Contents
Inflammation of the appendix of the caecum is called appendicitis. The disease is characterized by a variety and complexity of symptoms. The text contains information about what you need to know about appendicitis, how to independently determine the signs of appendicitis, what symptoms the doctor pays attention to in the differential diagnosis of the disease. The features of appendix symptoms in men, children, women, including pregnant women are shown.
What is appendicitis?
Appendicitis – a common diagnosis of surgical pathologies. Inflammation of the appendix is more often diagnosed in women aged 20 to 40 years. The incidence of men of the same age is two times lower. At the age of 12 to 20 years, boys and young men get sick more often.
The main treatment for the acute form of the disease is the surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy).
! More than a million such surgeries are performed annually in the country. Complications at the stages of treatment are detected in approximately 5% of operated young patients and 30% of elderly patients. The main cause of complications is peritonitis.
If active therapy is not carried out, acute peritonitis develops within one to two days.
Complications are often the result of a person’s vague idea of dangerous signs of appendicitis, delay, delay in going to the doctor, arrogance in a favorable outcome of the pathology after the removal of unpleasant sensations.
Appendicitis is an insidious disease
It is manifested by pain in the abdomen, high fever, nausea, vomiting, defecation disorder (diarrhea or constipation). Similar symptoms are observed with:
intoxication, poisoning;
infections, inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
infections, inflammation of the female, male genital organs;
inflammation, infections of the kidneys, ureters, bladder;
painful female cycles, ectopic pregnancy, menopause;
obstruction of the duodenum;
ruptures of the arteries of the abdominal cavity, others.
In medicine, there is a term – “acute abdomen syndrome”, which combines pathological conditions accompanied by pain in the abdominal cavity, intoxication, fever.
The variety of acute abdomen syndrome makes the diagnosis of appendicitis a difficult medical task. During the period of diagnosis, the doctor, depending on the gender, age of the patient, must exclude signs of infectious, urological, gynecological, obstetric, male, children’s, and other pathologies. The complexity is added by the unstable location of the organ in the abdominal cavity. In different people, the appendix is determined in different projections of the abdominal wall. The anatomical feature is manifested by a variety of outgoing points of pain.
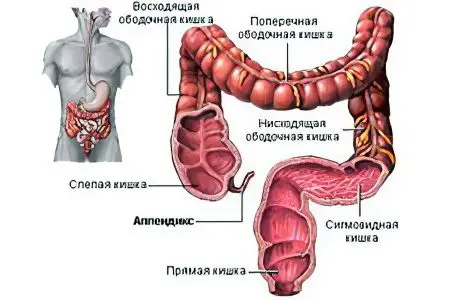
Where is appendicitis located?
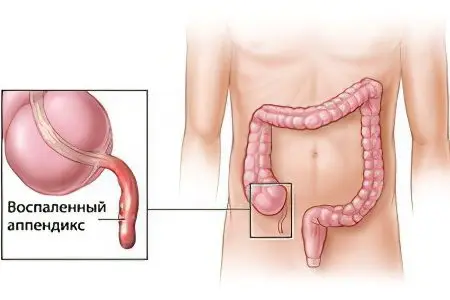
Almost every adult knows the location of internal organs in the body – heart, liver, kidneys, lungs. It is more difficult to determine the localization of the gastrointestinal tract. The total length of the human intestine, compactly located in the abdominal cavity, is 4-5 meters. Topographic landmarks of the projection of the appendix are found inside the crosshairs of two imaginary lines:
horizontal, from the navel and around the abdomen;
vertical, from the right breast nipple and down.
The area of the abdomen, to the right of the vertical and below the horizontal line to the groin and right leg, is the right iliac region. The right sigh is considered the most likely site of projection onto the abdominal wall of the appendix.
Unfortunately, this is not the only place where the appendix is localized. Due to the long mesentery, the appendix can be displaced, at some distance, from its normal position. Before surgery, using ultrasound, the doctor determines the location of the organ and optimal access to it. The location of the organ is important to the surgeon and practically irrelevant to the patient.
Causes of appendicitis
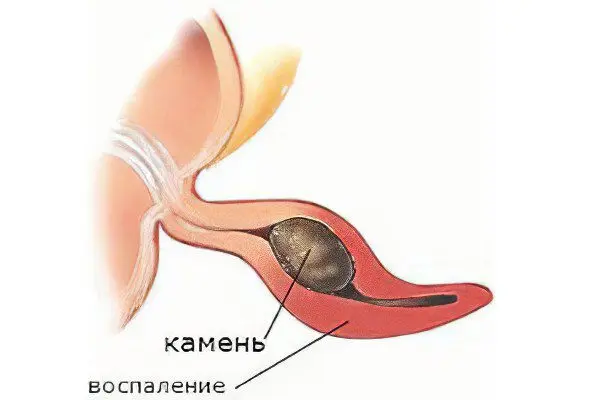
Until now, there is no common understanding of the causes of appendicitis. Why do only a fraction of people suffer from inflammation of the appendix? Several theories have been proposed for the causes of appendicitis.
The most common is the infectious factor. In acute appendicitis, pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, and other pyogenic bacteria are isolated. Under normal conditions, they are normal inhabitants of the intestine. They become pathogenic as a result of the action of concomitant external or internal causes.
The main factors provoking the development of microflora in appendicitis:
blockage (narrowing) of the lumen of the appendix – congenital anomalies (bends, narrowing), neoplasms, fecal stones, foreign bodies);
vascular reactions, defects in the blood vessels feeding the intestinal wall, reducing the blood supply to the walls, causing blood stasis and further necrosis of the appendix;
neurogenic reactions, slowing down of the peristalsis of the intestinal walls, accompanied by abundant mucus formation, acute expansion of the intestinal lumen.
Appendicitis often develops in people suffering from: constipation, diseases of the cardiovascular system, some infectious diseases (intestinal forms of tuberculosis, amoebiasis, other infections). In men, appendicitis can be evidence of bad habits, latent pelvic infections. It may be the result of gynecological inflammatory diseases in women. In children, it develops against the background of congenital narrowing of the lumen of the caecum, severe tonsillitis.
There are acute and chronic forms of appendicitis. The most common form of inflammation of the appendix is acute. It manifests itself with pronounced symptoms. The chronic form is rare, the symptoms are erased.
The first symptoms of appendicitis
Symptoms of appendicitis are manifested mainly by a sharp pain in the abdomen. The usual pathogenesis of appendicitis is manifested by the following sequentially developing symptoms: pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, dyspepsia.
Details of each symptom in the debut of appendicitis.
Sudden pain in the solar plexus or above the navel – the most characteristic first symptom of an acute form of appendicitis. During this period, pain in the abdomen without a specific localization is also possible. It is characterized by pains of varying intensity (strong, weak) and nature (constant, intermittent). Further, there is a shift in the emphasis of pain to the right sigh, that is, to the region of the topographic projection of the appendix. The nature of the pain is constant, the intensity is moderate, it is aggravated by coughing, movement, changing the position of the body in space.
Nausea and vomiting. Vomit consists of previously taken food with an admixture of bile. Vomiting on an empty stomach in the form of liquid, yellow mucus. Vomiting in appendicitis develops as a reflex to pain, accompanied by a decrease in appetite, often a single one.
Fever. A frequent companion of appendicitis is an increase in body temperature. Usually it does not rise above the indicators of febrile fever (37,0-38,00FROM).
Dyspepsia. The increase in intoxication is accompanied by a disorder in the act of defecation – dyspepsia in the form of constipation or loose stools. Dyspepsia occurs against the background of frequent urination, the result of the involvement of the bladder in the pathogenesis. The color of urine is intense, dark.
The insidiousness of appendicitis can manifest itself as a debut with the priority of other symptoms, against the background of a weak pain reaction. In addition, pain can subside under the influence of painkillers, as well as with necrosis of the wall of the appendix.
Dangerous symptoms of appendicitis

Despite the obvious pain in the abdomen with appendicitis, there are difficulties with diagnosis.
Dangerous symptoms of appendicitis
Dangerous, with appendicitis, there may be symptoms:
distracting from the underlying disease;
incipient peritonitis.
In women, pain accompanies many inflammatory gynecological pathologies, in children – intestinal infections, colic. Clinical signs, with stomach ulcers, inflammation of the pancreas, gallbladder, other pathologies of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs, also resemble the symptoms of appendicitis.
With the help of diagnostic methods, the doctor can easily distinguish the source of pain. To facilitate the work of the doctor, inform him about previous diseases, unusual manifestations of the body during the period of the disease, including those not related to the main pathogenesis, for example:
previously transferred sexual infections – a possible hidden microbial focus in the body – a provocateur of appendicitis or a source of inflammation of the urinary organs;
prolonged absence of menstruation in a woman is a possible sign of an ectopic pregnancy;
black feces – a sign of gastric or intestinal bleeding of a perforated ulcer;
belching, heartburn, gas formation, bulky feces – a sign of inflammation of the pancreas;
vomit without bile is a sign of cholecystitis or blockage of the gallbladder.
The danger of these symptoms is that they distract from making the correct diagnosis, direct the doctor along the wrong path of making a diagnosis, and lengthen the time for making it. Another group of symptoms indicates a serious condition of the patient – peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal wall) with appendicitis.
The most dangerous symptoms:
The most dangerous symptoms are:
pain subsided for several hours – may be associated with a rupture of the walls of the appendix inside the abdominal cavity, a subsequent sharp increase in pain intensity, cannot be stopped – evidence of peritonitis;
constant vomiting, and vomiting itself does not bring relief to the patient;
a sharp rise in temperature above 390C, or vice versa, a rapid drop to critically low values;
muscle tension, soreness at the time of touching, tapping the skin of the abdomen;
altered consciousness (confusion, delirium, extinction of reflexes).
Clinical trial of appendicitis

Differential diagnosis of appendicitis is carried out in a hospital. Physical, instrumental, laboratory methods for diagnosing appendicitis are used. At the first stage, the patient is interviewed and traditional research methods, palpation, palpation, tapping, pressure in the abdomen. Pay attention to pain, temperature, vomiting, which most often accompany appendicitis.
Pain with appendicitis
Despite the variety of symptoms, pain is the most stable sign of appendicitis, it almost always accompanies the disease. Characterization of pain is important in the differential diagnosis of appendicitis. The doctor finds out the localization, nature, duration, intensity, time of occurrence of pain.
Localization of pain. Many diseases are accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the form of pain. According to its localization, it is determined which organ is affected. Pain with a clear source of impulses occurs if the organ is close to the wall of the peritoneum. Therefore, inflammation of the kidneys is more often felt in the lumbar region, the heart – in the left side of the chest. In acute appendicitis, the subject, as a rule, cannot show on himself where the pain is localized. Another important diagnostic sign is the displacement of pain of unclear localization after 3-4 hours to the right iliac region.
If pain is immediately felt in the right sigh, then the appendix is located in a close projection. If the appendix in the abdominal cavity is displaced, indirect methods are used. Diagnostic techniques are based on identifying an excessive pain response to a weak impact (touch, tapping) of a certain point.
With uncomplicated appendicitis, increased pain appears if the patient tries to retract the stomach in the supine position, and also if you press with your fingers:
on the stomach in the region of the right iliac;
at several points, to the right of the navel;
at several points along a diagonal line from the navel to the right iliac tubercle (this bony protrusion of the pelvic bones is determined in front of the iliac region).
With appendicitis, the patient experiences pain during defecation in the anus, raising the right leg, right arm, taking a deep breath, coughing. In the position of the patient lying on his back – soreness is felt in the right sigh, a change in position to the left side – the source of pain is shifted to the navel;
Dangerous signs of appendicitis – this is increased pain with light pressure with fingers in the navel, palpation of the abdomen is determined by the muscles in the form of tense strands. In a laboratory blood test, an increase in the number of leukocytes above 14 thousand is detected. Leukocytes are a marker of inflammation, almost always, in any acute process, the number of leukocytes involved in the immune defense of the body increases. A low white blood cell count (leukopenia) is a sign of a depleted immune system. These are signs of peritonitis – inflammation of the abdominal wall.
Reflected pain. With appendicitis, pain is sometimes diagnosed that is manifested far from the inflamed organ. Irradiating (reflected) pain is diagnosed with:
appendicitis – in the right leg, also pay attention to the appearance of right-sided lameness;
pelvic location of appendicitis – is given in men, boys in the scrotum, its location is closer to the back – is given in the same place;
The nature of the pain. Distinguish between visceral and somatic pain. Visceral is formed in the internal organs with a sudden increase in pressure in a hollow organ, with stretching of the walls of the organ, tension of the ligaments of the mesentery. Somatic pain is caused by pathology in the wall of the peritoneum adjacent to the organ and connected to it by nerves. Appendicitis can cause constant and cramping pain.
Pain duration. One or two peaks of pain reactions are characteristic. The first attack is associated with inflammation of the appendix. The second peak is observed with the development of peritonitis, in advanced cases. Pain in acute appendicitis lasts from several hours to several days. Prolonged, lasting several days, weeks, aching pain is not typical for appendicitis.
Within 1-2 days, necrosis develops with a high probability of rupture of the appendix wall. In the first hours after the purulent contents spread into the abdominal cavity, the pain disappears, an imaginary recovery occurs.
The second wave of pain is intense and is associated with the development of inflammation of the peritoneum. Peritonitis, without treatment, lasts seven to ten days, often ends in the death of the patient. During treatment, the formation of adhesions of the internal organs, which cause constant pain, is possible.
Intensity of pain. Pain is a subjective sensation that depends not only on the strength of the traumatic factor, but also on the individual characteristics of the person. Appendicitis is characterized by sudden intense pain. In some cases, an erased picture of pain is possible. The intensity of pain cannot serve as a criterion for appendicitis. More important is the combination of pain with other symptoms, high fever, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia. The intensity of pain is high, in young people, often accompanied by forced postures, irritability, headaches.
Vomiting symptoms
An attack of acute appendicitis is accompanied by signs of nausea, then vomiting. Vomiting, with appendicitis, has a reflex character, coincides with the peak of pain. As a rule, it occurs in the first hours, therefore, the phenomena of intoxication do not have a significant effect on this symptom. Appendicitis is characterized by a single vomiting. Repeated bouts of vomiting are characteristic of intoxication of the body. This is an important sign for the prognosis of the disease, indicating the severity of the pathogenesis that threatens human life. Vomiting is accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Hyperthermia
Febrile fever (37-380C) a characteristic symptom. More often appendicitis occurs against the background of moderate hyperthermia. Temperature in appendicitis is an important symptom for differentiation from other similar diseases. With intestinal, renal colic, the temperature is within the normal range or lower. Sometimes an interesting phenomenon is observed when the temperature measured by an ordinary mercury thermometer is 0,5-1,0 on the right side0From a degree above the temperature determined in the left armpit. It is better to try to measure the temperature in the armpit and immediately after – rectally. The differences are more visible.
Appendicitis in women and men
Appendicitis in men
The symptomatology of this category of patients does not differ. Under the age of twenty, young men and boys are more often ill. It has been noticed that ruptures and necrosis of the caecum of the intestine are more often diagnosed in men.
Diagnostic techniques for detecting signs of appendicitis in boys and men are manifested:
spontaneous pulling up of the right testicle during palpation of the abdomen in the right sigh, cessation of feeling the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe greatest pain – the testicle descends, both testicles with pressure on the stomach;
pain in the right testicle with slight pulling of the scrotum;
Appendicitis in women
Over the age of twenty, women are more likely to get sick. In girls from twelve years of age and older, during a clinical examination, it is necessary to take into account the gynecological status. Acute pain can be caused in girls in adolescence by painful periods. In women, inflammation of the appendages, ovaries, ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, kidney disease should be excluded.
Appendicitis in children of younger age group
A child of a younger age group does not allow research, cannot explain pathological sensations, pain is accompanied by incessant crying, fear. This introduces confusion in the diagnosis of appendicitis.
The disease manifests itself with an acute onset. Pain in the right iliac zone is determined using a simple technique – try to bend the right leg of the child at the knee. A weak attempt is manifested by a strong reaction. Another diagnostic technique – after removing the examiner’s hand, pressing on the stomach, a strong pain response occurs in the right iliac zone. When palpated, the abdomen is tense, but not swollen due to gas formation.
The child refuses to get up, prefers to lie down and move less. The pain is aggravated by movement, running, jumping. When standing, a forced posture is noted in order to relieve pain on the right side of the body. Vomiting, unlike adult patients, occurs as a result of intoxication, and is not caused by severe pain. In a child, vomiting may be the first symptom of appendicitis, preceded by pain.
The final diagnosis can be made by the doctor on the basis of instrumental and laboratory research methods.
In small children, appendicitis is often marked by pulling the right leg towards itself. Symmetrical palpation of the abdomen is manifested by a violent response to touch on the right side. You can apply other similar methods to determine the localization of pain.
Clinical symptoms of appendicitis in children
High temperature 38-390C, the pulse is quickened, the tongue is lined – reminiscent of signs of infection. The complexity of the study adds diarrhea and vomiting. In the absence of signs of intestinal upset, the gases pass freely. Sometimes the temperature is normal. In this case, one of the causes of pain may be intussusception of the small intestine. Invagination is the entry of the intestine into the intestine, occurs in children. As a result of intussusception, a cuff is formed on the intestine, causing severe pain, bloating, obstruction, and vomiting. The success of the diagnosis depends on the doctor’s attention to detail.
Enlarged lymph nodes, a rash, on the skin and mucous membranes may indicate an infection. In severe cases, consultation of a pediatric infectious disease specialist, express methods of laboratory blood tests are required.
Appendicitis in a child aged 5 years and older
From about this age, the child is able to describe pathological sensations at a primitive level. The clinical picture is the same as in children of the younger age group.
Initial signs of appendicitis in a child. The localization of pain is indicated by the forced postures of the child, the tension of the abdominal wall when palpated on the right side of the abdomen in the region of the sigh. Sparing, right side, gait, holding the right iliac region with hands. Do not try to relieve pain with medication, applying a cold compress to the affected area.
Palpation establishes pain, tension of the abdominal wall on the right side. Differential diagnosis is carried out in order to exclude: scarlet fever, measles, tonsillitis, helminthic invasions, intussusceptions of the small intestine. The localization of pain is determined using indirect methods that are used in the diagnosis of appendicitis in adults.
The attenuation of pain can be a formidable symptom of perforation of the appendix. Vomiting precedes nausea, more often it is single.
Appendicitis in the elderly
Appears as a calm debut. The general condition is satisfactory. Pain in the right iliac zone, often diffuse, of unclear localization, not intense. The temperature is normal or slightly elevated.
Confusion in the diagnosis is made by possible intestinal paresis. Intestinal paresis is a condition when the intestine ceases to function, manifested by obstruction (vomiting, lack of defecation, bloating). Vomiting in this case occurs every time after eating. Vomit contains undigested food. Diagnostic methods used to determine the location of pain are unclear.
The erasure of the signs of the disease does not mean an easy pathogenesis. In older age groups, complications and deaths are more common.
Appendicitis in pregnant women
In the first months of pregnancy, the difficulty in diagnosis is at the usual level. Difficulties in diagnosis arise after the fourth month of gestation, when the growing uterus displaces the intestinal loops. Usually the appendix is displaced to the top, closer to the liver. Therefore, there is a difficulty in differentiating appendicitis and inflammation of the biliary tract of the liver. Sometimes appendicitis during pregnancy radiates to the region of the right kidney. The abdominal wall is tense as a result of uterine distension, so palpation is not an effective diagnostic technique during pregnancy.
Clinical methods for diagnosing appendicitis in pregnant women are manifested by pain:
in a lying position on the right side – a consequence of the pressure of the uterus on the focus of inflammation;
in the supine position with pressure on the left rib;
During this period, it is preferable to use effective methods of instrumental diagnostics of ultrasound, MRI, radiography (the introduction of pharmacological agents contrasting for x-rays into the studied cavities). When confirming the acute form of appendicitis, urgent surgical intervention is indicated. The gestational age in this case does not matter. The priority in the operation is to preserve the pregnancy.









