Contents

Dropsy of the brain, or hydrocephalus, is the result of an excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain and the spaces between the meninges. Pathology can develop after suffering injuries and certain diseases. The cavities of the brain expand, put pressure on the surrounding tissues, causing neurological failures.
With hydrocephalus, the balance between the formation of cerebrospinal fluid and its reabsorption into the bloodstream is disturbed. As a result, the volume of cerebrospinal fluid significantly exceeds the reserve capacity of the cavities of the brain (cistern, ventricles, subarachnoid fissures). Normally, the constant renewal of cerebrospinal fluid allows you to get rid of toxic metabolic products.
Liquor is responsible for the depreciation of the brain during blows to the head and sudden movements, its circulation provides nutrition to the cells of the cerebral cortex. When the balance between the incoming and absorbed cerebral fluid is disturbed, it presses on the walls of the internal cavities of the brain, in some cases causing irreversible damage.
The cause of hydrocephalus can be all sorts of lesions of the brain and meninges. In most cases, it occurs as a complication of infectious diseases (meningitis, meningoencephalitis) or traumatic brain injury. Dropsy may be associated with difficulty in the reverse flow of blood from the cavities of the skull, such a violation is usually caused by the pathology of the venous vessels, the formation of blood clots in the sinuses, cicatricial and adhesive process in the cavity of the efferent veins. Tumors, high blood pressure, kidney disease, brain parasites can also cause dropsy of the brain. In some cases, hydrocephalus is associated with underdevelopment of the brain, growth of cerebral or spinal hernia.
Classification of hydrocephalus
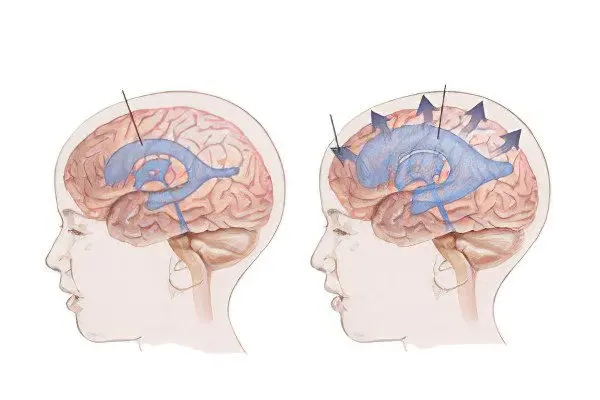
The division of dropsy of the brain into categories is carried out for several reasons.
Depending on the etiology of the disease:
Closed or non-communicating – the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is impaired due to the fact that the ways of its transportation to the bloodstream are blocked due to the formation of a tumor, cyst, closure of the openings of Magendie and Luschka, narrowing of the cerebral aqueduct or the occurrence of a blood clot. An increase in craniocerebral pressure leads to infringement and compression of the brain structures.
open or communicating – the physiology of the absorption of cerebral fluid into the systemic circulation is disturbed, this process occurs very slowly due to inflammation of the meninges, cysticercosis, sarcoidosis, cerebral hemorrhage, metastases. Stably high craniocerebral pressure gradually destroys the medulla.
Hypersecretory form – excess liquor is produced.
Classification of dropsy of the brain by etiology:
Congenital hydrocephalus – is formed during fetal development due to infection of the fetus, genetic diseases, birth trauma, hemorrhage in the fetal brain. This type of pathology is not compensated in childhood in all patients and sometimes passes into adulthood.
Acquired hydrocephalus – occurs against the background of craniocerebral infections, brain injury, cysts and tumors.
Replacement hydrocephalus – occurs against the background of brain atrophy due to age-related changes, encephalopathy.
Types of dropsy, depending on the nature of the course of the disease:
Acute form – develops within a few days, the patient’s condition quickly becomes extremely severe;
Chronic form – develops over several months or six months with a gradual increase in intracranial pressure and worsening of symptoms.
Classification of the disease depending on the localization of excess cerebrospinal fluid:
External form – cerebral fluid accumulates in the subarachnoid space under the meninges without expansion of the ventricles, occurs with brain atrophy;
Internal form – CSF accumulates in the tanks and ventricles of the brain;
Mixed form – cerebral fluid accumulates in all cavities of the brain.
Classification of dropsy of the brain, depending on the severity of violations of its structures:
Compensated – an excess of CSF does not compress the brain structures, there are no pronounced symptoms, the patient feels normal;
Decompensated – due to compression of the brain tissue, a variety of neurological symptoms, disorders of the central nervous system are diagnosed.
Causes of dropsy of the brain

If we exclude the congenital form of adult hydrocephalus, which appeared in him in early childhood due to intrauterine infection, birth trauma or congenital pathologies, the following causes of dropsy can be distinguished:
Hemorrhage due to rupture of an aortic aneurysm, breakthrough of a hematoma under the meninges or into the ventricles;
Traumatic brain injury;
Inflammation of brain structures due to complications of neuroinfections and systemic pathologies (meningitis, neurosyphilis, sarcoidosis, encephalitis);
Helminthosis (cysticercosis, echinococcosis);
Benign and malignant brain tumors;
Metastases in the brain;
ventricular cysts;
Vascular encephalopathy as a consequence of diabetes, atherosclerosis, hypertension;
Toxic encephalopathy as a result of poisoning with substances toxic to the central nervous system.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus

Symptoms of an acute form of hydrocephalus:
Severe headaches without a specific localization, most pronounced in the morning;
Nausea and vomiting, most felt in the morning;
Persistent hiccups;
Weakness, constant fatigue;
Tachycardia (over 120 beats per minute) or bradycardia (less than 50 beats per minute);
Lethargy, indicating an increase in craniocerebral pressure;
Confused mind;
Violation of oculomotor movements, maintaining a forced posture of the head.
Symptoms of a chronic form of dropsy of the brain:
Lethargy, passivity, indifference to what is happening;
Violation of cognitive functions, memory, ability to count;
Failures in sleep and rest;
Inhibition of speech function and intellectual abilities;
Violation of the process of walking, when the patient in the prone position imitates the movements of the legs when walking, but in the standing position is incapable of coordinated movements;
restlessness, nervousness, inability to concentrate;
increased sweating;
Involuntary urination – appears in the later stages of the development of the disease.
When the brain is compressed, visual impairments such as double vision, visual field loss, pupil dilation with no reaction to light, optic nerve atrophy up to blindness, decreased visual acuity, strabismus appear.
Children suffering from congenital hydrocephalus or who fell ill in early childhood are retarded and inactive. They have a violation of the main metabolic processes: water, carbohydrate and fat. Changes in fat metabolism can cause general obesity. Against the background of the disease, exhaustion can also occur, a characteristic shape of the head is formed: it increases in size and becomes like a ball, the forehead is large and overhanging, the orbits of the eyes are deeply set, the eyes are half-closed.
The skin on the head of patients is thinned, with a translucent network of venous vessels. Fontanelles during the disease increase in size, bulge outward and tighten, the bones become thinner, the sutures connecting the bones of the skull may diverge. The disease is accompanied by neurological symptoms – these are paralysis, paresis of individual limbs, weakening of reflexes and muscle tone, there may be a violation of coordination of movements, statics, and a change in gait. Among the symptoms of dropsy of the brain, there is also a decrease in visual acuity, in some cases complete blindness can be observed.
Cerebral edema is often manifested by mental disorders, which can be conditionally divided into conditions associated with insufficiency of intellectual activity, and personality disorders. Intellectual deficiency can manifest itself as a reversible mild form of mental retardation, or it can be aggravated by oligophrenia, which is characterized by varying degrees of mental retardation. In most cases, euphoria prevails, which is quickly replaced by apathy. Among the clinical manifestations, symptoms characteristic of high intracranial pressure are noted: headache, vomiting, bouts of nausea.
In addition to collecting an anamnesis, when making a diagnosis, additional examination methods are also used to determine the form, stage, etiology and severity of symptoms of the disease. For these purposes, oscillography, echoencephalography, ventriculography, angiography are used.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus
The doctor determines the diagnosis of “hydrocephalus” on the basis of the collected history and the existing clinical picture of the pathology.
Instrumental diagnostic methods:
Magnetic resonance imaging – with a high degree of probability diagnoses the disease, determines its causes, reveals damage to the structure of the brain. The criteria for dropsy are periventricular edema, the value of the interventricular index is more than 0,5.
Radiography of the cisterns of the base of the skull – determines the ways of resorption of the cerebrospinal fluid, helps to establish the form of hydrocephalus.
Computed tomography – determines the contours of the brain and its cavities, diagnoses neoplasms in brain structures.
Examination of the fundus – swelling of the optic nerve discs indicates an increase in craniocerebral pressure.
Treatment of hydrocephalus
Treatment of dropsy of the brain can be conservative, in some cases – surgical. The goal of therapy is to reduce intracranial pressure (Lasix, Furosemide, Fonurit, Mannitol, Diacarb, other diuretics) and stabilize indicators. As part of conservative treatment, general strengthening procedures are carried out, for example, salt-coniferous baths, drugs are prescribed to reduce body temperature and anti-inflammatory drugs, dehydration and desensitizing therapy is carried out.
Mental disorders are treated in combination with the above conservative methods. With pronounced affective-volitional disorders and with individual episodes of psychosis, psychotropic drugs are prescribed. If conservative methods of treatment are ineffective, then surgical intervention is indicated.
An operation performed on patients with hydrocephalus, which is caused by trauma or inflammation, can help the patient completely get rid of all the symptoms of the disease.
Bypass surgery
Silicone catheters equipped with special valves are inserted into the cavities of the brain. They contribute to the removal of excess cerebrospinal fluid into the abdominal cavity. Contraindications to shunting are pathologies of vision, a chronic form of hydrocephalus.
The operation helps to restore the quality of life, maintain the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid at an optimal level. A complication of shunting can be infection of the tube, the need for its urgent replacement due to loss of properties. The bypass surgery takes 1,5 hours and is performed under general anesthesia.
Types of shunting for the removal of cerebral fluid:
ventriculoperitoneal shunt – between the brain and the peritoneum;
Ventriculoatrial shunt – between the brain and the heart;
Ventriculovenous shunt – between the brain and veins;
Ventriculopleural shunt – between the brain and lungs;
Ventriculo-urethral shunt – between the brain and the urethra.
endoscopy
This method of treatment of dropsy of the brain requires the availability of special equipment in the clinic and a high classification of a neurosurgeon. Endoscopy is a modern and safe way to eliminate excess cerebral fluid by inserting a neuroendoscope into the channels of brain structures.
Under the control of a miniature video camera, the doctor makes a hole with a special catheter to remove the cerebrospinal fluid along a pre-prepared path. The effectiveness of the method allows you to achieve success in just one procedure. Endoscopic intervention is not always possible, it has contraindications.
Patients who have undergone surgery for the treatment of hydrocephalus should be observed by a surgeon and a neurologist for a long time, replace the shunt in a timely manner, and take antibacterial drugs to prevent infection.
It is not easy to predict the development of hydrocephalus. With timely treatment, there is a chance to avoid disability and intellectual impairment. If the full range of therapeutic measures is not carried out in time, there is a high probability of symptoms of CNS pathology, psychoemotional and cognitive impairments.
The development of dropsy of the brain, especially if the disease is congenital, can stop at any stage, but complete healing never occurs. The prognosis is favorable only if treatment is started in a timely manner. If the therapy is delayed, then the accumulation of fluid in the brain will lead to the fact that irreversible changes will begin and some brain functions will be impaired. The success of surgical intervention depends on the time of its implementation, the severity of the disease, as well as on the competent consideration of all indications and contraindications for surgical intervention.









