Contents
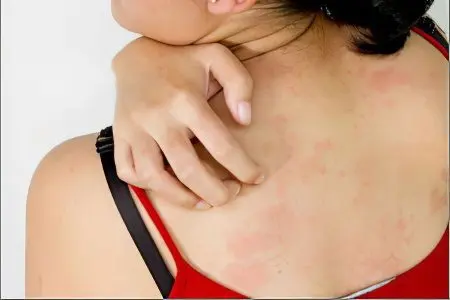
Lichen colorus is a skin disease that most often affects people living in countries with a hot and humid climate. Dermatological manifestations of the disease most often occur after a person has spent a long time in the sun. In Russia, no more than 10% of the population suffers from color lichen. You can also find such names for colored lichen as “pityriasis versicolor” or even “solar fungus.” However, they will denote a single problem.
Lichen colorus has an undulating course, with periods of exacerbation and calm. At risk for the development of the disease are people who are prone to the occurrence of various dermatomycosis. Relapses of pathology most often occur in the warm season. There are no signs of an inflammatory reaction on the skin during an exacerbation of the disease.
Colored lichen cannot be called a dangerous disease, since it does not pose a threat to health. The therapy is usually simple and highly effective. However, the presence of spots on the skin can cause a feeling of psychological discomfort associated with a defect in appearance.
Causes of color deprivation
Colored lichen is caused by fungi called Malassezia furfur and Pityrpsporum orbiculare. They parasitize in the upper layer of the epidermis. Therefore, to detect a mycotic microorganism, a simple examination of skin particles under a microscope is sufficient. Fungi gather in bunches that look like curved threads.
Lipophilic yeast-like fungi Malassezia furfur have unique properties. They are able to show their pathogenic activity depending on changes in the environment, as well as depending on the immunity of the host. In addition, this is the only fungus from the human microflora that needs fats for its existence. This quality is called obligate lipophilicity.
Malassezia furfur and Pityrpsporum orbiculare are able to exist both in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. In addition to the fact that these microorganisms can cause multi-colored lichen, in some cases they become the cause of systemic pathology. This occurs when an infected person has severe immune deficiency. For example, there is evidence that a fungus of this species and genus led to sepsis in premature newborns and to sepsis in HIV-infected people.
Most people have a strong belief that it is impossible to get infected with color lichen. In fact, the fungus can be passed from one person to another. However, the clinical symptoms of the disease are not manifested in every patient. Therefore, dermatologists refer to causative agents of color lichen as conditionally pathogenic flora.
This means that it can exist on the skin, but will not manifest itself in any way. So, many people are infected with pathogenic fungi, but the symptoms of the disease develop only if the body’s defenses are weakened. It has been established that the causative agent of color lichen is isolated in 10-12% of the population, 2 times more often it is found in men. The disease develops in people aged 15-40 years. This type of mycosis worsens in the summer, and spontaneous recovery is also possible. In some people, lichen becomes a relapsing chronic course.
The fungus is transmitted in the following ways:
During personal contact with a person. Therefore, the pathogen is most often found in all family members.
Through the use of personal hygiene items. It can be items of clothing, a towel, a washcloth, etc.
While using public locker rooms or fitting rooms in stores.
Sometimes the fungus can exist on the skin for a long time, and the person will not know about it. However, if provoking factors appear that contribute to its reproduction, the pathogenic flora will begin to actively increase its numbers. The incubation period is equal to 2 weeks.
The provoking factors
Provoking factors that can lead to the development of colored lichen:
Increased sweating. In particular, the danger is hyperhidrosis, in which sweat changes its chemical composition. This promotes the growth of mycotic microorganisms.
Predisposition of a person to various skin diseases. It can be inherited, or be a feature of a particular organism. In this case, an increased level of cortisol in the blood plasma is observed.
Too oily skin. So, in 15-year-old patients with color lichen, lipophilic fungi are found in 93% of cases. While in children under 5-7 years old, these mycotic microorganisms are absent on the skin.
Violation of metabolic processes in the upper layer of the epidermis.
Weakening of the body’s defenses. This can occur due to many reasons: with inflammation of the tonsils of a chronic course, against the background of caries, or with pyelonephritis. Often color deprive is a companion of tuberculosis. Moreover, the bacillus is able to parasitize not only in the tissue of the lungs, but also in the kidneys, the reproductive organs, bones, etc. Tuberculosis often has a latent course and is discovered by chance. Therefore, all patients diagnosed with lichen color should be tested for tuberculosis.
Living in countries with high humidity. A high prevalence of color lichen is observed in cities and towns with a tropical and subtropical climate. The incidence rate in them is 40%, while in residents of countries with a temperate climate it does not exceed 5-10%.
Presence of seborrhea.
Colored deprive can accompany such diseases as: AIDS, rheumatism and diabetes mellitus. If a patient has one or more of the listed pathologies, then the probability of developing color lichen in him is equal to 63%.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia. In addition to colored lichen, a person will suffer from weakness, frequent dizziness, panic attacks, etc.
Pathologies of the digestive and hepatobiliary systems always affect the condition of the skin. Violations in their work can be manifested by colored lichen.
Middle-aged people are at risk. Lichen colorus is extremely rarely diagnosed in children under 7 years of age, only if the child has a serious illness.
Diseases of the respiratory system can provoke the development of colored lichen. In this case, we are talking about asthma, pneumonia or chronic bronchitis.
Itsenko-Cushing’s syndrome and obesity.
Long-term topical or systemic treatment with corticosteroids.
Hormonal imbalance is another factor contributing to the onset of ringworm symptoms. As a rule, this happens in pregnant women, as well as in people suffering from pathologies of the adrenal glands and ovaries.
The next risk factor for the development of colored lichen is the use of shower gels that have an antibacterial effect. Of course, after a single use of such a remedy, the disease will not develop. However, if a person uses them on a regular basis, then the likelihood of this dermatomycosis increases significantly.
Chemotherapy, which cancer patients undergo, can provoke the development of a persistent form of color lichen. After completion of treatment, spontaneous self-healing is most often observed.
Color lichen symptoms
In those places where skin manifestations of the disease are observed, the number of corneocytes is exceeded three times. The change in the skin color of a person infected with lichen versicolor is also due to the fact that fungi colonize unevenly on the skin.
The primary place of occurrence of colored lichen is the mouth of the sebaceous hair follicles. Here, fungi, under the influence of provoking factors, begin to multiply, forming colonies. The fatty secret that the sebaceous glands produce, they use for their own nutrition. It contains all the fatty acids necessary for fungi.
The disease debuts with the appearance of yellowish dots on the skin, which are located near the mouths of the hair follicles. Then spots of pinkish-yellow color are formed around these points. As the disease progresses, they darken, turning brown. On their surface, bran-like scales appear. If you just look at the stain, then the peeling is almost imperceptible. However, it is worth scraping it off and the scales instantly move away. This symptom is called Besnier’s symptom.
So, the following symptoms will indicate color lichen:
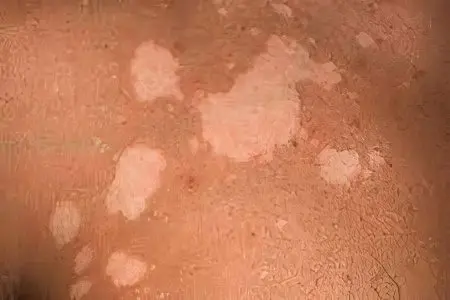
The spots that appear on the skin can have a different color: yellow, pink, brown. As the pathology progresses, they merge together, forming large foci with uneven contours. The initial spot size is equal to 3-5 cm in diameter.
The spots can make a person itchy. It is rarely intense.
If a person has been in the sun for a long time and got a tan, then the color of the spots will change. They become lighter and therefore more visible. In winter, the spots, on the contrary, darken. This feature of the course of the disease is also one of the reasons why this dermatomycosis is called color lichen.
A favorite place for the localization of the fungus are the shoulders, back, abdomen. Less commonly, spots occur on the neck and on the scalp. At the same time, a person does not lose hair on his head. They can only fall out on the body.
Although the pathology lends itself well to correction, sometimes it can bother a person for years, then calming down, then aggravating again.
As a rule, a person does not indicate any subjective symptoms. A burning sensation and pain in the affected area can be a signal of a secondary infection.
Depending on how deeply the dermis is affected and where exactly the spots are located, the following types of colored lichen are distinguished:
Erythematosquamous form. The spots are located in the upper body, there are no symptoms of inflammation.
follicular form. The spots are accompanied by the appearance of papules and pustules, which have an average size of 2-3 cm. This form of the disease is typical for people suffering from severe concomitant disorders.
inverted form. The spots are located in the folds of the human body.
Regardless of the form of the disease, its treatment is carried out according to the same scheme.
It is important to draw an analogy between the symptoms of color lichen and the symptoms of other diseases:
Gibert’s lichen is characterized by the appearance of pink oblong spots on the skin. In the center of these foci, the dermis peels off. The spots are located along the lines of Langer, they themselves are surrounded by a collar of scales.
Syphilitic roseola is characterized by pinkish spots on the skin, which, when pressed, discolor. Peeling of the dermis is not observed, the spots do not merge and do not grow.
Lichen colorus should be distinguished from vitiligo.
Sometimes color deprive has an atypical course. In this case, the spots are located on the skin of the soles. This form of the disease is difficult to treat, and after the elimination of the acute phase, brown spots remain on the feet, which have an irregular shape. They are located on the heels and on the transitional fold from the sole to the toes.
In people with AIDS, lichen color spots reach a size of 5 cm, while in a person with a normal immune system, their diameter rarely exceeds 1 cm.
Diagnostics

For an experienced dermatologist, an external examination of the patient is enough to suspect that he has color lichen.
However, to clarify the diagnosis, a number of tests will be required, including:
Microscopic examination of skin scrapings from spots. Under a microscope, the doctor examines the scales of the dermis, which are pre-treated with a 20% KOH solution. The fungi that cause lichen color will be represented by long threads, with rounded growths located on them.
Test using iodine. During the study, the skin is treated with a 5% iodine solution. After a few minutes, the spots of lichen color become dark brown.
Using Wood’s lamp for diagnosis. In the light of its rays, the spots acquire a reddish-yellow hue, or a greenish-golden color.
Check for Benye’s symptom, in which skin particles are easily exfoliated, even with a slight scraping.
This is a complete list of diagnostic methods to determine lichen color. In practice, doctors most often use only the iodine test and Wood’s llama.
Treatment of colored lichen
You should not treat lichen on your own. First you need to seek the advice of a specialist. Only a doctor will be able to make a correct diagnosis, for which he will need to carry out a series of diagnostic procedures. A dermatologist is engaged in the treatment of colored lichen. It begins in finding out the cause of the development of ringworm. As practice shows, color lichen is often a marker of AIDS, tuberculosis, rheumatism and diabetes. Therefore, the patient must be carefully examined.
General recommendations to be followed during the treatment of colored lichen are as follows:
In summer you should be in the sun more. Ultraviolet rays are detrimental to the fungus. Although discolored spots can remain on the dermis for several more months. This phenomenon is called pseudoleukoderma.
Ointments, creams and gels that have an antifungal effect must be applied to the affected areas of the skin. Treatment should last for 2 weeks.
When the scalp is affected, shampoos with an antifungal effect are used.
If color lichen is accompanied by the appearance of severe itching, then you should wash with running water without using soap. The temperature of the water should be comfortable, if it is too hot, then the itching will increase. After completing hygiene procedures, it is necessary to apply creams with a moisturizing component to the skin.
Antihistamines may be prescribed to reduce itching.
If the disease covers large areas of the body and is difficult to treat, then oral antifungal drugs are possible.
To prevent re-infection, every day in the room where the patient lives, wet cleaning with the use of disinfectant solutions should be performed. Bed linen is changed daily and washed at the highest temperatures. Clothes must be ironed carefully. The washcloth that the person used before the start of treatment must be disposed of.
After getting rid of colored lichen, a person should think about what exactly caused it. In the future, they should be avoided in order to prevent the recurrence of the disease.
General recommendations for the prevention of color lichen are as follows:
Strengthen immunity.
harden.
Eat right.
According to the doctor’s prescription, a second course of treatment with antifungal drugs is possible.
As far as possible, it is necessary to avoid stress, as well as to abandon increased physical activity, which contribute to increased sweating.
Be sure to maintain sufficient hygiene.
If you follow these simple recommendations, then you can forget about such a disease as color lichen forever.









