Contents
Swelling of the upper and lower eyelids is a very common problem because the skin of these eye protection barriers is very thin and delicate. Often it is the eyelids that are the first to give an alarm when pathological abnormalities occur.
What is eyelid edema?
Edema of the eyelids is a localized, localized excess accumulation of fluid in the eyelids. Only 1 eyelid can swell: lower or upper (in most cases). Sometimes it happens with 1 eye – unilateral edema. An attack can be single or recurrent. This deviation occurs in both the elderly and children, although it is predominantly adults over 30 years of age.
The eyelid is a skin fold behind which the eye “hides” in case of potential danger: a bright flash, dust ingress, the threat of traumatic injury, etc.
There are 2 layers of the eyelids:
superficial or anterior – musculocutaneous. The circular muscle consists of the orbital and palpebral parts. When it is reduced, flashing occurs;
deep or posterior – conjunctival-cartilaginous. The cartilages of the eyelids are plates of very dense connective tissue under the eye muscles. The conjunctiva of the eyelids is a transparent connective sheath that covers the posterior surface of the eyelids.
The human body is 70% fluid, most of which is in the cells, and the rest is in the intercellular space. As soon as the water content between the cells exceeds the threshold value of 1/3 of the total volume, edema appears.
Types of edema depending on the causes:
hydrostatic;
hypoproteinemic;
membranogenic.
Eyelid edema is diagnosed visually. To identify their causes, blood tests may be additionally prescribed to determine the concentration of proteins in the serum, especially albumin, a urine test to rule out kidney disease. If this is not enough, you can use the results of ultrasound or computed tomography.
The swelling usually subsides after a while, but in some cases it can progress. Most often this happens if there is any deviation. Not only the area around the eyes, but also various parts of the body can swell.
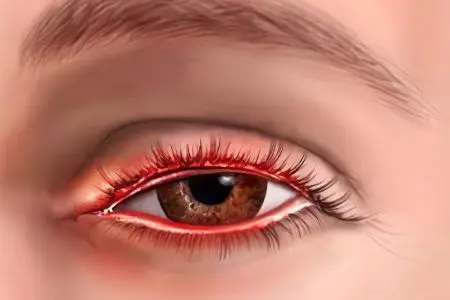
If left untreated, complications may occur:
swelling of the eyeball (Vickers);
increased intraocular pressure;
fever;
elephantiasis or elephantiasis – elephantiasis, elephantiasis;
glaucoma, which causes visual field defects, decreased vision and atrophy of the optic nerve;
blindness.
Preventive measures that prevent the appearance of edema include:
timely treatment of inflammatory diseases;
a healthy lifestyle with proper diet and physical education, hardening, getting rid of bad habits;
good rest;
the use of table salt and liquid in volumes corresponding to the state of health;
compliance with safety regulations when working in hazardous production, including wearing special eye protection;
taking antihistamines for allergy sufferers during potentially dangerous periods;
avoiding contact with infectious patients (especially eye diseases).
Stopping the inflammatory process, maintaining a normal metabolism, observing reasonable care, you can save yourself from many health problems. People who follow simple precautions, with attention to their well-being, never have to deal with swelling of any part of the face.
Eyelid swelling symptoms
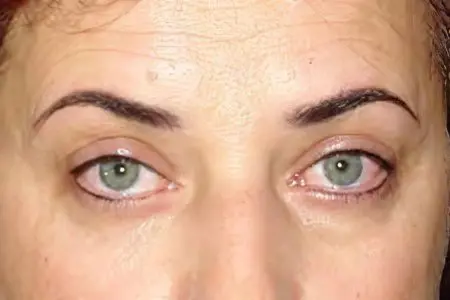
redness – hyperemia, cyanosis or pallor of the skin;
the skin is tight and tense;
thinning of the skin with increased luster of its surface;
tortuous and dilated saphenous veins;
punctate rash – abnormal pathological elements on the skin;
swelling, enlargement of the eyelids;
narrowing or complete closure of the palpebral fissure;
pain on palpation – “palpation”;
inflammation and soreness of regional lymph nodes located in front of the auricle, under the parotid fascia, on the face;
density of surrounding tissues;
itching is an unpleasant sensation of irritation, burning or stinging in the eyes.
Redness is caused by excess blood flow. This is due to the expansion of the arteries or difficulty in the outflow of blood into the veins. Venous congestion is accompanied by a significant increase in the release of the liquid part of the blood – plasma – into the tissue gaps – transudation.
Transudate – accumulated edematous fluid. Congestive or passive hyperemia causes pathological expansion of veins and capillaries, as well as slowing of blood flow. Swelling of blood vessels leads to a local increase in the affected area of the body, due to which the skin is stretched.
The blood supply to the eyelids is carried out by the lateral branches of the lacrimal and medial branches of the anterior ethmoid arteries. The outflow occurs through the veins of the same name to the face and eye sockets. The lymphatic system of the eyelids is located on the sides of the cartilaginous plate. Lymph drainage occurs from the upper eyelid to the anterior, and from the lower eyelid to the submandibular lymph node.
Features of the skin of the eyelids – good turgor or swelling. This is the pressure of the contents of the cells on their walls. That is why this area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe skin is so sensitive. Intracellular pressure is high and edema appears rather quickly.
palpebral fissure or eyelid slit – an almond-shaped opening between the edges of the eyelids. There are many diseases that lead to its decrease, and, consequently, the deterioration of the review.
Bluish skin also becomes with venous congestion. In the tissues, oxygen starvation begins – hypoxia, the blood darkens, more translucent through thin skin, hence the blue.
Pain on pressure – a protective property of the body, indicating a deviation from the norm. It informs about the development of the pathological condition. The innervation of the eyelids is carried out by the first and second branches of the trigeminal nerve, facial and sympathetic nerves. Interestingly, pain and swelling in the eye area may indicate a cluster headache.
By its nature, edema of the eyelids is referred to as a tissue type. It occurs in the subcutaneous tissue (a type of fatty tissue). Rapidly progressive swelling compresses the underlying parts of the body, which causes their dysfunction.
The symptoms of extravasation are quite wide, although most often a person does not experience any discomfort. If edema is a sign of an illness, then it will be accompanied by other symptoms. In the case of frequently recurring seizures without apparent reason, a specialist consultation is required.
Why are eyelids swollen?

Causes of edema of the eyelids can be divided into 3 groups:
excess pressure in the thinnest blood vessel – the capillary;
a decrease in the level of proteins (especially albumins) and colloid-osmotic (oncotic) blood plasma pressure with the release of water from blood vessels into adjacent tissues;
an increase in capillary permeability that occurs after toxic damage, the onset of inflammation, and failures in nervous regulation.
These phenomena can be triggered by factors such as:
diseases: pseudomembranous, membranous or purulent conjunctivitis, endophthalmitis, erysipelas, iridocyclitis, ascites or abdominal dropsy – swelling of the peritoneal cavity, pseudotumor, phlegmon, blepharitis, eyelid abscess, barley caused by staphylococcus bacteria, dermatitis, SARS, acute respiratory infections, influenza, tonsillitis, allergies angioedema angioedema, vegetovascular dystonia, anemia, dacryocystitis, cancer, meibomitis, eyelid hernia, ophthalmic rosacea or rosacea, chalazion – tumor-like inflammation of the meibomian gland inside the eyelid, sinusitis, demodicosis caused by ciliary mites, hypothyroidism, keratitis – inflammation of the cornea, subcutaneous emphysema, helminthic infestations, for example, trichinosis;
unhealthy lifestyle leading to protein deficiency, lack of sleep, stress, eye strain, including late eating, including excess salt, drinking too much fluid, smoking and alcohol abuse;
Incorrect position of the head during sleep (it is better to sleep on a flat and small pillow);
Long-term ultraviolet radiation;
Hormonal disruptions, for example, during the premenstrual period;
Insect bites (more often in summer);
Injuries with extensive subcutaneous hemorrhage – a bruise;
Microtrauma while wearing contact lenses. ;
Venous congestion, for example, during sleep;
Violation of lymphatic flow and water-electrolyte balance;
Drug treatment (taking salicylates, sulfonamides and antibiotics);
Exposure to allergens: citrus fruits, seafood, strawberries, milk, chocolate, eggs, pollen, drugs, chemicals (paints, varnishes, household chemicals), wool or dust;
Increased intracranial pressure;
Congenital disorders of the structure of the eyelids;
Permanent make-up.
First of all, swelling is provoked by diseases that cause dysfunction of organs that respond to the “processing” of the incoming fluid and its excretion. These are pathologies of the digestive, excretory, circulatory systems.
Any eye disease is very dangerous. Among them, blepharitis can be noted. In addition to swelling, its symptoms are sores, loss of eyelashes and even eversion of the eyelids. The value of the eyes is difficult to overestimate. Blindness is a diagnosis that turns one into a disabled person.
Allergy can be of 2 types: acquired anaphylaxis or congenital atopy. Quincke’s edema affects the gastrointestinal tract and skin. More often occurs in children. It is dangerous because it instantly spreads to the corner of the mouth, cheek, temple and neck, covers half of the face. Allergic dermatitis can occur due to prolonged use of eye ointments, drops or cosmetics.
Salt retains water in the body. This happens as follows: sodium chloride, or rather, such a component of this chemical compound as sodium, contributes to the swelling of tissue colloids due to the “absorption” of liquid.
There are many reasons why swelling can begin. Their identification is the primary task of the doctor, because. the only way to avoid complications is to eliminate etiological factors.
Edema after eyelid tattoo
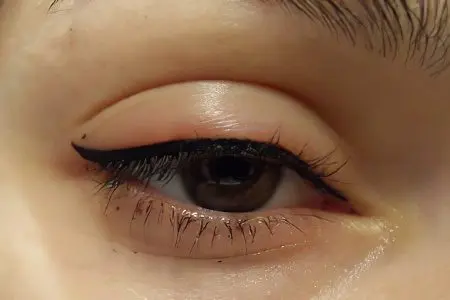
Tattooing – tattoo, microinjections, in other words, injections with permanent staining. In this case, the skin integuments are injured, because their integrity is violated. Natural or inorganic colored pigments are injected into the subcutaneous tissue.
Traditionally, cosmetics are applied to the surface of the skin, but then it is not possible to obtain such a lasting effect. Over time, the colors fade and disappear. Permanent makeup is permanent. This does not mean that it does not need to be refreshed at all. Cells are continuously updated, coloring substances are gradually removed from the body.
Crusts and swelling appear on the tattooed area of the skin. This is an open wound, traumatic eyelid edema. Until complete healing, wounded skin is defenseless against infection. It is necessary to treat injured eyelids with special antibacterial and wound healing agents.
For several days these places should not be wetted. The swelling persists for a couple of days. It appears due to damage to blood vessels at the level of the superficial or deep choroid plexus.
The severity of eyelid edema depends on the following factors:
individual tendency to swelling;
depth and quality of pigment introduction;
skin type;
method of anesthesia.
A tattoo or tattoo on the eyelids is applied with a special thinnest needle. There are contraindications, so if before the start of staining the specialist did not take an interest in the state of health of the customer, he does not have the necessary level of qualification. The beauty salon is required to have an appropriate license for this procedure and hygiene certificates for the equipment used. Tools must be sterile, materials must be safe for health.
Any tattoo is painful, so local anesthesia is required. Special drops are instilled into the eyes. At the same time, unpleasant sensations may appear: the eye becomes as if glassy, frozen, the movements of the eyeballs are difficult. There were cases of burns of the cornea with low-quality drugs. Patients even had to urgently consult a doctor.
Depending on the chosen option, the paint is applied dotted between the cilia – interlash, strokes or lines above and below the eyelashes on each eyelid. The arrows in the corners visually change the shape and size of the palpebral fissure. If the client is not satisfied with the final result, she can insist on correction or removal of pigments in the skin.
The mistake of the master may be the wrong shape of the tattoo, too deep introduction of the coloring matter. Laser technologies allow to make corrections. The laser removes the pigment through the skin.
Women are attracted by tattooing because makeup will remain bright at any time of the day. In front of the eyes, or rather, the upper and lower eyelids, they make eyeliners and arrows. This takes approximately 3 hours. Tissue healing can take several weeks. Whether it is worth exposing the most delicate skin of the eyelids to such a harsh cosmetic procedure, everyone decides for himself. The cosmetologist is obliged to warn clients about all possible consequences.
Edema of the eyelids in the morning

The liquid slowly fills the intercellular space at night, while a person sleeps or is forced to stay in a horizontal position for a long time. The rate of blood flow during the rest period is significantly reduced. During the day, such swelling usually resolves itself.
Puffy eyes do not paint anyone. Most of all because of them women complex. Swollen eyelids cannot be hidden with any makeup. Most often, morning swelling is a symptom of a disease of the genitourinary system. Sometimes a person does not recognize himself in the mirror after waking up, if he ate pickles for the night, drank a lot of alcohol the day before, or decided to try out a new cosmetic product in the evening.
Kidney diseases do not allow the urinary system to fully function. In a healthy state, the kidneys pass through themselves about 2000 liters of blood per day, thereby ensuring the water-salt balance of the body. The excretory function is to remove excess fluid and not only. When it is violated, excess water is released, “squeezed out” from tissue cells as a result of an increase in intracellular pressure. So there is an overflow of intercellular space.
The edematous fluid is usually colorless, transparent, sometimes may have a pale yellow tint. Turbid solution becomes due to the admixture of lymphocytes, fat. About 3% of the transudate are serum proteins – albumins and globulins. The fluid is easily infected.
Cardiovascular diseases also interfere with the outflow of blood from the tissues. Puffy eyes may indicate a disturbance in normal blood flow. Mucoid swelling may develop – mucoid edema. As a result of a failure in the cell walls, the concentration of hydrophilic, “water-loving” substances that attract fluid, provoking swelling, is exceeded.
Frequently repeated attacks lead to dystrophy and atrophy of parenchymal cells, sclerosis. Violation of metabolism – metabolism – in the parenchyma is fraught with tissue damage, a pathological decrease in cell size, their “shrinkage”. Sclerosis leads to the replacement of parenchymal tissues with seals.
Catabolism occurs as follows: proteins, amino acids and fats are gradually broken down into water and carbon dioxide. In the process of such oxidation, the energy necessary for the body, as well as eicosanoids, is released. Lipids are hydrophobic compounds, energy depots, they are “convenient” for the body to store water reserves. The fact is that the liquid consumed by a person is sometimes not enough for the specific chemical reactions that are necessary for the normal functioning of organs.
Eicosanoids – derivatives of fatty acids that regulate the excretion of water by the kidneys and not only. These are highly active regulators of cellular functions. To a large extent, due to their action, tissue swelling occurs. The slightest violation of metabolic processes leads to an imbalance of fluid in the body.
Getting rid of diseases of the kidneys, heart, reasonable caution in eating and using cosmetics before bed will help to look attractive from the very beginning of the day. If the eyes swell every day, regardless of what was eaten, drunk or applied to the skin the night before, then the person suffers from some kind of ailment.
What to do if the eyelids swell?

The main thing is to establish the cause, and then eliminate it. If this is an allergic reaction, then the swelling will go away as soon as the action of the allergen ends. If it is a symptom of the disease – after recovery, a consequence of a bite or mechanical damage – after the wound has healed, the result of a physical defect in the eye area – after surgery. In any case, the resorption process can be tried to facilitate and speed up.
Ways to treat swelling of the eyes:
Medication with eye drops and ointments (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone, Celestoderm), gels and drops (Vizin) with steroid substances and / or plant extracts, antihistamines (Opatanol, Lecrolin, Cromohexal, Suprastin, Tavegil, Claritin, Zirtek), desensitizing anti-allergy drugs orally and / or externally, 15-minute lotions with a 2% solution of boric acid, taking diuretics to speed up the removal of excess fluid. In case of infection, ophthalmologists recommend instilling a 30% solution of sodium sulfacyl sodium into the affected eye 5-6 times a day and injecting antibiotics intramuscularly.
Physiotherapy. First of all, microcurrent therapy or microcurrents is electrical stimulation, in which the subcutaneous lymphatic pathways are stimulated using thin electrodes with pulses of low-frequency electric current. This is a massage at the cellular level.
Mesotherapy – microinjections with specific active substances.
Cosmetics: masks, sticks, creams, lotions, serums.
Various types of massage: manual, hardware vacuum-roller – dermatonia. The purpose of the procedures is lymphatic drainage – the removal of excess fluid to stabilize the lymphatic system.
An extreme measure is a plastic lift of the outer part of the upper eyelid in case of its sagging – blepharoplasty.
The goal of the therapeutic course is to relieve inflammation, improve blood circulation and excretory processes, and stimulate metabolism. Some physiotherapeutic and cosmetic procedures have contraindications.
Mask for eyelids from edema

Facial skin care products can be made independently or you can use ready-made formulations by purchasing them in stores, pharmacies or specialized organizations. The procedure is carried out at home or in a beauty salon.
Before applying a homemade mask, it is advisable to conduct a simple anti-allergy test. A small amount of the product is applied to the inner bend of the elbow. Wait half an hour. Check for redness on the treated area, for a rash.
Recipes for homemade eye masks:
Grind parsley, mix with sour cream in a ratio of 1 to 2, make lotions for 7-10 minutes. Parsley improves blood microcirculation, and sour cream nourishes the skin.
Grate carrots or parsley root, apply to the eyes for 15 minutes.
Make lotions from black / green tea or tea leaves, as well as from a strong decoction of chamomile flowers for 10-15 minutes.
Apply compresses from chilled decoctions of sage, calendula, dill, thyme, Ivan-tea (fireweed), mint, linden, fennel or cold milk for 10 minutes.
Ten-minute mask of grated raw potato, apple or cucumber. You can apply to the eyes and warm crushed boiled potatoes. A very pleasant mask-cream from the pulp of pumpkin and cucumber with honey.
Conclusion
Some diseases, for example, furunculosis, barley, in the absence of therapeutic measures, provoke the development of other pathologies, accompanied by edema of varying severity. This indicates the need to seek help from a doctor in a timely manner and not to start even “trifle” diseases.
Unexplained swelling of the eyelids is a serious reason for visiting an ophthalmologist. We must not forget that constantly recurring attacks can contribute to a hereditary predisposition to edema in descendants.









