nerve endings, so even a slight irritation of their delicate skin can lead to painful sensations. Naturally, the blow and pressure will cause quite intense pain. In addition, traumatic pain occurs against the background of hypothermia and overheating, with self-satisfaction, when using sex toys. Too active frictions during intimacy respond with pain. Other causes of pain include chemical exposure to the delicate tissues of the testicles and wearing tight underwear.
infectious causes. Since the genitals have a developed blood supply, inflammation of the organs located in this area leads to severe edema. It develops due to sweating of plasma through the vascular wall. Nerve fibers are pinched, which provokes severe pain. A similar situation is observed with orchitis, urethritis, urolithiasis, prostatitis and epididymitis.
vascular causes. The testicles can hurt if the vessels that feed them are damaged by one or another pathology, for example, a blood clot or an atherosclerotic plaque has formed in them. Also, pain can be a consequence of varicocele, in which the veins expand. The danger of vascular pathology is reduced not only to pain, but also to tissue death.
Pain due to damage to other organs. The pudendal nerve is generally responsible for the innervation of the perineum. If he is irritated, then this will lead to painful sensations not only in the penis, but also in the testicles. Pathologies that can affect the pudendal nerve: urethritis, urolithiasis, ureteral tumor, etc.
To understand what kind of disease caused pain in the testicles, you need to know the main symptoms of such disorders.
What diseases are characterized by pain in the testicles?
If a man experiences pain in the testicles, then he should not postpone a visit to the doctor.
Pain in the scrotum can be triggered by diseases such as:
Abstinence >>
Testicular injury >>
Orchitis – inflammation of the testicles >>
Epididymitis – inflammation of the epididymis
Testicular torsion >>
Pain in renal colic (indirectly) >>
Varicocele >>
Vesiculitis >>
Cystitis >>
testicular tumors >>
STD >>
Urethritis >>
Inguinal hernia >>
Hydrocele (hydrocele) >>
Chronic prostatitis >>
Abstinence
Abstinence in itself is not a disease, but it is one of the most common causes of discomfort in the testicles. Pain is explained by the interdependence of all organs of the reproductive system from each other.
When a man is in an excited state, in addition to an erection, a whole cascade of reactions occurs in the body. The ductal and circulatory system of the testicles is activated. This is necessary to prepare them for the upcoming ejaculation. If ejaculation does not occur, then there is a risk of spasm of blood vessels and ducts, which will lead to pain in the scrotum.
To get rid of pain, there is no need to take any action. As a rule, the discomfort will pass on its own after a short period of time. If pain worsens the quality of life and causes discomfort to a man, you can take a tablet of Drotaverine, No-shpa or Spasmalgon.
Provided that after 7-8 hours there is no relief, you need to consult a urologist to make sure that there is no pathology.
Injuries

Injuries, like abstinence, cannot be attributed to the disease, but since any damage to the tissues of the testicles will lead to pain, it must be mentioned. The pain in case of an organ injury will be the more intense, the heavier it is. If a man received a minor bruise of the soft tissues, then the pain will soon pass on its own. When the blow was very strong, the victim may even experience pain shock. This will worsen your general well-being.
Sometimes there are stab and cut wounds, which are complicated not only by pain, but also by intense bleeding. The likelihood of infection, the development of inflammation, with further tissue necrosis increases. The pain becomes more and more intense, it will be impossible to endure it. If the testicles are regularly damaged, then this leads to chronic pain.
Minor injuries can be treated on their own. It is enough just to take painkillers, medicines to relieve inflammation. Cold helps to cope with swelling, for which ice can be applied to the testicles.
A man should rest more, adhere to a half-bed regimen. This will reduce the load on the sex glands and ducts.
To reduce pain in the scrotum and eliminate the tension of the seed-bearing ducts, as well as prevent blood stasis, you can apply a suspensory bandage that will fix the testicles in one position. Thus, it will be possible to stop the progression of edema, the pain will become less intense.
To stop the spasm, you should take Baralgin or Spazmalgon. The use of medicines can be supplemented by the application of cold compresses.
If the victim develops bleeding, then measures must be taken to stop the progression of the hematoma. In this case, home treatments will not be enough. Medical assistance will be required. In this case, drugs such as Vikasol, Dicinon, Etamzilat can be used.
To speed up recovery and normalize the work of the sex glands, it is necessary to visit a physiotherapy room. The doctor can prescribe gentle thermal procedures, among which the most popular are heating, low-intensity ultraviolet radiation, and magnetotherapy.
If the injury was severe, then you should not hesitate to contact the doctor. It is necessary to call a team of doctors, or go to the emergency room on your own. If you do not get qualified help in time, this can threaten to disrupt sperm production and lead to infertility.
If the injury was very severe, then the victim is hospitalized. In such cases, surgical assistance is required. The damaged testicle is removed, the hematoma is aspirated, and the bleeding is stopped. The field of which the skin is sutured.
Orchitis
Orchitis is an inflammation that is concentrated in the testicles. Men suffer from orchitis after a viral infection: after mumps, rubella, etc. However, such a complication develops no more than in 30% of cases. The pain in the testicles is aching, tends to increase. They swell, the skin of the scrotum turns red.
The disease leads to a violation of the reproductive function, in one testicle a smaller number of spermatozoa will be produced. If the process is bilateral, then the work of both organs worsens.
What to do? What to do with orchitis and epididymitis?
Epididymitis (inflammation of the appendage)
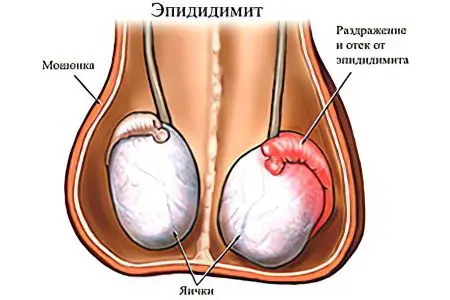
Epididymitis in men develops due to the fact that the bacterial flora penetrates the appendage. The appendages are located in the testicle, in its lower part and stretch along its back side.
When examining the genital organs, the patient himself may not notice any pathological changes. However, in the affected area, the skin becomes painful and tense. The pain is pulling, it can spread to one or two testicles at once. A bilateral process is observed only when there is no treatment for unilateral epididymitis.
As the pathology progresses, the organ begins to increase in size, the body temperature rises, the pain intensifies, becomes sharp. If at this stage the man is not prescribed treatment, then the bacteria can penetrate into other organs, which significantly worsens the prognosis for recovery.
What to do? What to do with orchitis and epididymitis?
Pain with testicular torsion
If a man does not suffer from any diseases and pain in the testicle occurs against the background of complete physical well-being, then it may indicate organ torsion.
The testicle is suspended on the spermatic cord. This cord is represented by blood vessels and vas deferens. If the testicle makes a complete revolution in the scrotum, then the cord is pinched. Doctors call this condition testicular torsion.
This happens only in adolescence. In adult men, the tissues lose their elasticity, which makes it impossible for the testicle to torsion in the scrotum.
What to do? What to do about testicular torsion?
Pain in renal colic

Sometimes pain in the testicle has no direct connection with pathologies and disorders in the reproductive system. So, pain can develop when the ureter is damaged. It is through it that urine flows from the kidneys to the urethra. The pudendal nerve passes behind the ureter. If a tumor or other neoplasm forms in the ureter, then it will certainly begin to put pressure on this nerve, which will lead to lumbar pain that will radiate to the groin and scrotum.
Symptoms of renal colic can be distinguished as follows:
The pain is concentrated in the right or left testicle, as most often only one ureter is affected. In this case, the genital nerve is irritated only on one side.
Pain occurs unexpectedly, against the background of complete health.
Pain in the lower back, lower abdomen, thighs and genitals.
The process of urination is disturbed, urine is excreted in small portions. It may contain blood, which changes its color to pink and reddish.
What to do? What to do with renal colic?
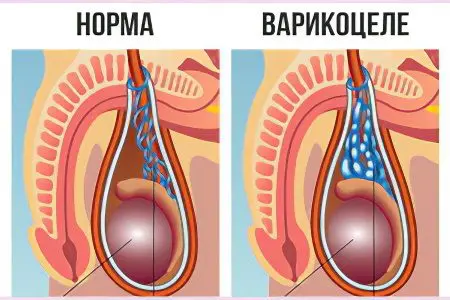
Varicocele
Varicocele is a pathology that is characterized by the expansion of veins in the testicles. In this case, a person has pain in the abdomen and in the scrotum. Varicocele is a consequence of a violation in the anatomy of the genitourinary system.
For a long time, this disease can be asymptomatic. Sometimes the pathology is discovered by chance, during a medical examination. If a man complains of pain in the testicle and it turns out that this pain is a consequence of a varicocele, then we can judge the severe course of the process.
The pain is pulling, it can become more intense if a person has been motionless in one position for a long time, or after prolonged sexual arousal. During the examination, an increase in the size of the scrotum on one side is visualized. At the same time, the skin is no different from a healthy dermis.
What to do? What to do with varicocele?
Vesiculitis
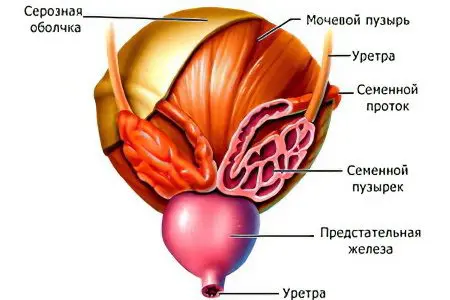
Vesiculitis is an inflammation of the seminal vesicles. Pathology develops against the background of urethritis, when infectious agents with blood flow from the urethra are transferred to the seminal vesicles.
The following symptoms will indicate vesiculitis:
Sharp pain that radiates to the coccyx, but is concentrated mainly in the perineum.
The pain tends to increase on one side of the prostate.
During urination or during bowel movements, the pain becomes intense.
A small amount of blood can be seen in the ejaculate.
Ejaculation is accompanied by discomfort.
A man is haunted by headaches that proceed like a migraine.
What to do? What to do with vesiculitis?
Cystitis
Cystitis develops due to hypothermia of the body, against the background of a decrease in immune forces, as well as with hormonal imbalance.
What to do? What to do with cystitis?
Cancer
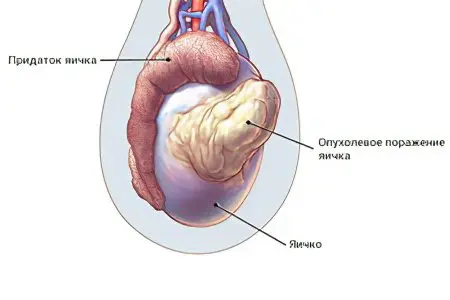
A clear sign of testicular cancer is the appearance of a tumor-like neoplasm (bump) on one of these paired organs. At first, the tumor is small, but as the disease progresses, it becomes larger. However, not every neoplasm that forms in the testicles is a tumor. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Other symptoms of testicular cancer include:
Acute pain in the testicles.
For a long time, pulling pains disturbing a man.
Discomfort and feeling of heaviness in the testicles.
Compaction of the testicle, change in the texture of the tissues of the scrotum.
Enlargement of one organ in size.
Testicular cancer is classified according to the TNM system and stages of development. In the TNM system, there are:
T is the size of the tumor.
N is an indicator of how much the lymph nodes were involved in the pathological process.
M – characterizes the presence of metastases in distant organs.
There are 4 stages in the development of testicular cancer, including:
Stage one. The tumor has spread only to the testicle or to the epididymis.
Stage two. Pathology captured the lymph nodes located in the immediate vicinity.
Stage three. Metastases are found in the cervical and thoracic lymph nodes.
Stage four. Metastases are present in the brain, lung tissue, liver, and bones.
What to do? What to do with cancer?
STDs
STDs are diseases that are sexually transmitted.
These infections include:
Syphilis.
Genital herpes.
Ureaplasmosis.
Mycoplasmosis.
Chlamydia.
Gonorrhea.
Granuloma.
Bacteria, fungi and viruses can provoke the development of the disease. Pain will bother a man on an ongoing basis. She is dumb, stingy. As the disease progresses, the male reproductive organ increases in size, the lymph nodes become larger, and ulcerative defects may appear.
What to do? What to do with an STD?
Urethritis
Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra, which develops due to the ingress of bacterial flora into it. Microbes enter the testicles with the blood stream, infecting their tissues. At the same time, the man has severe pain, they are burning, spread to the testes.
What to do? What to do with urethritis?
Hernia
An inguinal hernia is a protrusion of the peritoneum into the inguinal canal. It is in it that a man has a spermatic cord. If the hernia is strangulated, then the person will need surgery. If the hernia is not restrained, then it is possible to correct it yourself.
Sometimes inguinal hernias appear during fetal development of the child. Hernias can form during life, for example, due to heavy lifting.
What to do? What to do with an inguinal hernia?
Hydrobodies
A hydrocele is dropsy of the testicles. With this pathology, an increase in the size of the testes occurs. A man experiences aching pains, his body temperature rises, aching muscles appear. One of the testicles begins to pull.
What to do? What to do with a hydrocele?
Diagnosing

If a man began to be disturbed by pain in the testicles, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. It can be either an andrologist or a urologist. Doctors of these specialties are engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of male diseases.
The doctor will interview the patient, prescribe him certain diagnostic measures, after which he can select the optimal treatment, if necessary.
Before you go to a specialist, you should stop taking painkillers. Otherwise, it will be difficult to determine the exact cause of the problem.
If a testicle was injured, or a torsion of the spermatic cord occurred, help should be provided immediately.
During the first appointment, the doctor implements the following algorithm of actions:
Listens to the patient’s complaints, conducts a survey.
Performs a digital examination of the testicles and penis, clarifies the presence of edema, palpates the localization of pain.
These actions will allow the doctor to insert a preliminary diagnosis, on the basis of which further studies will be prescribed.
They may include:
Urine for general analysis.
Donating blood for clinical and biochemical analysis.
Performing a spermogram.
Performing semen analysis.
Ultrasound of the scrotum and testicles.
Testicular biopsy.
MRI.
Sometimes these studies are not necessary, since the doctor makes the correct diagnosis after the first examination of the man and when questioning his complaints.
Treatment of testicular pain in men
Pain in orchitis and epididymitis

With orchitis and epididymitis, the pain is severe, tends to increase while walking, when touching the gonads. At rest, the pain subsides a little, but still it cannot be called weak. Taking drugs from the NSAID group leads to symptom relief (Citramon, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, etc.).
In addition to pain, a person with epididymitis and orchitis will present with the following complaints:
The skin becomes red.
The testicles are very swollen.
A person develops signs of intoxication of the body: appetite disappears, body temperature rises, nausea and dizziness occur.
The established diagnosis of “epididymitis” or “orchitis” requires the start of treatment.
The therapy is based on the following principles:
Compliance with a gentle regimen. The testicles should not be injured. To do this, a man should rest as much as possible, adhere to a half-bed regime, wear a suspensory bandage.
Taking medications aimed at the destruction of pathogenic flora. Most often, the causative agent of inflammation is bacteria, so the patient is prescribed antibiotics. If a man is hospitalized, then he is prescribed Ceftriaxone or Clarithromycin. When treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, Amoxiclav, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin are used.
To reduce pain and relieve swelling, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. It is possible to use such medicines as: Citramon, Ibuprofen, Ketorolac, Nimesulide, etc.
To restore the functioning of organs after recovery, you can resort to methods of physiotherapy treatment.
The average duration of the treatment course is 10-14 days. Treatment should be started as early as possible, as delay threatens with a serious violation of the reproductive function.
Pain with testicular torsion
If a man has a twisted testicle, then emergency surgical care is required. To begin with, the patient should be examined by a urologist.
To give the testicle a normal position, it is necessary to perform an incision in the scrotum, after which the organ is either straightened or removed (if it has lost its viability). To prevent testicular resection, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Pain in renal colic
With renal colic, a person must be hospitalized without fail. To relieve pain, you need to eliminate the obstacle that led to the difficult outflow of urine.
Until that moment in time, until the medical team arrived, you need to apply warmth to the stomach and lower back. For this purpose, hot water heaters are used. Slightly reduce spasm allow drugs such as: Drotaverine, No-shpa, Spazmalgon, Baralgin. However, it will not be possible to completely cope with the problem with their help; the help of a specialist is needed.
More: Renal colic – what is it?
Varicocele
It will not be possible to quickly get rid of varicocele. It is necessary to tune in to long-term therapy. It is important not only to receive medications, but also to reconsider lifestyle.
To do this, you must follow the following recommendations:
Eliminate alcohol consumption, stop smoking.
Focus on balancing your body weight.
Do sport. Exercise doesn’t have to be exhausting. It is enough to start moving more, for example, jogging in the morning, doing exercises, walking.
You need to stand or sit as little as possible. Static postures lead to stagnation of blood and progression of the disease.
Since varicocele develops due to problems with the veins, a man needs to take medicines that will strengthen the valves of the vessels and their walls:
Angioprotectors: Tagista, Detralex, Troxerutin, Actovegin.
Vitamins C, E, PP.
Combined means: Tocopherol, Askorutin, etc.
In some cases, they resort to surgical intervention – sclerosis of the veins of the scrotum. This method allows you to cope with the symptoms of the disease and reduce the likelihood of its recurrence.
More: Causes and symptoms of 1, 2, 3 and 4 degrees of varicocele
Vesiculitis
If a man develops vesiculitis, he may be prescribed the following medications:
Antibacterial agents: Penicillin, Rifampicin, Streptomycin, etc.
Uroseptics: Furadonin, Furagin, etc.
Physiotherapy, such as laser therapy, ultrasound phoresis, iontophoresis, etc., allow you to quickly deal with the problem.
Cystitis

Cystitis is a disease that requires treatment, and a doctor should prescribe therapy. Self-selection of drugs and the use of alternative therapy methods will lead to the fact that acute inflammation of the bladder becomes chronic and will disturb a person on an ongoing basis. In addition, it threatens with serious complications: infertility and impotence.
A man with cystitis needs to undergo a comprehensive examination to determine what the cause of cystitis is. Only after that it will be possible to begin etiotropic treatment. If the disease is severe, then hospitalization is necessary. On an outpatient basis, a mild form of cystitis is treated.
Basics of therapy:
Compliance with bed rest.
Abundant drink.
Salt restriction on the menu.
Refusal of spicy, pickled, spicy and other aggressive dishes.
Taking herbal preparations, including: Phytolysin, Canephron, Cyston, etc. They can reduce inflammation and pain, relieve swelling.
However, the most important point in the treatment of cystitis is taking drugs aimed at eliminating the causative agent of the disease. If the inflammation is provoked by microbes, then antibiotics are required. With specific inflammation caused by candida, mycoplasmas and other pathogenic microorganisms, the use of drugs of a narrow focus is required.
More: Cystitis in men – causes, symptoms, how to treat? List of medicines
Cancer

Treatment for testicular cancer depends on whether a man has seminoma or not, as well as on what stage of development the disease is at.
The main directions of therapy:
Surgical intervention.
Radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy.
Tumor monitoring.
Chemotherapy combined with stem cell therapy.
Most often, the patient is referred for an operation to remove the testis (orchiectomy). If a man has seminoma, then he will have to undergo chemotherapy and / or radiation therapy without fail.
A man should not despair after being diagnosed with testicular cancer. This type of oncopathology is recognized as one of the most favorable in terms of prognosis for recovery. The annual survival rate of patients is 99%, and the five-year survival rate is 98%. The disease rarely recurs – no more than 5% of cases. At the same time, the removal of one testicle does not have a significant effect on the sexual capabilities of a man and on his childbearing function.
STDs
Treatment of sexually transmitted diseases requires taking drugs that are aimed at destroying a specific pathogen. Chlamydia is treated with Azithromycin and Doxycycline. For gonorrhea, ceftriaxone or ciprofloxacin is prescribed. The doctor takes into account not only the infectious agent that provoked the pathology, but also the characteristics of a particular organism.
Urethritis
To get rid of urethritis, antibiotics are required. If the disease is caused by candida, then antifungal drugs are prescribed.
Chlamydial urethritis is treated with doxycycline, chloramphenicol, or fluoroquinolones.
If mycoplasmas were found in a smear from the urethra, then Tetracycline is prescribed.
Sometimes urethritis develops when the body is infected with herpes viruses. In this case, it is advisable to take drugs such as: Penciclovir, Ganciclovir, Ribavirin, Aciclovir.
More: Symptoms and causes of urethritis
Hernia
To get rid of an inguinal hernia, an operation is needed. It can be performed in an open or closed way (using laparoscopic equipment).
Patients over the age of 18 can undergo inguinal canal plasty. In this case, a special synthetic mesh is used.
Hydrobodies
If the accumulation of fluid is insignificant, then men with hydrocele are prescribed therapy with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and decongestants. The patient is shown bed rest and wearing a special bandage.
When the edema is pronounced and there is a threat of tissue necrosis, the man undergoes an operation or a hydrocelectomy. Surgery can be of 3 types. If the hydrocele communicates with an inguinal hernia, then the Ross operation is performed. The Bergman operation or the Winkelmann operation may also be implemented. They are used when a man is diagnosed with an isolated hydrocele and lymphocele (clamping of the lymph nodes).
More: Dropsy in men – symptoms, consequences and methods of treatment
Video: Elena Malysheva’s program “pain in the scrotum, as a symptom”:









