Kidney carbuncle may develop due to a massive purulent focus as a result of bacterial invasion. Pathology can become a primary disease, which is accompanied by the formation of a bacterial thrombus in the lumen of a blood vessel located in the kidney cortex or in a number of small vessels located close to each other. If the lumen of one large vessel closes, then a massive focus of septic infarction will soon form, if several small blood vessels are blocked, a number of small foci are formed that quickly merge with time. Purulent fusion of the carbuncle can lead to the spread of the infectious process to the medulla of the organ or the opening of the focus into the renal pelvis, perinephric tissue. The consequence of the last complication may be the development of purulent paranephritis.
If the pathology develops against the background of acute pyelonephritis, then the occurrence of carbuncle becomes both a consequence of hematogenous septic thrombosis of one large blood vessel, and a consequence of the narrowing of its lumen due to the inflammatory process (the formation of an infiltrate).
The most common causative agents of the disease are Staphylococcus aureus and white, as well as Escherichia coli or Proteus. In 40% of cases, one patient has two diagnoses simultaneously: apostematous pyelonephritis and carbuncle of the kidney.
Kidney carbuncle symptoms
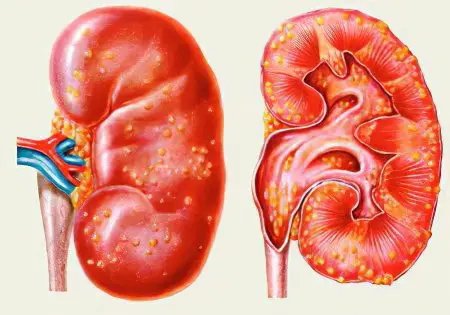
Outwardly, the carbuncle of the kidney looks like a volumetric formation of a rounded shape. When it is opened, necrotic tissue is visible with numerous small pustules that merge and wedge-shaped deepen into the parenchyma of the organ. The base of the focus of inflammation is adjacent to the membrane of the kidney involved in the infectious process (perinephritis).
At the first stage of the disease, the bottom of the carbuncle is thicker, infiltrated and soldered to the shell of the kidney; over time, its purulent fusion occurs. In most cases, perirenal tissue is involved in the inflammatory process. At the initial stage, it swells and infiltrates, then purulent paranephritis develops.
If the carbuncle develops in the upper segment of the kidney, then the resulting infiltrate can pass to the adrenal gland, provoking a decrease in its function and causing reactive pleurisy.
In the event that secondary acute pyelonephritis is complicated by purulent inflammation of the tissues with the formation of a carbuncle, the clinic of the disease resembles apostematous pyelonephritis in its manifestations, the cause of which is a violation of the outflow of urine.
In those few cases when the pathology develops without changes in urodynamics and the carbuncle is a hematogenous localized focus in the organ, the symptoms of the disease have much in common with the clinical picture of a general infectious disease. The patient suffers from high fever (39–40 °C Celsius), severe chills, excessive sweating, general weakness, high pulse and respiration rates, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and constipation.
Symptoms of kidney carbuncle at the initial stage of the disease are not accompanied by local pain in the kidney area, in addition, during the study, no leukocytes and bacteria are found in the urine, there is no urination disorder, which causes difficulties for doctors in making a diagnosis. For this reason, patients with kidney carbuncle are hospitalized with misdiagnoses such as influenza, pneumonia, typhoid fever, etc.
Treatment of carbuncle of the kidney

Treatment of renal carbuncle with the strongest broad-spectrum antibiotics is not effective without surgical intervention. The carbuncle must be opened and its cavity drained.
Making such a diagnosis implies an urgent operation, which includes lumbotomy, decapsulation of the kidney, cruciform dissection of the carbuncle or its excision, and drainage of the paranephria. The kidney is tamponed with rubber-gauze tampons without suturing one of the corners of the wound. With stagnation of urine, it is drained.
On the second day after the operation, tampons must be changed to rubber graduates. The wound is drained for a long time until it is completely cleansed of dead cells until juicy granulations appear.
Taking into account the results of urine culture, antibiotic treatment is carried out, detoxification therapy is prescribed to patients, and therapeutic exercises are performed.
In case of severe purulent or septic intoxication after the operation, the treatment is supplemented with extracorporeal detoxification methods, patients are prescribed hemosorption, plasmasorption, plasmapheresis. Operated patients are observed by specialists of dispensaries for another year.
With numerous carbuncles of the kidney, the intactness of the second kidney and its normal functioning, it makes sense to perform nephrectomy, especially if the patient is elderly or in old age.









