Contents
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint – these are persistent changes in the integrity of the articular surfaces, which are based on a violation of metabolic processes. As a rule, coxarthrosis is a slowly progressing disease that gradually affects the cartilage tissue, followed by bone deformity and impaired functionality of the articular system.
Coxarthrosis is the most common disease among all degenerative-dystrophic pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, occurring at the age of 40 years.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
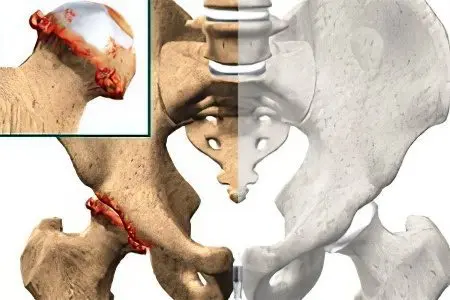
Symptoms at different stages of development of coxarthrosis differ slightly. However, there are a number of general signs by which one can determine the onset of the development of the disease and take all necessary measures to restore health. Often, patients turn to doctors already in the later stages of the pathology, which significantly reduces the chances of a full recovery.
General symptoms:
severe pain in the area of the affected joint is the main sign of joint damage; in the first stage, the pain manifests itself during movement, in the subsequent ones it is permanent;
stiffness (restrictions in movement) – in the early stages, this condition is observed after awakening or heavy physical exertion;
a change in the length of the legs is a sign of an advanced form of the disease accompanied by deformity of the pelvis;
muscle atrophy is the most severe symptom that manifests itself in the later stages of coxarthrosis; in the early stages there is a slight weakening of the muscles;
lameness, a clear change in gait – a sign of deformation of the skeletal system;
a pronounced crunch in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe joints, which may indicate a pathological lesion.
Causes of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
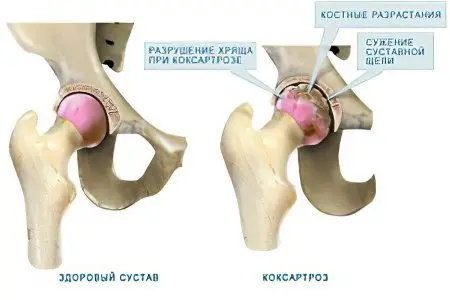
The reasons for the development of this disease can be very different, consider the most common:
Violation of blood circulation in the area of the affected joint. Due to a variety of reasons, a person experiences a malfunction of the circulatory system – a deterioration in venous outflow and arterial inflow. As a result of all these processes, metabolic products accumulate in the tissues surrounding the hip joint, which contribute to the production of enzymes that destroy cartilage.
Injuries. The development of coxarthrosis is promoted by chronic microtraumas that contribute to the thinning and damage of the cartilage.
Excessive stress on the joint. The development of degenerative processes is facilitated by constant heavy physical exertion, often in combination with predisposing factors.
Obesity. A large body mass overloads the joint, thereby causing an inflammatory process, and subsequently the deformation of the joint itself.
genetic predisposition. The disease is not directly inherited; structural features of cartilage, bone tissue and joints are transmitted. Therefore, with a number of adverse factors, this cause can affect the development of coxarthrosis more than with others.
Hormonal background. Frequent changes in hormone levels can affect the metabolic processes in the human body, thereby contributing to the development of inflammation of the joint tissues.
A sedentary lifestyle is one of the main reasons for the development of pathologies of the hip joint.
Other diseases (necrosis of the femoral head, severe infections). In the case of improper treatment or timely medical care not provided, a number of diseases can affect the development of coxarthrosis in the future, as a complication or concomitant disease.
Congenital pathologies (dysplasia, congenital hip dislocation).
Degrees of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the first degree
Grade 1 is the mildest form of the disease, which may not bother the patient for a very long time, but if the disease is not orientated and treated in time, it will develop to more severe forms.
At the first stage of the disease, there are periodic pains in the area of the affected hip joint after prolonged and intense physical exertion. With bilateral joint damage, pain manifests itself in both joints, with unilateral damage in one. This stage is not characterized by the appearance of lameness and severe muscle rigidity. The pain syndrome disappears immediately after the end of physical activity and is not permanent. On the x-ray, you can see a slight narrowing of the gap located between the joints.
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the second degree
Grade 2 is characterized by more significant damage to the joint – the destruction of cartilage. In this degree, all symptoms are aggravated.
The pain syndrome in the second stage of the lesion intensifies, often there is irradiation of pain in the inguinal region and thigh. Pain occurs not only after physical exertion, but also at rest. In the absence of restorative measures, the normal mechanism of movements is disturbed – the patient begins to limp, the gait gradually changes. The strength of the muscles responsible for hip extension and abduction is reduced. Over time, morning stiffness syndrome develops.
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the third degree
Grade 3 is one of the most severe forms of pathology, which is characterized by almost complete destruction of the articular cartilage. The x-ray shows a filiform narrowing of the joint space. The joint is severely deformed.
The pain syndrome in this condition is permanent, it can be eliminated only temporarily with the help of medications. It is difficult for the patient to move without a cane or other assistive devices, since the joint is constrained, its movements are limited. Edema develops in the joint area, tissues atrophy.
Coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the fourth degree
This is the last stage of the disease, the most severe. This condition is characterized by complete fusion of the bones of the hip joint with each other. Constant pain that prevents you from leading a normal life, severe swelling of the surrounding tissues. Complete lack of movement in the hip joint.
Diagnosis of diseases of the musculoskeletal system

At the first stage, the diagnosis of coxarthrosis includes a survey, anamnesis of life and disease, patient complaints, joint examination and functional tests.
In a clinical blood test with coxarthrosis, there is a slight increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) – up to 30 mm / h and above.
In a biochemical blood test, the level of inflammatory markers was significantly increased: c-reactive protein, globulins, immunoglobulins, and seromucoid. This analysis is of great help in the differential diagnosis of joint damage: arthritis or arthrosis?
The basis of all diagnostic measures is instrumental methods.
The main method for detecting joint damage is an x-ray, which notes:
the presence of osteophytes – bone growths along the edges of the articular cartilage;
narrowing of the gap between the joints;
areas of ossification of articular cartilage;
osteoporosis (bone thinning);
compaction of bone tissue under the cartilage.
The downside in conducting an x-ray examination is that only the bones are visible, the soft tissues of the joint (cartilage, joint capsule) are not visible in the pictures.
An equally informative diagnostic method is magnetic resonance or computed tomography, which allows you to recognize the disease at the earliest stages of its development.
Treatment of coxarthrosis of the hip joint
With such a pathology as coxarthrosis, the treatment is quite complex and lengthy, consisting of many stages. The main condition for effective treatment is the early start of therapeutic measures, regardless of the stage of the disease.
For the treatment of the initial stage of the development of pathology, it is enough to correct the lifestyle, nutrition, eliminate problems with blood circulation and metabolism. More severe forms of the disease require the maximum amount of effort aimed at recovery.
Drug treatment for destructive changes in the hip joint
Drug therapy is mainly symptomatic treatment. The main actions that are required from drugs are the elimination of pain, the removal of swelling and inflammation, the improvement of blood circulation, the nutrition of cartilage tissue and muscle relaxation.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Shown in the reactive stage of the inflammatory process. Excellent relieve swelling, inflammation, eliminate pain due to the strongest anti-inflammatory effect. The downside of using this group of drugs is rapid addiction, cartilage tissue ceases to regenerate on its own, and a number of side effects negatively affect internal organs.
Vasodilator drugs. The purpose of these drugs is to relax the smooth muscles of the vessels and expand their lumen to ensure good blood circulation. When used correctly, drugs in this group have a minimum number of contraindications and complications. Vasodilator drugs have a very important effect – they relieve spasm, including nightly “vascular” pains, which bring maximum discomfort to patients. Before using these drugs, you should consult your doctor, as one of the most common side effects is an allergic reaction to the components. Efficiency depends on this factor.
Muscle relaxants. Preparations of this group for coxarthrosis should be taken with extreme caution. They are used to eliminate painful muscle spasm and improve blood circulation. The danger when using muscle relaxants is that they affect the nervous system, manifesting itself in the form of frequent dizziness, nausea, mental retardation or intoxication.
Chondroprotectors. This category of drugs is the most useful and effective, its actions are aimed at restoring the structure of the cartilage. Regular use of chondroprotectors can stop the development of coxarthrosis in the early stages. Contraindications for use are pregnancy, allergies and inflammation of the joints.
Hormonal drugs (injection). This kind of therapy has a positive effect in the absence of inflammatory processes affecting the tendons of the femur. Injections are not recommended to be done more than once every two weeks and no more than three injections in one joint.
Local medicines (ointments, lotions, compresses)
Such therapy is not fundamental in the treatment of coxarthrosis, since the likelihood that all the necessary substances will penetrate the skin, fat layer and muscles is very small, therefore, the rubbing process directly has a positive effect, increasing blood circulation in the affected area.
Surgery for coxarthrosis of the hip joint
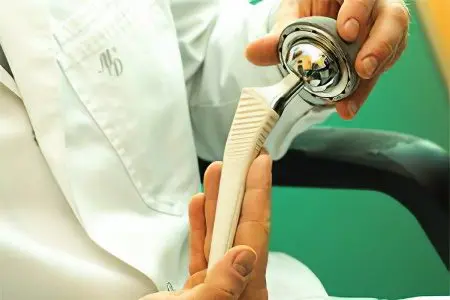
Surgical intervention is performed at the last stage of the development of the disease, when the functionality of the joint is completely impaired.
Types of operations:
Endoprosthetics – Joint replacement. This is the most difficult of all operations related to the hip joint, its success is almost 70% of all interventions performed. When choosing a prosthesis, the patient’s age, gender, weight and anatomical features of the body are taken into account, the amount of time that the implant will serve depends on this. Often this is the only way to restore the patient’s ability to walk.
Outwardly, a conventional endoprosthesis is identical to a conventional joint, it is designed for the same functions and is able to withstand the same loads as a natural joint.
By type of prosthetics, the following joints are distinguished:
unipolar (only the head of the hip joint is prosthetized);
bipolar (all anatomical elements of the joint are replaced).
Arthrodesis – the bones of the joint are fastened with special screws and plates to restore functionality. The disadvantage of this technique is that the joint, as before, is constrained in movements. This surgical intervention is prescribed only in cases where other types of treatment do not give any result.
Arthroplasty – This is a modeling of the destroyed surface – cartilage.
osteotomy – specific dissection of the bones to eliminate the deformity. Unlike arthrodesis, this surgical intervention restores not only the support function, but also the motor function.
Gymnastics with coxarthrosis of the hip joint
Therapeutic exercises for this disease is one of the most effective therapeutic methods of treatment that bring a positive result. In the initial stages, exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles surrounding the joint can prevent further development of coxarthrosis.
It is very important that therapeutic exercises are carried out under the supervision of a highly qualified specialist, since there are a number of exercises that can both benefit and harm the patient.
Exercises for the treatment of coxarthrosis of the hip joint have a certain mechanism. Training of the gluteal and parafemoral muscles improves blood circulation, fixation and nutrition of the cartilage. Stretching exercises allow you to align shortened limbs due to the specific stretching of the joint capsule.
Statistical exercises, rational dynamic loading and stretching are excellent for treatment. A set of the most rational exercises:
in the supine position, it is necessary to lift and strain the gluteal muscles as much as possible;
without getting up, in the same position – bend the leg at the knee and gradually expose it;
while remaining in a prone position, straighten your legs and try to raise them as high as possible at the same time without raising the upper end of the body;
sitting on a chair, squeeze the fitness ball between your legs and try to squeeze it with maximum force;
in a sitting position, straightening your legs, try to clasp your toes with your hands.
All exercises must be performed regularly and correctly. To relieve tension, you can take a relaxing bath with oils.
Contraindications for therapeutic exercises:
increased body temperature (over 37);
inguinal hernia, hernia of the abdomen and back;
rehabilitation period after surgery;
acute inflammatory processes affecting internal organs;
heart and pulmonary insufficiency;
hypertensive crisis;
severe pain syndrome;
exacerbation of diseases of the joints;
menstruation;
increased blood pressure.
Watch the visual video:









