Contents
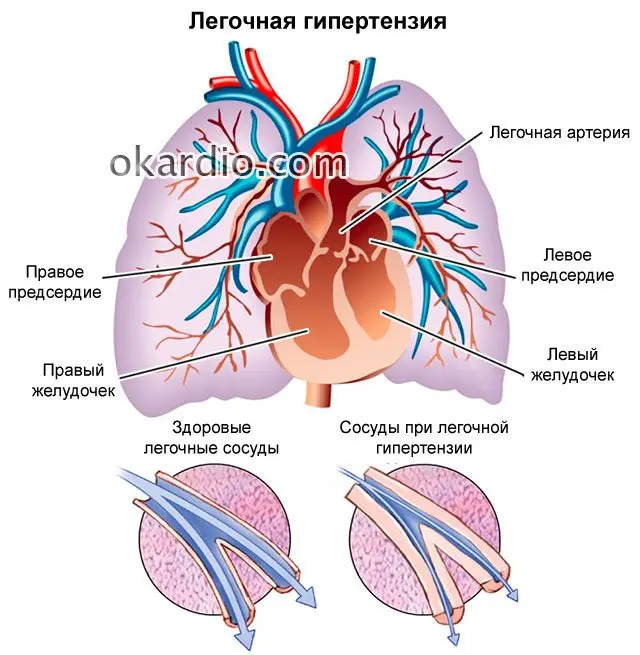
Pulmonary hypertension is expressed in an increase in pressure inside the vessels that supply blood to the respiratory system. This entails the development of heart failure, namely, insufficiency of the right ventricle of the heart. As a result, the person dies.
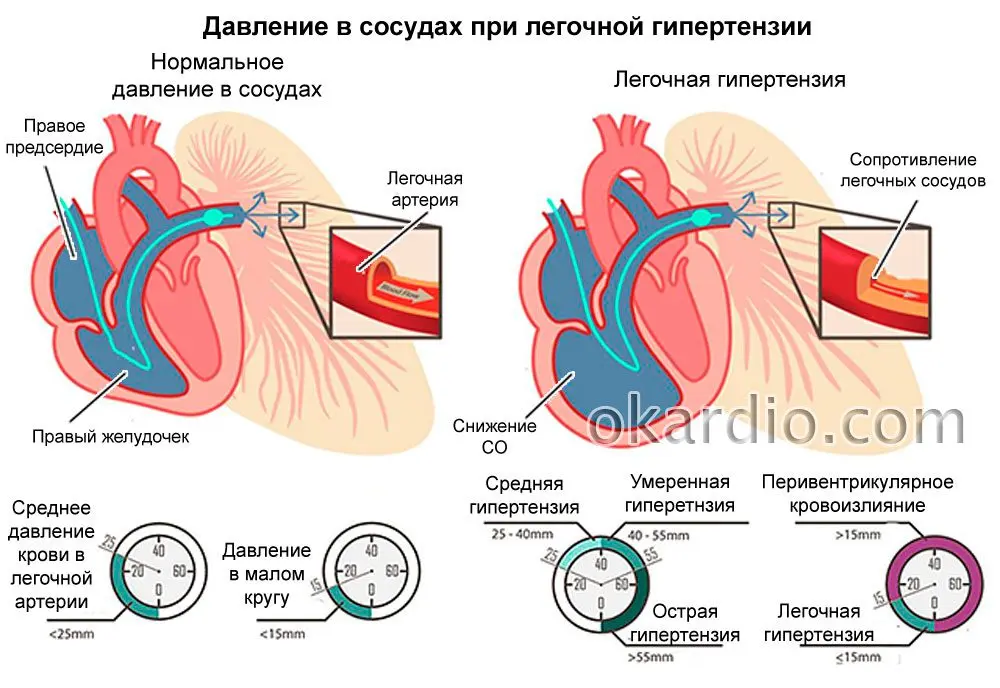
Normally, the pressure in the pulmonary artery is equal to 17-23 mm. rt. Art. With pulmonary hypertension, it will exceed 25 mm at rest. rt. Art. Under load, this figure rises to 30 mm. rt. Art. and more.
Violations that occur in the body during the development of pulmonary hypertension:
Vasoconstriction, which is characterized by vasoconstriction and spasm.
Loss of elasticity of the vascular wall.
The formation of small blood clots inside the vessels of the lungs.
Growth of smooth muscle cells.
Vessel obliteration.
The growth of connective tissue inside the vessels against the background of their destruction.
All this leads to the fact that the blood is no longer able to circulate normally in the vessels of the lungs. During its passage through the arteries, there is an increase in pressure in them. This entails an increase in pressure in the right ventricle, which provokes a violation of its functioning.
A person begins to show signs of respiratory failure, and then symptoms of heart failure join. Even at the initial stages of the development of the disease, the patient’s quality of life deteriorates significantly, which is caused by the impossibility of normal breathing. As the pathology progresses, a person has to more and more restrict himself in physical activity.
Pulmonary hypertension is a serious disease that claims the lives of people. If the patient does not receive adequate therapy, then he will not live longer than 2 years. At the same time, he will need outside help for life support. Pulmonary hypertension can and should be treated, but a complete recovery cannot be achieved.
The detection and treatment of pulmonary hypertension is the task of a therapist, pulmonologist, cardiologist, geneticist and infectious disease specialist, that is, doctors of several specialties. If necessary, vascular and thoracic surgeons are involved in therapy.
Symptoms of pulmonary hypertension

The disease begins to develop imperceptibly for a person. Pathological processes at the initial stage are hidden, as the body includes compensatory mechanisms. Therefore, the patient feels well.
When the pressure in the pulmonary arteries exceeds 25 mm. rt. Art., a person begins to notice deterioration in health. However, they appear only during physical activity. As the pathology progresses, the patient will experience more and more difficulties during the performance of even the most familiar activities.
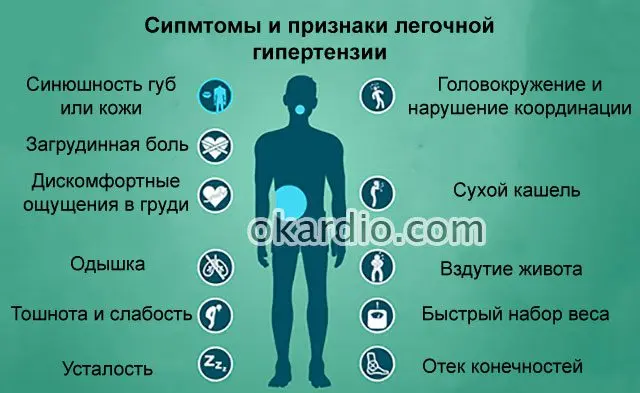
The main symptoms of pulmonary hypertension are:
Shortness of breath, which occurs as the first manifestation of the disease. At first, it appears only during physical effort, it worries a person on inspiration. In the future, shortness of breath will be present on an ongoing basis, even when the patient is at rest. He does not suffer from asthma attacks.
Pain in the sternum. Their nature varies, the pains can be aching, pressing, stabbing. A person cannot accurately tell the doctor about the time of manifestation of pain, however, he notes that they become more intense during physical effort. Nitroglycerin does not eliminate the pain syndrome.
Fainting and dizziness are observed during the performance of any actions. Dizziness can last from 2 to 25 minutes. The same applies to episodes of loss of consciousness.
Heart failure, palpitations. During the ECG, the patient is diagnosed with sinus tachycardia.
Cough haunts 1/3 of patients. It is most often dry, while there are no signs of infectious diseases in humans.
Blood may be present in the sputum, but this symptom occurs in no more than 10% of patients. More often, blood in the sputum is observed as a single occurrence. The reason for its appearance, experts call the presence of blood clots in the pulmonary arteries.
Causes of pulmonary hypertension
As an independent pathology, pulmonary hypertension is diagnosed in only 6 people out of a million. In this case, its cause can either not be established, or it is inherited. In the rest of the case histories, pulmonary hypertension is the result of some disturbance in the functioning of the organs.
The following pathologies can lead to pulmonary hypertension:
Classification group of pathology | Illness as its cause |
Primary arterial pulmonary hypertension |
|
Pulmonary hypertension due to pathological changes in the left side of the heart. | Dysfunction of the valves of the left ventricle, or the left ventricle of the heart. |
Pulmonary hypertension due to disorders in the respiratory system. |
|
Pulmonary hypertension associated with embolism or thromboembolism. |
|
Mixed pulmonary hypertension. |
|
Pulmonary hypertension due to disorders in the structure of the heart. |
|
Thus, the following risk factors that can lead to the development of the disease can be distinguished:
Taking medications, getting into the body of toxic substances. It has been established that pulmonary hypertension can occur while taking Fenfluramine, Rapeseed oil, Aminorex, Dexfenfluramine. Scientists also suggest that substances such as amphetamine and L-tryptophan can provoke pathology.
Demographic risk factors and medical factors. It has been proven that women are more likely to suffer from pathology. It is also believed that hypertension may be associated with high blood pressure and pregnancy.
Some diseases. The relationship between PAH and HIV infection has been established. Pulmonary hypertension may develop in liver pathologies.
Degrees of pulmonary hypertension
There are four degrees of pulmonary hypertension, which determine the severity of the course of the disease:
The first degree is characterized by the absence of any symptoms.
The second degree is manifested by all the symptoms of the disease, which are described above. At the same time, their intensity is extremely low, the patient does not complain. Pathological manifestations will disturb a person only during physical activity.
The third degree of the disease is manifested by a deterioration in well-being even against the background of slight physical exertion. At rest, the patient feels normal.
The fourth degree of the disease is expressed in the fact that it is difficult for a person to perform even elementary actions. Symptoms of pulmonary hypertension do not go away during a state of complete rest.
Diagnostics

If a person suspects that he is developing pulmonary hypertension, he should see a doctor.
The doctor will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis, which boils down to the following activities:
Examination of the patient. During the initial examination, the doctor may detect cyanosis of the skin on the upper and lower extremities. The patient’s nails may be thickened, have the shape of “drum” sticks. If the patient has emphysema, then his chest will be expanded like a “barrel”. The liver is often enlarged, which is noticeable on palpation. It is possible to identify ascites and pleurisy, in which fluid accumulates in the peritoneal cavity and in the pleura. The patient’s legs are swollen, the veins in the neck are dilated.
Listening to the heart and lungs. Above the pulmonary artery, the noises are increased by 2 tones, characteristic single rales are heard. With valvular heart failure, systolic murmurs will be heard. It is possible to listen to noises that characterize heart disease, if any.
In 55% of cases, the diagnosis allows you to perform an ECG. 87% have an enlarged right ventricle with thickened walls. The load on the right parts of the heart increases significantly, which can be determined by the corresponding signs. To the right, the electrical axis of the heart deviates in 79% of people.
Vector electrocardiography can detect pulmonary hypertension in 63% of cases. As for the indicators, they change similarly to the ECG indicators.
Phonocardiography, which allows you to record heart murmurs, which increases the probability of making a correct diagnosis, at least up to 76%. At the same time, it is possible to detect an increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery, changes in the structure of the right ventricle, congestion in the pulmonary circulation, and malformations of the heart.
X-ray examination of the chest reveals the bulging of the pulmonary artery, the expansion of the roots of the lungs, the right side of the heart becomes larger in size. The edges of the lungs are characterized by increased transparency.
Ultrasound of the heart or ECHOCG makes it possible to detect an increase in pressure in the trunk of the pulmonary artery, to identify abnormalities in the work of the tricuspid valve and the interventricular septum. Also, studies make it possible to detect malformations of the heart, expansion of the right heart, thickening of the walls of the right ventricle.
The introduction of the device into the heart through large veins (catheterization of the right heart). This invasive procedure allows you to determine the pressure in the pulmonary artery and in the ventricle, the level of oxygenation of the blood, disorders in the blood circulation of the ventricle of the heart and lungs. In parallel, drug tests can be performed that allow you to find out the body’s response to calcium antagonists. These drugs are the main ones in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
If the listed research methods are not enough to make a correct diagnosis, then the doctor will refer the patient to additional examinations, including:
FVD – determination of the function of external respiration. This method allows to exclude pathologies of the respiratory system. If the pressure in the pulmonary artery system is increased, then the doctor diagnoses a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen and carbon monoxide.
Carrying out ventilation-perfusion lung scintigraphy. During the study, the doctor injects radioactive particles into the bloodstream that reach the lungs. This makes it possible to detect thrombotic masses in the pulmonary artery system.
Multispiral computed tomography of the lungs and heart with the introduction of contrast. This method allows you to create a three-dimensional model of the respiratory organs and display them on the screen. As a result, the doctor receives maximum information about the disease.
Angiopulmonography. During the study, a contrast agent is injected into the pulmonary vessels, and then a series of images are taken on x-ray machines. This study allows you to detect blood clots in the arteries.
Prognosis of the disease
The prognosis of pulmonary hypertension is poor. It will not be possible to achieve a complete recovery. If the patient receives treatment, then heart failure, leading to death, will still occur, but the patient will still be able to prolong life.
If the cause of pulmonary hypertension is systemic scleroderma, then the prognosis is as unfavorable as possible. When the disease occurs, the degeneration of normal organ tissue into connective tissue occurs. As a result, a person dies within the first year.
In idiopathic pulmonary hypertension, the prognosis improves slightly. Such patients can live, on average, three years after diagnosis.
If heart disease leads to pulmonary hypertension, then the patient is sent for surgery. The five-year survival rate of such patients is equivalent to 40-44%.
If, against the background of pulmonary hypertension, heart failure rapidly increases with damage to the right ventricle of the heart, then a lethal outcome will occur within 2 years after the manifestation of the disease.
If pulmonary hypertension has an uncomplicated course and is amenable to medical correction, then about 5% of patients cross the line of 67 years.
Treatment of pulmonary hypertension

Treatment of pulmonary hypertension can be either conservative or surgical. Full recovery does not occur. If the human body perceives the ongoing therapy, then this helps to improve its overall well-being. A person is able to perform physical work. Life expectancy can be increased by 2 times.
To alleviate the course of the disease, as well as improve the quality and life expectancy, it is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations:
Physical activity should be limited. Especially strictly this rule must be observed immediately after eating, as well as under the condition of being in a too cold or too hot room.
Physical activity should be regular, but complexes should be made only on the basis of medical indications. This allows not to burden the heart and lungs, but to maintain adequate vascular tone.
When traveling by plane, you need to use oxygen therapy.
It is necessary to prevent various diseases of the respiratory system.
It is necessary to stop taking hormonal drugs during menopause.
Women with pulmonary hypertension are not recommended to have children.
You should stop taking hormonal drugs to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
It is necessary to monitor the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
Medication is the main treatment for pulmonary hypertension. For therapy, several medications are used, combining them with each other.
Drugs that a person will receive throughout life:
Antiplatelet drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots.
Anticoagulant drugs, which thin the blood, make it less viscous, which is also aimed at preventing the formation of blood clots.
Cardiac glycosides that contribute to the normal functioning of the heart muscle.
Calcium antagonists are drugs that are used for the main treatment of the disease. Their use is aimed at expanding the small vessels of the lungs.
Sildenafil – helps relieve spasm from the vessels of the lungs and reduces the load on the right ventricle of the heart.
Oxygen therapy allows you to saturate the blood with oxygen. This is especially true in the event of adverse environmental conditions, or with a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being. It is also possible to perform inhalations with nitric oxide, which are performed in a hospital ward. This procedure allows you to expand the vessels and alleviate the patient’s condition.
If medical correction does not achieve the desired effect, the patient is referred for surgery. It is indicated when the cause of pulmonary hypertension is heart disease.
Depending on the disease, various surgical techniques can be applied, including:
Atrial septostomy. This method allows you to establish communication between the atria. It is recommended for those patients who suffer from right ventricular failure. Septostomy is used as a preparation for a patient before a heart or lung transplant operation.
Thrombandarterectomy. This procedure is aimed at removing blood clots from the pulmonary arteries. The operation allows you to reduce the load on the heart, make the symptoms of the disease less pronounced. The procedure will be performed only if the thrombotic masses have not yet begun to degenerate into connective tissues.
Organ transplant. Lung and heart transplants are possible. The complexity of the operation makes it rare.









