Contents
What is diarrhea?
Diarrhea is a condition of a person in which there is frequent defecation, while the stool is watery. This condition is dangerous because it can lead to dehydration. Diarrhea can be caused by infections of the digestive tract, malnutrition, stressful conditions, drug poisoning.
Also, the cause of the disease can be the presence of worms or intestinal dysbacteriosis. It is necessary to carefully monitor the frequency of the stool, pay attention to its smell (sour, putrid), color (gray, white), blood.
There are several types of stool disorders, to determine them there are specific characteristics that, in fact, distinguish this symptom from the norm.
Clear criteria and differences between them are given in the table:
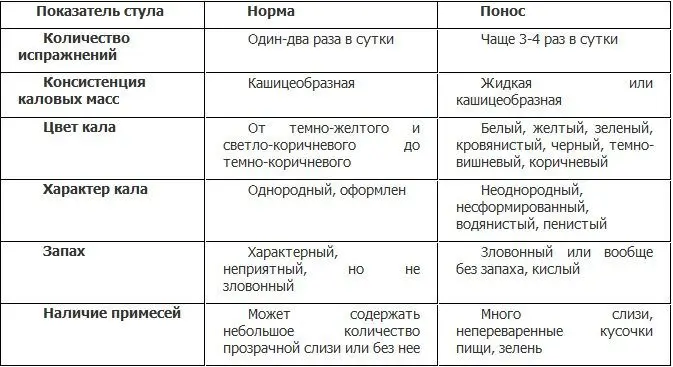
The data given in the table require a little clarification, since the boundaries of the norm and pathology are individual for each person. All generally accepted physiological indicators are of an average nature, combining a fairly wide range of them. First of all, it is worth clarifying the indicator of the number of daily bowel movements. In some people, it ranges from once every 2-3 days to 3-4 times a day. Similarly, this applies to the consistency of feces, which can be from liquid-mushy to solid-shaped.
The most important thing in evaluating these characteristics of bowel movements is their duration. If they take place for a long time (long months and years), without causing any negative manifestations in a person, then there is no need to worry, since such features are individual. It’s not diarrhea.
The situation is quite different with other characteristics of the stool, such as smell and the presence of impurities. Their change always indicates diarrhea. Moreover, from time to time, by their appearance, one can clearly determine its origin. Therefore, it is so important to always pay attention to feces, because they speak about the state of digestion and the health of the body as a whole.
Causes of diarrhea in adults
Diarrhea is a consequence of the improper functioning of the intestinal tract: the digestive process is accelerated, and this leads to liquefaction of stools and frequent bowel movements.
As a rule, diarrhea is caused by viral or bacterial infections or food poisoning. Diarrhea is usually caused by Escherichia coli and Salmonella bacteria, which can be found in food or water. Diarrhea, which is caused by a bacterial infection, most often affects tourists traveling to exotic countries. No wonder this type of disease is sometimes called “tourist’s diarrhea”.
The causes of diarrhea can be herpes simplex or hepatitis viruses, as well as taking antibiotics.
Another cause of diarrhea can be ulcerative colitis. It also causes severe diarrhea, but colitis is determined very late and, as a rule, during an internal examination of the intestine.
Considering the close contact of the digestive system with the external environment and the internal systems of the body, one can safely notice its persistent dependence on them. That’s why she gets sick so often. Most often, any irritation or malfunction in normal functioning is manifested by the acceleration of motor skills, mucus secretion, and ultimately diarrhea.
The full list of causes of diarrhea is given below:
Viral infections
Rotaviruses;
Enteroviruses;
Adenovirus;
Bacterial infections
Salmonellosis;
Dysentery (shigellosis);
Cholera;
food poisoning;
Escherichiosis;
Enzymatic deficiency
Pancreatitis
Cholelithiasis with a violation of the outflow of bile;
Fermentopathies;
Congenital intolerance to certain foods;
Bowel disease
Enteritis;
Enterocolitis;
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
Crohn’s disease;
Whipple’s disease;
Tumor growths
Polyps;
Adenocarcinomas;
Diverticula complicated by inflammation;
Autoimmune diseases
Intestinal damage in lupus erythematosus;
Rheumatoid arthritis;
Atopic dermatitis and allergic reactions;
Intoxication
Nitrate poisoning;
Heavy metals;
Pesticide;
Household chemicals;
Medicamentous influences
antibiotics;
Cytostatics;
Overdose of laxatives;
Anticholinesterase agents and prokinetics;
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Open ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
Small bowel bleeding;
Colonic bleeding;
Diarrhea after taking antibiotics
This is due to the fact that it is caused by iatrogenic (medical) influences, which are originally designed to help a person. They are very common and can cause serious illness and even death. First of all, this concerns the side effects of antibiotic therapy, which causes dysbacteriosis, and subsequently pseudomembranous colitis. The peculiarity of the last complication is that it responds very poorly to any methods of correction, accompanied by debilitating diarrhea.
No less important are infectious diarrhea of bacterial and viral origin. They are more common than others, but fortunately, they end happily in most cases. This is due to the body’s ability to eventually defeat aggressive pathogens, since they are natural components of nature. The same cannot be said about diarrhea caused by toxic influences and other external influences. They, being unnatural, cannot be overcome only by protective immune mechanisms without outside influence.
As for the mechanisms of diarrhea, they can also be different. The inclusion of a particular one depends on the cause that caused the diarrhea. The most typical pathogenetic mechanisms and their corresponding causes are presented in the table.
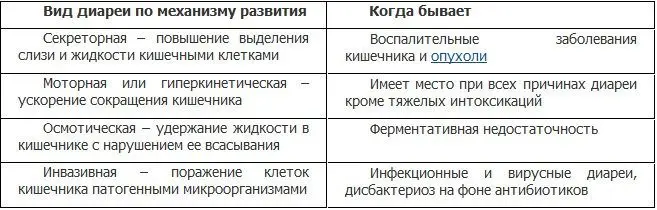
Usually, with diarrhea, there is not only one mechanism for its implementation. Their combination with the predominance of one over the others is characteristic.
Types of diarrhea
infectious diarrhea observed in dysentery, salmonellosis, foodborne infections, viral diseases (viral diarrhea), amoebiasis, etc.
Alimentary diarrhea occur with malnutrition, with allergies to any products.
Dyspeptic diarrhea occur when there is a violation of the digestion of food masses due to secretory insufficiency of the stomach, pancreas, liver, with a lack of secretion of any enzymes by the small intestine.
toxic diarrhea accompanies uremia, poisoning with mercury, arsenic.
Medical diarrhea happens when the physiological flora of the intestine is suppressed, the development of dysbacteriosis.
neurogenic diarrhea are the result of a violation of the nervous regulation of the motor activity of the intestine (for example, diarrhea that occurs under the influence of excitement or fear).
Light and short diarrhea practically does not affect the general condition of a person. Severe or chronic – depletes the body, leads to hypovitaminosis, significant changes in the organs.
Diarrhea symptoms

Clinical manifestations of diarrhea are usually characterized by a standard set of complaints and objective examination data. For some of its species, there are specific distinguishing features by which you can accurately determine the specific nature of the disease. But it also happens that even additional laboratory and instrumental data are not always informative. In order not to miss anything, you must be very attentive to everything that happens to the body, accompanying diarrhea.
High fever with diarrhea
It is noted by many patients as an additional symptom. Its development is characteristic of many types of diarrhea. First of all, this concerns its microbial (viral and bacterial) species. After all, any penetration of foreign protein structures into immune cells causes the production of antibodies, which is accompanied by the release of inflammatory mediators and a temperature reaction.
Given that the gut is one of the most powerful immune organs, its appearance should come as no surprise. On the contrary, when a person has signs of an infectious bowel disease, but there is no temperature, this indicates the presence of an immunodeficiency. As for its specific values, they depend on the pathogenicity of the microbe and the reactivity of the organism and can range from 37,1°C to above 39°C.
Nausea and vomiting with diarrhea
Nausea is by far the most common symptom of diarrhea of any origin. There is a logical explanation for this. After all, a violation of the normal movement of food and feces through the intestines necessarily leads to their incorrect casting in the opposite direction.
In addition, intoxication that occurs against the background of any intestinal catastrophe necessarily leads to the absorption of these toxic products into the systemic circulation with their distribution to all organs and tissues. The vomiting center of the brain is the first to react to them, which is clinically manifested in the form of nausea followed by vomiting. By the way, the last reflex act refers to one of the most physiological mechanisms for cleaning the body of toxins of any origin.
Abdominal pain
It is always a consequence of increased intestinal motility. As a rule, it has a spastic strong and intense character. It is characterized by a paroxysmal course with periods of sharp increase with a gradual subsidence and complete cessation. Usually after, or during a painful attack, there is an urge to defecate, which is manifested by severe diarrhea.
The appearance of pain is characteristic of almost all types of diarrhea, but most often occurs with its microbial types and food poisoning. All other types of it are accompanied by discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen.
Rotten eructation with diarrhea
It occurs as a primary symptom or gradually against the background of diarrhea. In the first case, when it precedes diarrhea, its appearance indicates enzymatic insufficiency of the pancreas, stomach and biliary system.
As a result of the fact that the food entering the body is not digested, it rots. This eventually pours out into the formation of foul-smelling gases, which come out of the stomach by belching. Naturally, undigested particles entering the intestines cause irritation and diarrhea. When rotten belching occurs against the background of diarrhea, this is a consequence of secondary digestive disorders caused by the underlying disease, and indicates its progression.
The color of diarrhea in an adult
An experienced clinician can determine the origin of diarrhea by the color and typical characteristics of liquid stools. In this case, it is necessary to add up the remaining symptoms. This will make it possible to understand and clarify some details of the origin of the true culprit of diarrhea.
Diarrhea green
Characteristic exclusively for bacterial and viral lesions of the intestine. The appearance of greenery is associated with the direct accumulation of leukocytes in the feces, as well as the active reproduction of pyogenic coccal flora (staphylococci) against the background of weakened local immune mechanisms in the intestine.
Clinically, it looks like liquid feces of an inhomogeneous consistency with small greenish blotches or thickly coated and mixed with viscous green mucus. Usually, such diarrhea is accompanied by a pronounced hyperthermic reaction, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, signs of severe intoxication, and inflammatory changes in the blood system.
Yellow diarrhea
It belongs to the most favorable types of it, since most often it is due to increased peristalsis (contraction) of the intestine. As a result of the acceleration of the movement of fecal masses, they do not have time to fully form into a normal shape and consistency. But at the same time, their almost complete enzymatic processing and partial absorption of the active components into the bloodstream occur. As a result, the stool is of a normal color, but of a liquid consistency. The absence of additional symptoms is characteristic, with the exception of minor pains and heaviness in the abdomen.
Black diarrhea (dark color)
Refers to very formidable or, conversely, natural symptoms. First of all, it is worth stopping at it as a threatening sign. The appearance of black, like tar or resinous feces, can only speak of one thing – bleeding from the stomach. The appearance of just such a color is due to the destruction of erythrocyte hemoglobin under the action of hydrochloric acid of the stomach. In this case, hematin hydrochloride is formed, which provides the characteristic color. In such situations, you can not waste a minute and urgently seek medical help.
The second situation, as a result of which black feces may appear, is the consumption of foods based on animal blood (bloody blood), a large amount of beets, blueberries, or certain medicines (activated charcoal, bismuth preparations – vikalin, de-nol). It is this fact that often causes people to seek medical help. The differential diagnostic criterion for the origin of black diarrhea is the presence of an appropriate history of the use of these substances or a decrease in hemodynamic parameters (hypotension, tachycardia) in case of gastrointestinal bleeding.
White diarrhea (light color)
Along with black feces, it is one of the most specific, characterizing only one reason for the appearance. In this case, this is insufficient processing of food masses in the intestines by bile. This is possible with compression or blockage of the common bile duct by a tumor or stone.
In typical cases, such diarrhea is necessarily accompanied by yellowness of the skin and a strong darkening of the urine. Pain syndrome, temperature reaction and dehydration are not typical. It is often of a non-intense nature, occurring only a few times, after which the white color of the feces remains with their normal consistency.
Diarrhea with blood
The most formidable of all types of diarrhea, as it indicates ongoing active bleeding into the cavity of the intestinal tract. Usually characteristic of disintegrating tumors of the large intestine, severe intestinal infections, as a result of which there is a complete destruction of the mucous membrane of the intestinal wall.
Sometimes the appearance of bloody diarrhea can be the result of a toxic effect on the intestines of various chemical compounds and poisons. Bloody diarrhea may not be pure blood, but liquid dark cherry stools. In this case, it is safe to say that the source of bleeding is located in the right half of the large intestine.
Diarrhea with mucus
This characteristic alone cannot determine the true origin of diarrhea. After all, mucus can be completely different and stand out in different quantities. Its transparent appearance is a sign of a relatively favorable course, which may be due to food poisoning and mild poisoning. When the mucus becomes greenish, brown or bloody, it always indicates a severe course of diarrhea or the absence of the effect of its treatment.
diarrhea with water
In any scientific manual or regular women’s health magazine, there is only one answer to the watery stool question. It is, of course, cholera. The causative agent of the disease is so arranged that when it enters the intestines, it includes all possible mechanisms of diarrhea, which is manifested by the indomitable release of water instead of feces. The most interesting thing is that the temperature rises extremely rarely. But the number of bowel movements is so great that the patients are not able to count them. As a result, severe dehydration occurs, which requires immediate correction by massive infusion therapy.
Treatment of diarrhea in adults
Only those who can clearly determine its nature and mechanism of occurrence can correctly and effectively treat diarrhea. The following table should help guide you a little.
Type of diarrhea | Basic groups of drugs |
infectious |
|
Enzymatic | Replacement therapy with enzyme preparations |
Bowel disease |
|
Bleeding |
|
Intoxication |
|
Diarrhea after antibiotics |
|
Diet for diarrhea in adults
The issue of nutrition in any disease of the digestive system should be given special attention. Especially with diarrhea. In general terms, it should be said that you can not eat rough, fried, fatty, smoked foods. Everything should be light, well absorbed and not load the already loaded intestines. It must simultaneously rest and provide the body with the most necessary substances for life. Be sure to regulate the water regime with the use of a sufficient amount of liquid in any form.
What can you eat with diarrhea? | Types of products | What can not be eaten with diarrhea? |
Black with bran, yesterday’s baking, croutons, biscuit cookies | Bread and flour dishes | Fresh white bread, buns, pies, rolls, cookies |
Diet chicken and rabbit meat, turkey, doctor’s sausages | Meat products | Pork, beef, duck and other fatty meats, smoked sausage |
Ryazhenka, cottage cheese, curdled milk, light yogurt | Dairy products | Whole milk, full fat sour cream, cream |
Lemon juice in water, blueberries, viburnum, cranberries, baked apples, potatoes | Vegetables and fruits, berries | Tomatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, orange, banana, plums, apricot |
Buckwheat, rice, oatmeal | Cereals and cereals | semolina |
Strictly prohibited | Legumes and peas | Beans, peas in any form |
Dried blueberries, apples, pears, rose hips | Nuts and dried fruits | Raisins, dried apricots, all kinds of nuts |
The power supply diagram shown is indicative only. Nutrition for diarrhea depends on the intensity of diarrhea, the form and stage of the disease that led to its occurrence. Naturally, in the first hours and even days after the onset of a problem, it is better to refrain from eating altogether, with the exception of sweetened tea and various liquids. This approach will provide trophism to the affected intestinal cells and will not irritate them. Gradually, the volume of nutrition expands, introducing permitted products as the condition stabilizes.
As for the method of cooking, it should be exclusively boiled or stewed. It is best to cook hateful soups, cereals, mashed potatoes, steam cutlets and meatballs. Various jelly and jelly from allowed fruits are well suited. With a decrease in the intensity of diarrhea, you can add half a soft-boiled egg to the diet, a little butter for dressing soup or porridge. Gradually, the diet expands with the transition to a normal habitual diet.









