Contents
Telaziosis in cattle is a seasonal epizootic disease that is widespread everywhere. It is characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye. In the initial stages, thelaziosis is quite difficult to determine, since the clinical signs are mild. Advanced cases of the disease can lead to a complete loss of vision, a decrease in the productivity of animals, therefore, each owner of a livestock of cattle should know how the clinical signs of thelaziosis manifest themselves, as well as ways to prevent this disease.
Causes of thelaziosis and sources of infection
The causative agent of bovine thelaziosis is a small nematode belonging to the genus Thelazia. There are three types of biohelminths in cattle. Each of the nematodes parasitizes in different places:
- rhodesi is localized in the conjunctival cavity and under the third eyelid;
- gulosa, T. skrjabini – in the lacrimal canal and ducts of the lacrimal glands (sometimes in the conjunctival sac).
Infection of cattle with nematodes occurs on a pasture. In spring, their females release first-stage larvae, which migrate with tears and mucus to the area of the inner corner of the eye, where they are swallowed by cowflies. In the body of the intermediate host, the larvae grow, go through two stages of molting, and after 2-4 weeks turn into infective larvae of the third stage. The latter move to the head of the fly’s body and through the proboscis enter the conjunctival sac of the animal’s eye. After 1-1,5 months, the larva turns into a sexually mature individual. Adult nematodes can parasitize in the body of an animal for up to a year, however, most often they die after 3-4 months.
Animals of all age groups are susceptible to thelaziosis. The most acute disease occurs in young cattle at the age of four months.
Nematodes are able to remain viable in the winter. Their females, having overwintered in the eyes of sick animals, begin to lay eggs with the onset of the summer of flies. Thus, livestock affected by telazia is the only source of infection in the spring.
Symptoms of thelaziosis in cattle
Telaziosis in cattle proceeds in three stages. Growing in the conjunctival region of the eyes, nematodes injure the delicate mucous membrane. Worms of the species T. rhodesi have chitinous spikes on the front of the body, so this type of pathogen is considered the most dangerous.
At the initial stage of the disease, it is noted:
- conjunctival hyperemia;
- profuse lacrimation;
- photophobia.
Recognizing the symptoms of the disease in the first stage is quite difficult. The clearest clinical picture develops after 2-3 days. The disease passes into the second stage, which is characterized by the following clinical signs:
- purulent or purulent-serous discharge from the diseased eye;
- abundant mucous secretion;
- corneal clouding;
- swelling of the century.
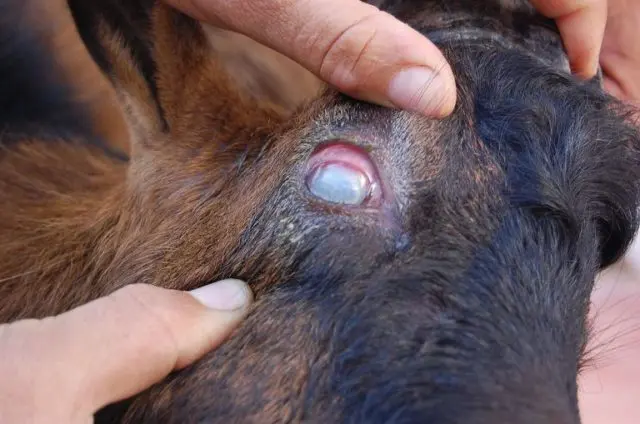
At the final stage of the disease, irreversible processes occur that can lead to blindness:
- the appearance of ulcers on the cornea of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe eye;
- soreness of the eyeball;
- increased body temperature;
- lack of appetite;
- depressed state.
In the third stage of the disease, cows have reduced milk production. Calves infected with biohelminths lag behind in growth and development.
Diagnosis of the disease
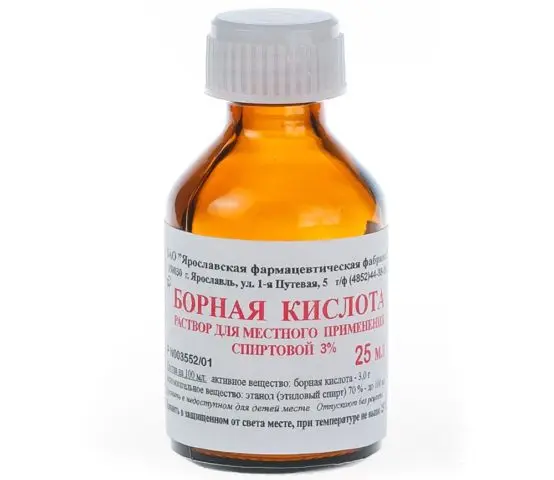
Diagnosis of thelaziosis in cattle is carried out according to the signs characteristic of this disease. To make a diagnosis at the first latent stage of thelaziosis, the conjunctival sac of a sick animal is washed with 50 ml of a solution of boric acid (3%). The resulting wash is collected in a container. Larvae and helminths can be seen with the naked eye or with a magnifying glass.
In a laboratory study of the lacrimal fluid, a decrease in the concentration of lysozyme is noted. When diagnosing thelaziosis, epizootological data and clinical signs are taken into account. In the absence of symptoms of the disease, for example, in winter, some types of helminths can be found in the lacrimal canal or excretory ducts of the lacrimal glands of the animal after slaughter. It is important to differentiate cattle telaziosis from:
- herpesvirus infections;
- Moracellosis;
- rickettsiosis.
Also, this disease must be differentiated from hypovitaminosis A.
Treatment of thelaziosis in cattle
For more effective treatment, the type of causative agent of thelaziosis is taken into account. When the eyes of T. gulosa and T. skrjabini are affected, a 25% aqueous solution of dithrazine citrate is used. The drug is injected subcutaneously into the neck area at a dosage of 0,016 g per 1 kg of animal weight. The next injection must be done after 24 hours. For the destruction of helminths and larvae, instead of ditrazine, you can use a 40% loxuran solution at a dosage of 1,25 ml for every 10 kg of weight.
Ivomek and Ivomek+ preparations are also used for deworming. The solution is injected once, subcutaneously into the neck area, at a dosage of 0,2 mg per 1 kg of animal body weight. A good therapeutic effect is given by washing the affected eye with a solution of chlorophos (1%).

In the treatment of thelaziosis in cattle, the following medications and solutions can also be used:
- febantel (rintal) orally (together with feed) at a dosage of 7,5 mg per 1 kg of animal weight;
- Pharmacin (Aversect-2) single dose of 1 ml per 50 kg of weight;

- ophthalmic medicinal films (OHL);
- a single injection of Fascoverm subcutaneously at a dosage of 5 mg per 1 kg of animal weight;
- tetramizole (20%) orally, a single dose of 7,5 g per 1 kg of body weight;

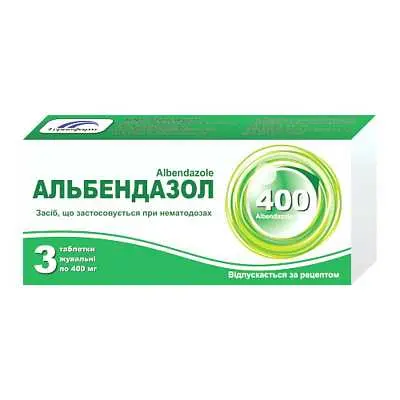
- albendazole inside a single dose of 0,0075 g per 1 kg of body weight;

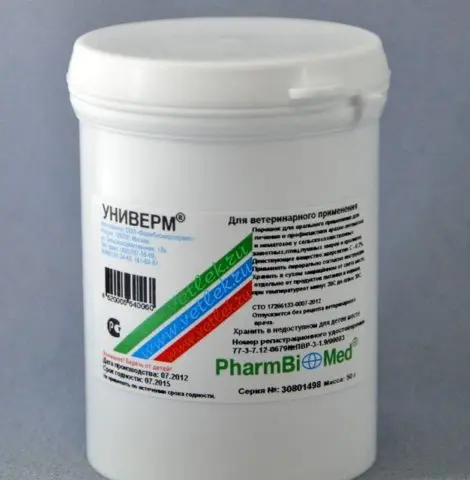
- univerm orally twice in 24 hours at a dosage of 0,0002 g per 1 kg of body weight;

- levamisole subcutaneously in a single dose of 0,0075 g per 1 kg of body weight.

In case of thelaziosis caused by the pathogen of the species T. Rhodesi, it is effective to use solutions for washing the conjunctival area of the eye mucosa:
- iodine solution with a concentration of 0,05%;
- 3% boric acid solution;
- emulsions of lysol or ichthyol with a concentration of 3%.
You can treat the affected eye with an emulsion of ichthyol in fish oil. The composition is carefully injected with a syringe in the amount of 2 ml, into the area of the third eyelid, and gently massaged. The procedure is repeated three times in 2-3 days.
For the treatment of the conjunctiva, you can also use herbal infusions:
- common tansy (fresh or dried);

- chamomile flowers;

- calendula;

- wild rosemary.

If complications occur in the second and third stages of the disease (purulent conjunctivitis, keratitis), the veterinarian prescribes antibacterial drugs. Most often, these are sulfa drugs and substances of the penicillin group.
If there are ulcers on the cornea of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe eye, you can use an ointment with novocaine and penicillin. When clouding the cornea of the eye, a freshly prepared ointment with potassium iodide is very effective.

With purulent conjunctivitis, it is recommended to treat with novocaine-chlortetracycline ointment, tanacet liniment, or wash the affected areas with a solution of furacilin.

Prognosis and prevention
It is quite difficult to identify the disease at an early stage. As a rule, the first obvious symptoms of helminth damage appear in the second and third phases of thelaziosis. Ignoring the symptoms in the early stages leads to irreversible consequences. In the absence of proper treatment, the animal may lose its sight. To prevent thelaziosis of cattle, it is necessary to carry out preventive deworming of the livestock in the autumn and spring.
In order to detect the symptoms of the disease in time, the owners of farms and household plots should regularly conduct general clinical examinations of animals from May to September.
Cowflies are intermediate hosts of the parasite and are highly active during the hot period. On such days, it is recommended to keep the livestock under sheds or in paddocks, limiting grazing on the pasture. It is also better to organize a cattle exercise at night. Young animals are recommended to be pastured separately from adult animals.
To combat the vectors of the larvae of the larvae (cow flies), treatment of the skin and wool of animals with a solution of chlorophos (1%) can be used.
During the grazing period, it is recommended to feed young cattle with phenothiazine-salt mixtures – the drug causes mass death of calf larvae in the feces of animals. For the extermination of flies on the surface of the animal’s body, drugs are used:
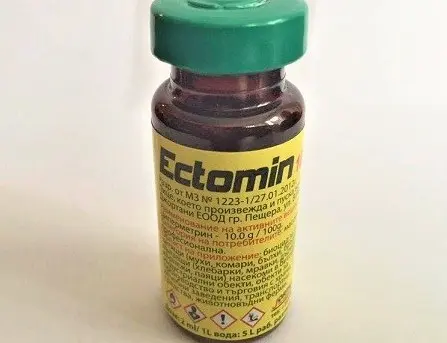
- ectomine with a concentration of 0,1%;

- 0,25% neostomazan solution;

- 1-2% dibrom emulsion;
- neocidol at a concentration of 0,1%.

Another option for the prevention of cattle from thelaziosis is the use of ear clips with pyrethroids. This option with the content of cypermethrin is a powerful insect control agent that can reduce the incidence of thelaziosis in livestock by half.

Infection with thelaziosis of cattle occurs more often on pastures in the summer. For the treatment of premises, ectomine (1-2%), an emulsion of neocidol with a concentration of 0,5% at the rate of 50-80 ml per 1 sq. m. After processing the stalls and other premises, it is impossible to start animals immediately – it is necessary to withstand at least two hours.
Conclusion
Telaziosis in cattle is a rather dangerous disease that, without proper treatment, can lead to blindness. It is possible to avoid the manifestation of this pathology in the livestock of cattle by observing the schedule of preventive measures. Most often, outbreaks of thelaziosis occur in the summer and autumn season. Therefore, during these periods, it is necessary to conduct regular inspections of the cattle population on time.