Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Telmisartan is an organic chemical compound found in many medicines. It fights hypertension by preventing spasms of the blood vessel walls. It is one of the so-called angiotensin II receptor antagonists; medicines belonging to this group are called sartans. The abbreviation is ARB (Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers). Read about the mechanism of action of Telmisartan, how to dose it and what side effects it causes.
Telmisartan – action
Telmisartan, according to the package leaflet (Telmisartan Apotex), is an orally active and selective angiotensin II receptor (type AT1) antagonist. Telmisartan displaces angiotensin II with high affinity from its binding site at the AT1 receptor subtype, which is responsible for the known mechanism of action of angiotensin II. Telmisartan does not exhibit any partial agonist activity at the AT1 receptor. Telmisartan selectively binds the AT1 receptor. This connection is long lasting.
Telmisartan has no affinity for other receptors, including the AT2 receptor and other, less understood, AT receptor subtypes. The function of these receptors is unknown; the effects of their excessive stimulation by angiotensin II, the concentration of which increases under the influence of telmisartan, are also unknown. Telmisartan lowers the levels of aldosterone.
Telmisartan does not inhibit plasma renin activity and does not block ion channels. Telmisartan does not inhibit angiotensin converting enzyme (kininase II), the enzyme also responsible for breaking down bradykinin.
See: Healers’ plasma is missing
Telmisartan – indications for use
Telmisartan is used alone or in combination with other drugs to treat high blood pressure. Telmisartan is also used to reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke or death in people 55 years of age or older who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Telmisartan, as already mentioned, belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin II receptor antagonists. It works by blocking the action of certain natural substances that tighten the blood vessels, allowing the blood to flow more smoothly and the heart to pump more efficiently.
High blood pressure is a common condition and, if left untreated, it can damage the brain, heart, blood vessels, kidneys and other parts of the body. Damage to these organs can cause heart disease, heart attack, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, and other problems.
In addition to taking medications, changing your lifestyle will also help control your blood pressure. These changes include eating a diet low in fat and salt, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising for at least 30 minutes most days, quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption, preferably stopping alcohol altogether.
Also read: Heart failure is a silent epidemic in Poland. The cardiologist tells you what the symptoms are
Telmisartan – dosage and method of administration
Telmisartan is a tablet to be taken by mouth. The dose of Telmisartan depends on the medical condition you are taking it under.
The dosage is as follows:
- primary hypertension:
the usual effective dose is 40 mg once a day. Some patients may experience improvement with a dose of 20 mg. If the blood pressure lowering effect is not satisfactory, the dose of telmisartan can be increased to 80 mg once daily.
- prevention of cardiovascular diseases:
the recommended dose is 80 mg once a day.
- children and youth:
The safety and efficacy of Telmisartan in children and adolescents below 18 years of age have not yet been established.
See: Poor sleep promotes resistant arterial hypertension
Telmisartan – contraindications
The main contraindication to the use of Telmisartan is hypersensitivity to the active substance (i.e. Telmisartan) or the auxiliary substance (mannitol, meglumine 15, povidone (K-30), potassium hydroxide, magnesium stearate).
The preparation should not be taken by women in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, people with biliary outflow disorders and severe hepatic insufficiency.
Concomitant use of Telmisartan Apotex with aliskiren-containing products is contraindicated in patients with diabetes mellitus or impaired renal function (glomerular filtration rate, GFR
Telmisartan – side effects
As with all medicinal preparations, Telmisartan can cause certain side effects. Some symptoms require immediate medical attention.
If you experience any of the following symptoms, see your doctor immediately:
- sepsis (often called blood poisoning, which is a serious infection with an inflammatory reaction throughout the body)
- sudden swelling of the skin and mucous membranes (angioedema).
These side effects are rare (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people) but can be serious and require you to stop taking this medicine immediately and see a doctor. If left untreated, these side effects could be fatal.
Possible side effects of Telmisartan:
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- low blood pressure (hypotension) in patients being treated to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- upper respiratory tract infections (e.g. sore throat, sinusitis, colds)
- urinary tract infections
- decreased number of red blood cells (anemia)
- high levels of potassium in plasma,
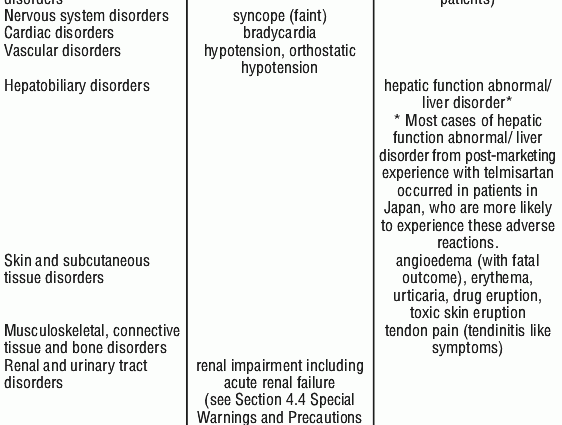
- depressed mood (depression), fainting, difficulty sleeping
- spinning sensation (vertigo),
- slow heart rate (bradycardia),
- low blood pressure (hypotension) in people being treated for high blood pressure
- dizziness when standing up (orthostatic hypotension), shortness of breath, coughing
- stomach pain, abdominal discomfort, gas, vomiting
- excessive sweating, drug rash, itchy skin, muscle pain,
- back pain, muscle spasms
- kidney problems, including acute kidney failure
- chest pain, feeling weak and increased levels of creatinine in the blood.
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people):
- sepsis,
- increase in certain white blood cells (eosinophilia), low number of platelets (thrombocytopenia),
- severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic reaction)
- allergic reactions (e.g. rash, itching, breathing problems, wheezing, facial swelling or low blood pressure)
- low blood sugar (in people with diabetes), feeling restless, sleepy,
- visual disturbance, fast heart beat (tachycardia), gastritis
- taste disturbance, dry mouth,
- liver dysfunction (more common in people of Japanese origin),
- severe drug rash, reddening of the skin, sudden swelling of the skin and mucous membranes (angioedema), which may also be fatal (angioedema, also fatal),
- eczema, redness of the skin, hives
- joint pain, pain in extremity, tendon pain, flu-like symptoms,
- increased levels of uric acid, increased levels of liver enzymes or blood creatine phosphokinase, decreased levels of hemoglobin (blood protein).
The editorial board recommends: So that the excess uric acid does not spoil the summer, that is, the diet of people with hyperuricemia
Telmisartan – precautions
Telmisartan may cause drowsiness, dizziness, light-headedness and even fainting. Do not drive a car or operate machinery until you know how the drug affects you.
Telmisartan should not be used in patients with cholestasis, biliary obstructive disorders or severe hepatic impairment as Telmisartan is mainly eliminated via the bile.. In patients with impaired renal function, periodic monitoring of potassium and creatinine serum levels is recommended during treatment with Telmisartan.
There is also an increased risk of severe hypotension and renal failure when drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system are administered to patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or with renal artery stenosis with only one active kidney.
Telmisartan should be used with caution in individuals suffering from aortic or mitral stenosis, or obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Hypoglycaemia may occur in people with diabetes taking insulin or an oral antidiabetic medicine and Telmisartan. Therefore, in these individuals, glucose levels should be monitored – the dose of insulin or antidiabetic drugs may also need to be adjusted. The use of Telmisartan may cause hyperkalaemia.
In the elderly, with renal failure, diabetes mellitus, people taking concomitant medications that may increase potassium levels, and / or in those with coexisting diseases, hyperkalaemia may lead to death.
Before considering the concomitant use of medicinal products that affect the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, the benefit / risk ratio should be assessed.
Telmisartan – drug interactions
Telmisartan may interact with other medications, herbs, or vitamins. An interaction occurs when a substance changes the way a medicine works. This can be harmful or cause the medications you are taking not to work properly.
Listed below are some examples of medicines that may interact with Telmisartan
Blood pressure medications
Telmisartan affects the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the body. Do not take the drug with other preparations that affect the above system. These drugs include:
I. aliskiren – telmisartan and aliskiren should not be used concomitantly in adults with diabetes or moderate kidney disease,
II. angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), such as:
- candesartan,
- eprosartan,
- irbesartan,
- losartan,
- olmesartan,
- walsartan.
III. angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, such as:
- benazepril,
- captopryl,
- enalapril,
- fozynopryl,
- lizynopryl,
- moxie pill,
- peryndopryl,
- chinapryl,
- ramipryl,
- trandolapril.
Painkillers
Taking a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with telmisartan may increase your risk of problems with the proper functioning of your kidneys. These drugs include:
- ibuprofen,
- naproxen.
Digoxin
Digoxin levels in the blood may increase while taking telmisartan. Blood digoxin levels should be monitored during initiation, intake and discontinuation of telmisartan.
Bed
The amount of lithium in your blood may increase while you are taking telmisartan. Blood lithium levels should be monitored during initiation, intake and discontinuation of telmisartan.
Telmisartan – overdose
The most important symptoms of telmisartan overdose are hypotension and tachycardia. There may also be bradycardia, dizziness, increased serum creatinine and acute renal failure.
Telmisartan is not removed by hemodialysis. In the event of an overdose, the person should be carefully monitored, and the treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Management depends on the time since ingestion and the severity of symptoms.
It is recommended to induce vomiting and / or gastric lavage. Activated charcoal may be helpful in treating overdose. Serum electrolytes and serum creatinine should be monitored frequently. In the event of hypotension, the person should be placed in the supine position, quickly replenished with electrolytes and the intravascular volume replenished.