Contents
Symptoms of celiac disease
The symptoms and their intensity vary a lot from person to person. In some people with a positive diagnosis for this disease, no symptoms are noticeable. We then speak of silent celiac disease.
In general, digestive problems are the most common, but they are sometimes absent. Here are some of the possible symptoms.
Symptoms of celiac disease: understand everything in 2 min
Celiac disease in children
- Chronic diarrhea sometimes alternating with constipation.
- Recurrent abdominal pain.
- Vomitings.
- Stunted growth or short stature.
- Delayed puberty.
- Anemia.
- A lack of appetite.
- Mood swings and irritability.
- Tiredness.
- Abnormalities of tooth enamel.
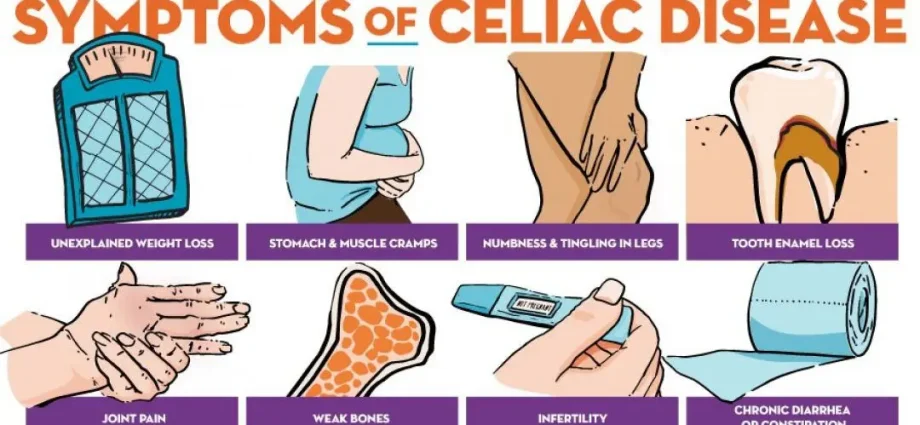
Celiac disease in adults
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation.
- Abdominal pain, gas and bloating.
- Weight loss.
- Fatigue and irritability.
- Pallor, in case of anemia.
- A depressive state.
- Pain in bones and joints
- Muscle cramps.
- Infertility or a lack of periods.
- Numbness or neuropathic pain in the limbs.
- Skin rashes.
- Canker sores or ulcers in the mouth.
Who is most affected by celiac disease?
Celiac disease can occur at any age. It can appear in young children from the age of 6 months, after the introduction of cereals in their diet, as it can be declared at age adult. women are 2 to 3 times more affected than men.
- People with a close relative who have celiac disease are more likely to have the disease.
- The disease appears to be more common in people with autoimmune disease, such as lupus, type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. It is also more common in people with trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).
Risk factors
The main risk factors are genetic factors (presence of the HLA DQ2 and DQ8 genes). Moreover, it seems that the eating habits of the baby could influence the onset of the disease. See the Prevention section.