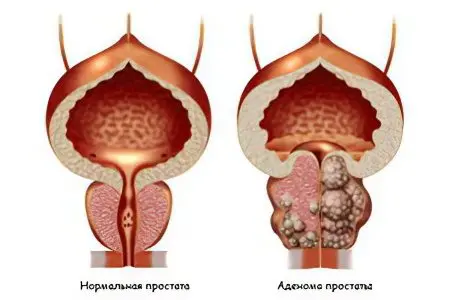
Prostate adenoma is a benign tumor arising from the stroma of the prostate or from the glandular epithelium. This disease is quite curable if it is diagnosed in a timely manner and treatment is started, using the recommendations of a doctor. Unfortunately, not all men take their health responsibly, and often they come to see a doctor with an advanced stage of the disease, the treatment of which is associated with great difficulties. Therefore, you should know the symptoms of pathology and the causes leading to its development.
Synonyms of the disease – prostate adenoma, benign prostatic hyperplasia. The prostate is an organ made up of lobules of glandular tissue and connective tissue, or stroma. The prostate produces a secret that supports the normal functioning of spermatozoa.
The dynamics of the development of prostate adenoma is disappointing. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, symptoms of prostate enlargement are rare before the age of 40, but already at the age of 51-60, almost 50% of men suffer from adenoma. After 80 years, it is present in 90% of older men. [1]
The incidence of adenoma depends on the race and nutritional habits of residents of different countries. Representatives of the Negroid race suffer from this disease more often than others, and residents of China and the Land of the Rising Sun are somewhat less likely due to food rich in phytosterols.
What are the causes of prostate adenoma in men?
The main cause of prostate adenoma (enlargement of the prostate) is low testosterone levels, and as a result, high estrogen levels. The closer the “male menopause” (the lower testosterone), the higher the risk of prostatic hyperplasia. Of primary importance is the neuroendocrine regulation of the activity of the prostate – a decrease in the production of testosterone, the main male hormone, and an increase in the concentration of estradiol. This hormone is able to stimulate increased reproduction of prostate cells.
[Video] Dr. Berg – PROSTATE ADENOMA: what is the real cause of an enlarged prostate?









