Contents
The accumulation of pus in the inner or outer surface of the alveoli of the upper or lower jaw, resulting from the introduction of an infection, is called a tooth abscess. According to medical statistics, most often this pathology is recorded during the off-season, that is, in autumn and spring.
Causes of an abscess
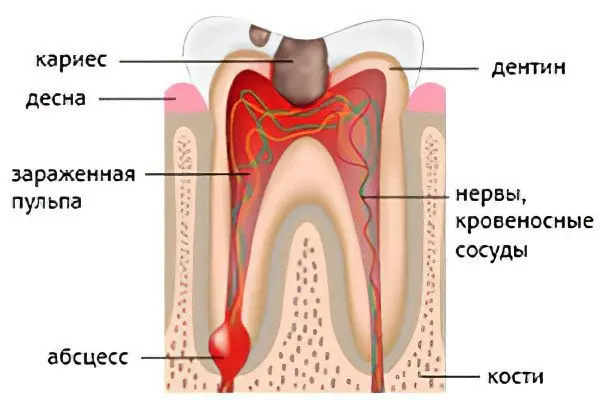
The disease develops as a result of the penetration of pathogenic bacteria through damaged enamel into the dental pulp.
Reasons for the development of purulent inflammation:
Diseases of the teeth and gums – caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, cyst;
Microtrauma of the gums and tongue;
Furuncles on the face;
Chipped or fractured tooth;
Complications of infectious and viral diseases (tonsillitis, influenza);
The ingress of bacteria during manipulations performed by the dentist, and violation of antiseptic rules by the doctor.
The development of an abscess is predisposed by insufficient observance of the rules of oral hygiene, excessive consumption of carbohydrates, lack of preventive examination by a doctor, and diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms and pathogenesis
Through damaged enamel or gum tissue, pathogenic microbes penetrate into the alveolar process. In the soft pulp of the tooth, they multiply, stimulating the formation of pus. If there is no way out for it, the inflammation spreads to the surrounding tissues – periodontitis, jaw bones, adjacent teeth.
Manifestations of a developing abscess:
Pain when pressing on the tooth, often occurs during meals;
Edema of the tissues of the gums, cheeks;
Throbbing pain outside of eating;
The appearance of a hyperemic seal in the affected area;
Increased temperature sensitivity;
The appearance of bad breath;
Increased regional lymph nodes;
Hyperthermia, feverish condition;
Violation of general well-being, restless sleep;
On visual inspection, you can see an open wound with purulent discharge.
The onset of the disease is associated with the appearance of a pronounced pain syndrome. With increased pain, edema and hyperemia of the gums develop, then the swelling spreads to the tissues of the cheek.
Classification
According to the stage of development of the inflammatory process:
The acute stage, or purulent abscess – in rare cases ends with a spontaneous opening of the focus of inflammation, the release of pus into the oral cavity;
Chronic stage – occurs after an independent resolution of the problem, is fraught with relapses, the formation of a purulent fistula.
According to the localization of the focus of inflammation:
Gingival abscess (flux) – the inflammatory process does not affect the tooth tissue;
Periapical abscess – occurs in a tooth with a dead pulp;
Periodontal abscess – develops in the periodontal canal in close proximity to the root.
The onset of a purulent abscess always proceeds with the development of swelling of the gums. Pain can join later, it is accompanied by swelling of the cheek tissues, swollen lymph nodes, headache. With the development of the inflammatory process, the tumor reaches the size of a walnut. At the same time, symptoms of intoxication increase – weakness, hyperthermia, deterioration in general well-being.
In the chronic form of an abscess that develops after spontaneous opening of the abscess, the pain becomes moderate, manifesting itself only when the tooth is pressed. The focus of infection remains, exposing the body to the risk of new relapses.
If an abscess appeared after surgical extraction of a tooth, the reason for this may be a violation of aseptic rules by the doctor, improper care of the open wound of the hole. Normally, a blood clot protects the wound from infection, stimulates the formation of granulation tissue.
If the patient did not follow the rules of hygiene, started eating hot or rough food early, he may develop symptoms of inflammation:
Incessant bleeding;
Strong pain;
Purulent plaque on the wound;
Bad breath.
These manifestations are a reason for urgent medical attention.
A periapical abscess that forms at the root of a tooth occurs as a result of the long existence of untreated carious teeth. The presence of an extensive network of blood vessels in the immediate vicinity of the focus of purulent inflammation increases the risk of infection spreading throughout the body. It is impossible to ignore the symptoms of this type of tooth abscess due to severe pain and the appearance of pronounced edema.
Often, an abscess occurs after the removal of a wisdom tooth, as sometimes it is necessary to divide it into fragments, while increasing the area of u2bu3bdamage to the gums. An extensive wound, abundant blood supply can provoke swelling, fever, slow wound healing. If after XNUMX-XNUMX days there is no relief, and the pain intensifies, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Flux, or gum abscess, does not affect the tooth tissue, affecting only the gum. However, if left untreated, the infection can spread to nearby structures, to the root of the tooth.
If an abscess occurs in a child on milk teeth, the germ of a permanent tooth under the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbinflammation may become infected. If the infection develops and penetrates into the tissues of the jaw, the risk of frequent tonsillitis and inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx increases. A constant focus of infection contributes to the formation of asthma, allergies. The decision to remove a tooth affected by an abscess is made by a pediatric dentist.
The frequent occurrence of tooth abscesses may be a sign that there is an untreated infection in the oral cavity. From there, it spreads through the tissues of the jaw and into adjacent teeth.
Complications of a tooth abscess and disease prognosis
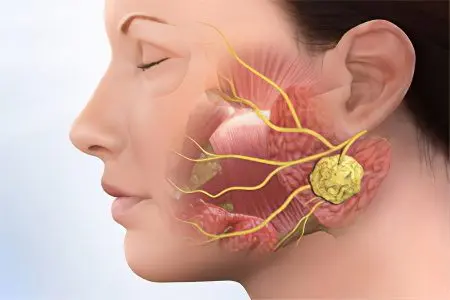
The consequences of the pathology are very serious, the delay in treatment causes the development of severe complications:
The appearance of a fistula;
The development of phlegmon – diffuse purulent inflammation of the tissue of the oral cavity;
Development of sepsis;
Increased risk of developing osteomyelitis, meningitis, pneumonia, diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Timely treatment under the guidance of an experienced doctor leads to a complete recovery.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, it is enough for a doctor to conduct a visual examination, supplemented by the patient’s complaints. The dentist fixes hyperemia and swelling of the gums, pain during mechanical action on the tooth, its sensitivity to high and low temperatures.
Laboratory and instrumental studies:
General blood analysis;
General urine analysis;
Microscopic examination of the puncture of the purulent contents of the abscess;
Bacteriological culture of discharge from the wound;
X-ray of the affected area;
Tomography of the maxillofacial area.
It is important to differentiate a tooth abscess from diseases with similar symptoms – phlegmon, gum tumor, purulent periostitis, tooth cyst, gum tissue hematoma.
Treatment of a tooth abscess
To treat a tooth abscess, you need to contact a dentist-surgeon. After evaluating the data of diagnostic studies, he will determine the tactics of treatment.
Possible options for medical manipulations and procedures:
Drainage of an abscess through an incision in the gum is performed in the absence of tooth damage;
Drainage of an abscess through drilling of the affected tooth, disinfection of the focus of inflammation, filling of the canal;
Extraction of a tooth with the ineffectiveness of other methods, with an extensive abscess, curettage of a purulent wound, aseptic treatment;
The use of antibacterial drugs to stop the inflammatory process and prevent relapses;
Local treatment in the form of rinsing with saline and soda solution;
The use of analgesics for pain relief.
The opening of the abscess is performed under general or local anesthesia.
After performing treatment procedures, a relapse of the disease may occur. Its symptoms are fever, hyperemia and swelling of the gum tissue, deterioration of the general condition. Relapse provokes alcohol abuse, smoking, overweight, hypertension, taking thrombolytics. The forecast provides for a long recovery period. The course of treatment includes taking antibiotics.
If an abscess occurs in a pregnant woman, antibacterial agents are used only when absolutely necessary to avoid their teratogenic effect on the fetus. Preference is given to topical products. Anesthesia is performed with drugs with a minimum content of vasoconstrictor components that slow down their absorption into the blood.
Medicinal products
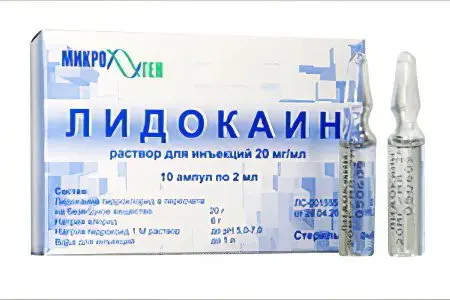
To treat a tooth abscess, anesthetics, antibacterial drugs, solutions for local treatment, vitamins, and immunomodulators are used.
To alleviate the patient’s condition and anesthetize manipulations, infiltration anesthesia is used when injections are performed in the gum tissue near the abscess.
Pain medications:
Lidocaine
Novocaine,
Ultracain,
scandalous,
Seventeen.
Ultracaine can be used during pregnancy, is contraindicated in allergies, heart failure, arterial hypertension. Septanest is not used in patients with myocardial infarction.
Antibiotics to relieve inflammation:
amoxicillin,
Metronidazole,
azithromycin,
clindamycin,
lincomycin,
Ciprofloxacin.
The dosage of drugs, the frequency of their use is determined by the doctor. To strengthen tooth enamel and prevent relapses, it is recommended to saturate the body with a sufficient amount of minerals and trace elements. It is better if vitamin-mineral complexes contain calcium and fluorine.
Physiotherapy
The combination of therapeutic methods with physiotherapy will accelerate tissue regeneration and shorten the recovery time.
Healing procedures:
Hypothermia with UV rays;
Fluctuorization (treatment with pulsed currents);
UHF;
Electrophoresis with antibiotics.
Author of the article: Muravitsky Boris Viktorovich, dentist, specially for the site ayzdorov.ru









