Contents
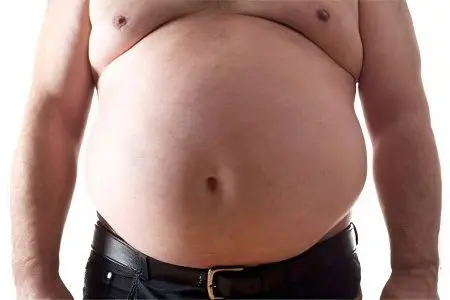
Abdominal dropsy (ascites) is a significant accumulation of transudate in the peritoneal cavity. The cause of this pathology can be portal hypertension, in which the flow of the portal vein is blocked above, inside or under the liver. Ascites can also be caused by edematous syndrome in chronic heart failure, kidney disease, alimentary dystrophy, impaired reverse flow of lymph through the thoracic duct as a result of injury or compression. Dropsy of the abdomen often develops with the growth of tumors and the development of the tuberculous process. The factors listed above are quite often found in various combinations.
Normally, a small amount of serous fluid is always present in the abdominal cavity, which makes it possible for the organs located there to move, protects from shock and injury. If the water exchange between the tissues of the peritoneum and the blood vessels is disturbed or stops, ascites, or dropsy of the abdomen, occurs.
Causes of the disease

Dropsy of the abdomen is not an independent diagnosis, but a symptom of severe diseases of internal organs or systemic disorders in the functioning of the human body. The addition of dropsy doubles the likelihood of death, worsens the condition of the patient, already suffering from a serious pathology.
Causes of dropsy of the abdomen:
portal hypertension. In this disease, the outflow of blood through the portal vein is blocked due to cirrhosis of the liver, thrombosis of the hepatic veins or portal vein, compression of the vein by tumors. Due to the high hydrostatic pressure, blood plasma from the veins of the digestive tract penetrates into the abdominal cavity and accumulates there.
Kidney diseases. The cause of ascites in these pathologies is nephrotic syndrome.
Decompensated heart failure. Ascites is caused by stagnation and edema in the systemic circulation resulting from a heart attack, myocarditis, and pathology of the heart valves.
Alimentary dystrophy.
Benign tumor of the ovaries.
Peritoneal carcinomatosis. Spread of malignant tumor cells through the tissues of the peritoneum.
Ascites-peritonitis. The development of the tuberculosis process in the peritoneum.
One patient may have several causes of abdominal dropsy.
Causes of ascites in young children:
Congenital edema caused by the incompatibility of the Rh factor of the mother and child (hemolytic disease of the newborn).
Diseases of the liver and gallbladder of newborns.
Hidden fetal blood loss.
Dystrophy against the background of protein deficiency in the child’s diet.
Congenital pathology of the kidneys.
Exudative enteropathy is the loss of plasma proteins through the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of dropsy of the abdomen
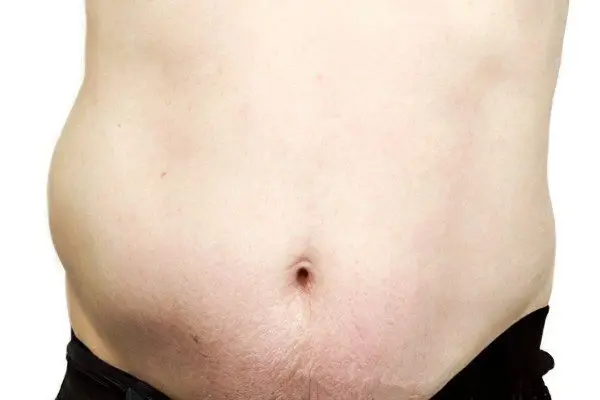
Ascites can manifest itself acutely – as, for example, with the formation of a blood clot in the lumen of the portal vein; symptoms of dropsy of the abdomen can also develop gradually over several months. The course of the disease is accompanied by flatulence, which in some cases is the dominant symptom.
The dropsy fluid is most often serous, rarely there are streaks and blood clots in it, and chylous transudate is practically not found. In some cases, up to 30 or more liters of fluid are retained in the abdominal cavity. The diagnosis of ascites is made when at least one liter of transudate accumulates in the peritoneal cavity.
In a patient suffering from severe ascites, the circumference of the abdomen increases: it takes the form of a ball with a half protruding forward or hanging down. The wall of the peritoneum is tense and stretched, the skin is thinned, the folds are smoothed. With the accumulation of a significant amount of fluid, the navel can protrude, resembling a balloon in shape, while the skin is greatly stretched, and white stripes are visible on the abdominal wall. During percussion of the abdomen, a dull sound is heard above its sloping part or on the sides. Methods for the early diagnosis of ascites include determining the presence of fluid in the Douglas space during rectal or vaginal examination.
As a result of increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity, an umbilical or femoral hernia may develop. In some cases, as a result of a rupture of the navel, the disease is complicated by peritonitis, and rectal prolapse may also occur. Patients have swelling of the lower extremities; free fluid, in addition, can accumulate in the pleural cavities, causing respiratory failure and cardiac overload.
An important diagnostic value is the study of dropsy fluid taken during the puncture of the abdominal cavity. Most often, the liquid is transparent, it has a neutral or slightly alkaline reaction. The transudate contains a large number of endothelial cells, and in neoplastic diseases – cancer cells. The specific gravity of the liquid does not exceed 1,015, the protein content is not more than 2,5%. With repeated punctures, leukocytes are detected.
Other symptoms of ascites:
The skin of the abdomen is stretched, thinned;
Abdominal wall in tension;
The navel protrudes outward;
Stretch marks appear on the abdomen – white stripes of stretched skin.
With dropsy caused by portal hypertension, edema appears on the legs. Around the navel and on the side of the abdomen, a characteristic symptom of the “head of a jellyfish” is observed – a pattern of dilated veins.
Diagnostics

When examining a patient, the doctor uses such a diagnostic technique as percussion. He taps on separate parts of the abdomen and analyzes the resulting sound. With ascites, the sound is dulled on the side of the abdomen or in its sloping part. The effect moves as the position of the body changes because the fluid flows freely in different directions. Another symptom of ascites, detected during percussion, is fluctuation, when the palm of one hand, attached to the side of the abdomen, feels the transmission waves caused by light blows of the other hand.
The most informative instrumental study in diagnosing ascites is ultrasound and CT of the abdominal cavity.
Planned result of the study:
Identification of even the minimum excess of the volume of liquid;
Assessment of the severity of the pathology;
Determine the cause of ascites.
Laboratory tests performed for ascites:
Complete blood count – with cirrhosis, anemia is noted, increased ESR;
General urine analysis – with cirrhosis of the liver, protein, cylinders and erythrocytes are found in the urine, and with ascites accompanying kidney pathology, the urine has an increased density, blood appears in it (hematuria);
Biochemical blood test – states a decrease in the protein content in the blood plasma and an increase in the concentration of bilirubin;
General analysis of the fluid obtained by puncture – ascertains the transparency or admixture of blood, chylous character, transudate density, protein content;
Rivolt’s test – differentiation of transudate from exudate, during which the liquid from the peritoneum is mixed with acetic acid, if the liquid falling into the acid does not cause turbidity, this is a transudate;
Cytology – differentiation of the tumor process from other pathologies;
Bacteriological seeding of transudate obtained from the abdominal cavity is carried out to identify the tuberculous process.
Treatment of abdominal dropsy
The doctor determines the method of treating ascites, based on the cause that caused it. Treatment can be both surgical and therapeutic. For conservative therapy, diuretics, aldosterone antagonists, a salt-free and protein-free diet with fluid restriction in the diet up to 1,5 liters per day are used.
If ascites is caused by heart failure, drugs of the following pharmacological groups are used:
Cardiac glycosides, alpha-adrenergic stimulants to reduce myocardial contractility;
Diuretics, thiazides, potassium-sparing diuretics to remove excess fluid;
Vasodilators to reduce the workload on the heart.
With ascites caused by renal failure, the patient is prescribed:
bed rest,
Removing salt from the diet
Fluid control in the body
Droppers with albumin courses,
Taking diuretics.
Children with congenital edema and exudative enteropathy are transfused with blood plasma, Veroshpiron and glucocorticosteroids are administered.
With severe edema, the peritoneal cavity is drained to remove fluid from it. For anesthesia, local anesthesia is used, the procedure is performed in a sitting position, in a hospital.
There are alternative methods of surgical treatment of ascites. This is the Kalb operation, which consists in excising the peritoneum and lumbar muscles to stimulate the absorption of the transudate by the subcutaneous tissue. The efficiency of the operation is only 30%, the result lasts up to six months.
Complications
With the accumulation of a large volume of excess fluid in the peritoneum, the diaphragm rises, squeezing the lungs and large blood vessels. Because of this, respiratory failure and overload of the heart muscle occur.
If an infectious factor joins the ascites, peritonitis develops, the treatment of which does not tolerate delay and is carried out only surgically.
To prevent dropsy of the abdomen, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease in a timely manner.









