Contents

Measles is a common highly contagious infectious disease, its causative agent is an RNA virus that has a specific form. The microorganism quickly dies outside the human body under the influence of disinfectants and physical factors. At the same time, the measles pathogen can spread over long distances in cold weather. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. The transferred disease contributes to the formation of stable immunity, so cases of re-infection are very rare.
The entrance gates of infection are the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, after which the virus spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body. Having fixed on the internal organs, the virus contributes to the formation of infiltrates at this site with the further formation of multinucleated giant cells.
Despite the fact that measles is considered a childhood disease, adults sometimes suffer from it. Those at risk are those who were not vaccinated in childhood, and also did not have measles. Increasingly, mass outbreaks of the disease are observed in Russia. Therefore, it is imperative to know the symptoms of measles.
Symptoms of measles in adults
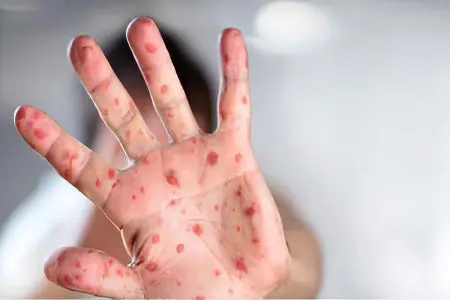
The incubation period when infected with measles lasts one or two weeks in adults. In a typical course of the disease, three successive stages can be distinguished: catarrhal, rash and convalescence.
catarrhal period begins with acute manifestations of the disease. The patient complains of general malaise, headache, loss of appetite, loss of sleep. In a severe course of the disease, the body temperature rises to 40 ° C, the patient is tormented by a dry cough, a runny nose with copious mucous or purulent discharge, during a medical examination, wheezing is heard in the lungs, and hard breathing is noted. The characteristic symptoms of measles in adults include an increase in the lymph nodes of the neck.
After 3-5 days, the fever becomes less pronounced, and the patient feels better. However, after a day, intoxication increases again and the patient’s body temperature again becomes high. During a repeated deterioration in well-being, white spots with a reddish border appear on the buccal mucosa.
Eruption period. It is characterized by the appearance of maculopapular exanthema, individual spots merge with each other over time. First of all, the rash appears behind the ears, then covers the scalp, over time it can also be seen on the face, neck and chest area. Then the rash gradually covers the entire torso of the patient, as well as the upper and lower limbs. This period is also characterized by increased runny nose, cough and profuse lacrimation.
Period of convalescence. In the final period of the course of the disease, the patient feels better: the patient’s body temperature returns to normal, rashes disappear.
The severity of the disease
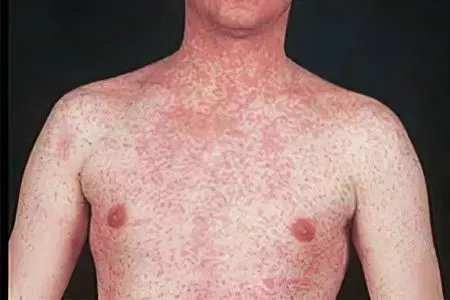
Depending on the intensity of the symptoms of the disease, it can be mild, moderate or severe. Also, the disease can give a typical and atypical clinical picture.
The atypical form of the disease is manifested by the following disorders:
Mitigated or erased infection. Thus, measles occurs in people who have been given a vaccine or gamma globulin. The symptoms are erased, there are very few of them.
Hemorrhagic measles. Multiple bruises form under the skin, blood is found in the feces and in the urine. It is possible to develop bleeding of internal organs, which can lead to the death of a person. It is important to diagnose measles in time and place the patient in a hospital.
Hypertoxic infection. The patient’s condition becomes severe, he suffers from severe intoxication of the body. Heart failure, meningitis, encephalitis may develop. Such patients should be urgently placed in a hospital.
Measles in adults and children – what’s the difference?
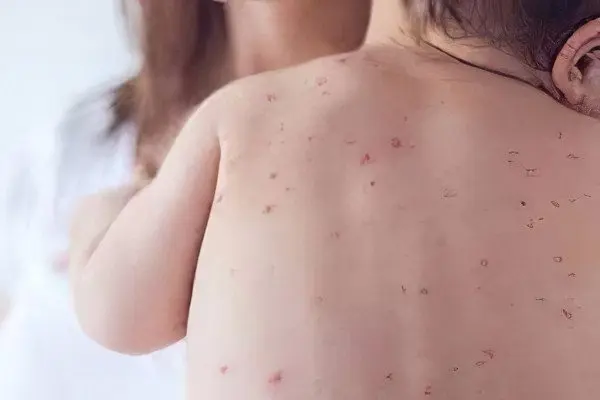
In adults, all the so-called “childhood” diseases have a severe course. Measles is one of those diseases.
In adults, body temperature always rises to extreme levels of 40-40,5 ° C. The patient feels very bad, he has to stay in bed all the time. The rash will be very intense, covering the entire body.
Almost always, adult patients are diagnosed with bronchitis, laryngitis. There are frequent cases of inflammation of the brain and lung tissue. Adults recover after an infection longer than children. Most often, such patients are hospitalized, since it is not possible to cope with the complications of the disease at home.
Complications of measles
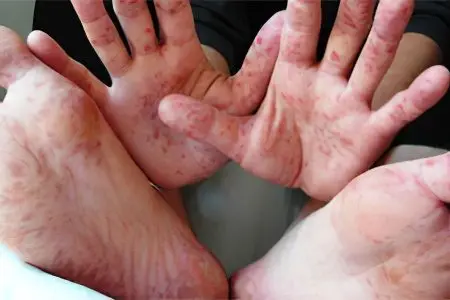
Complications of measles develop due to the fact that the bacterial flora joins the viral infection. The lower the immunity of a person, the higher the likelihood of a severe course of pathology.
Complications of measles include:
Damage to the upper respiratory tract and hearing organs: otitis media, sinusitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis.
Infection of the lower respiratory tract: pneumonia or bronchitis.
The defeat of the digestive system: diarrhea, inflammation of the intestine.
CNS damage: encephalitis, meningitis, polyradiculoneuritis, multiple sclerosis.
Kidney damage with the development of pyelonephritis.
Liver damage with hepatitis.
The most common complication of measles is pneumonia. It often develops in older people whose immune system is weakened. Measles is no less dangerous for pregnant women. It can lead to the development of an abortion or early birth.
Diagnostics
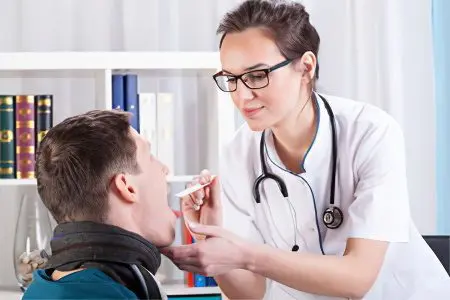
To make a diagnosis, the doctor often needs an external examination of the patient. However, laboratory tests will be required to confirm it.
A complete blood count indicates an increase in the level of neutrophils with a decrease in the number of leukocytes. If a patient develops a bacterial complication, then the level of leukocytes begins to rise. The ESR also increases.
Measles can be confirmed by enzyme immunoassay (ELISA). Its use allows to detect the infection at the earliest stage of its development. In the blood of a person, antibodies specific to the disease begin to circulate. Class M immunoglobulins increase from 1-2 days from the onset of the disease, and class G immunoglobulins increase from the 10th day of measles.
Immunoglobulins are proteins that are produced by blood cells. They bind to infectious agents and then neutralize them.
Less commonly, virus microscopy, RIF, and other virological techniques are used to detect measles.
Of particular difficulty is the diagnosis of measles in the first phase, when the patient develops exclusively catarrhal symptoms. In this case, it is necessary to differentiate measles from whooping cough, influenza, rubella, adenovirus infection, and an allergic reaction of the body.
Treatment of measles in adults
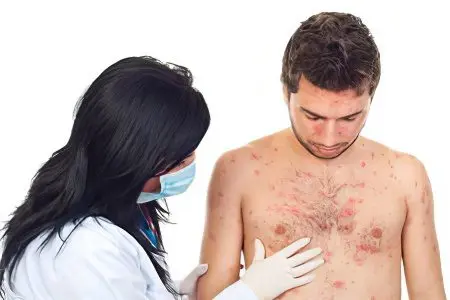
Treatment of measles in adults is most often aimed at relieving the symptoms of the disease. If bacterial complications occur, antibiotics may be prescribed. Mild forms of pathology do not require hospitalization. Treatment in a hospital is recommended in case of severe disease or according to epidemiological indications. In any case, the patient should observe bed rest during the manifestation of intoxication.
The patient does not need to adhere to any particular diet, it is only important for him to increase the amount of fluid consumed.
The oral cavity and eyes require special care during measles. The patient should be protected from bright sunlight and artificial light, as photophobia often develops during illness.
To reduce body temperature, to relieve headaches and relieve general intoxication from the body, you should take drugs from the NSAID group: Nimesil, Aspirin, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, etc. Doctors also prescribe antihistamine drugs to adult patients. In order to better sputum out of the respiratory tract, you should take drugs with a mucolytic effect, for example, ACC.
If the skin begins to itch, it is recommended to wash it with Delaskin’s solution. It is equally important to keep your mouth clean. To do this, it is rinsed with a solution of chlorhexidine, a decoction of chamomile or oak bark.
To relieve the symptoms of inflammation from the organs of vision, eye drops are used: Levomycetin, Sulfacyl sodium, etc. You can wash your eyes with a solution of Furacilin or baking soda.
Antihistamines, symptomatic drugs, interferon may also be recommended. Treatment of measles encephalitis requires prednisolone and antibiotics. It is important to remember the high risk of complications in adults, which can be avoided by constant monitoring by a specialist.
As a prophylactic, vitamin A in high dosages can be recommended.
Serious patients are admitted to the hospital. There they are prescribed detoxification, anticonvulsant and anti-inflammatory drugs.









