An infectious disease, which is characterized by a chronic form of the course and a specific inflammatory process, is called actinomycosis. The reason for its occurrence is radiant fungi, namely actinomycetes that have entered the body.
The defeat of actinomycosis of the oral cavity is quite widespread. In almost half of patients with actinomycosis, the cervicofacial region suffers. Mostly people belonging to the middle age category are ill, although children, both preschoolers and schoolchildren, often fall under the scope of microbes.
The most common cause of the disease is autoinfection (self-infection). Radiant fungi that live in the oral cavity are activated and, acquiring a pathogenic form, overcome the body’s defenses. The carriers of the infection are plaque on the teeth, caries, tartar, gum disease.
Scientists believe that radiant fungi can live in the oral cavity for a long time without causing any damage to the body. But as soon as the integrity of the mucous membrane is violated, they cease to be saprophytes and begin to penetrate into the tissue – actinomycosis of the maxillofacial region occurs. The process spreads further, gradually capturing the periosteum and bone tissue. The affected area of the bone dies and is rejected, osteomyelitis is diagnosed on the jaw.
It is much less common to find infection with actinomycosis from external sources. The same radiant fungi remain the causative agents, but they enter the body with a plant or dust. A person is rarely exposed to such danger; in most cases, grass-eating animals are affected.
For humans, the teeth remain the most likely place for the penetration of actinomycetes. And not only destroyed, but also wisdom teeth, which for a long time cannot come out. The inflamed gum, a pocket that is sure to form if the tooth does not find a way out, serves as a springboard for the penetration of radiant fungi into the tissues.
Contribute to their penetration and trauma, damage to the gums remaining after tooth extraction. Places of localization of actinomycosis in the oral cavity are postoperative wounds, gums, tongue.
Most often, actinomycosis affects the cervicofacial region and the lower jaw. The scheme of penetration is as follows: trauma, surgery, injection violates the integrity of the epithelium, and this is quite enough for the causative agent of actinomycosis to enter the tissue.
Symptoms of actinomycosis of the oral cavity
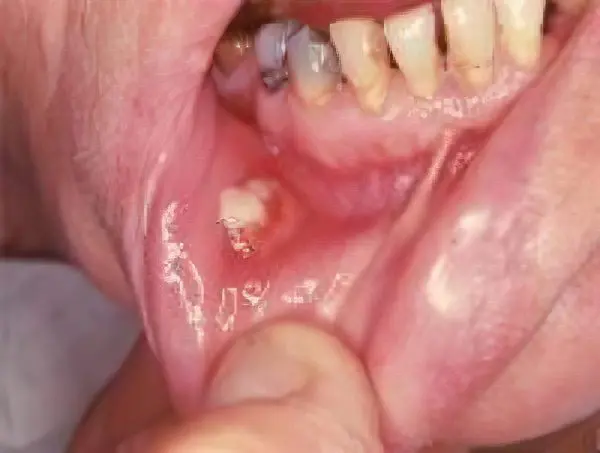
At first, the disease practically does not manifest itself. Dense nodes-granulomas, or actinomycomas, formed deep in the tissues or inside the mucous membrane, do not cause either an acute inflammatory process or an increase in temperature. The sick person feels fine.
When the disintegration of the nodes begins, which is accompanied by the release of pus from narrow fistulas, intoxication of the body is evident. It is accompanied by headaches, general weakness, subfebrile temperature. If the nodes are concentrated on the lower jaw, then convulsive spasms of the muscles of the mouth, or lockjaw, which makes it difficult to eat, are possible.
In the place where the nodes merge with each other, the inflamed infiltrate is usually strongly compacted, which serves as the basis for the diagnosis of actinomycosis. In the middle of the infiltrate, holes resembling nipples are visible. Their color is red, they seem to protrude on the surface. And the fistulas themselves secrete pus, liquid in consistency, yellowish-gray grains are noticeable in it, the diameter of which does not exceed 1 mm. The grains are called sulfur granules or Bollinger bodies. These are drusen – colonies of fungi, which are formed by mycelium. The presence of drusen gives every reason for making a final diagnosis.
If there are doubts, then they resort to a skin-allergic test, in which actinolysate is used – a protein extract of the culture. If the body is affected by actinomycosis, then the diagnosis is confirmed by the clinical manifestations of the disease: hyperemia and edema, which occur after 24 hours at the place where the injection was made.
Treatment of oral actinomycosis
Treatment of actinomycosis of the oral cavity is primarily aimed at strengthening tissues, restoring their functional usefulness, and strengthening immunity. If the treatment takes place in a hospital, then blood transfusion is prescribed. To strengthen the body, vitamin C, multivitamins, aloe extract, calcium gluconate, fortified fish oil, and quartz irradiation are prescribed.
In most cases, nonspecific flora present in the focus contributes to inflammatory processes. It can be treated with antibiotics in combination with sulfonamides.
The foci of infection are constantly washed with special preparations that destroy bacteria, and turundas soaked in antibiotics are injected.









