Contents
Perennial plants always attract the attention of gardeners. Especially appreciated are those that not only have a beautiful appearance, but can also be used for other purposes, for example, in cooking. One of these plants is Variegata mint, which combines both decorative and culinary, as well as medicinal properties.
Description of mint Variegata
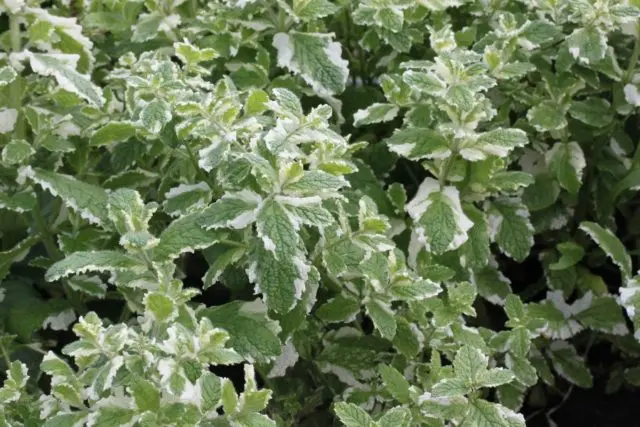
Mint Variegata is a common garden plant grown mainly for culinary and medicinal purposes.

Its main characteristics are given in the table:
Parameter | Value |
Synonyms | Flavored mint Variegata, pineapple mint, ginger mint Variegata |
Type of plant | perennial herbaceous |
Stem | Hard, straight, green, grows up to 0,4-0,5 m |
Leaves | Green, with a light beige edging, lowered down. The sheet plate is soft, strongly corrugated, with a wavy uneven edge |
Flowers | Small, white, collected in spike-shaped inflorescences at the tops of the stems |
Flowering period | July August |
Root | Branched, tree-like, superficially horizontal, with a small lobe of adventitious roots |
The use of mint Variegata in cooking
Cooking is one of the main areas of application of Variegata mint, in addition to medicine and cosmetology. The leaves of this plant are widely used as a dietary supplement. Moreover, for culinary purposes, they are used both fresh and dried.
What is the flavor of Mint Variegata?
Mint leaves Variegata contain a large amount of aromatic substances. They give the plant a characteristic pleasant aroma and a pronounced refreshing menthol flavor.
Where can I add mint Variegata
In cooking, Variegata mint leaves are used as a flavoring agent in the preparation of various meat and fish dishes, it is added to alcohol, tea and soft drinks. It is included in the recipes of a large number of jams, compotes, mousses, fruit drinks. Fresh mint leaves Variegata decorate various dishes and glasses with drinks. Often the leaves are used as spices in the preservation of various vegetables and fruits.

A short video about the use of mint in everyday life:
Rules of landing
There is nothing difficult in growing mint Variegata. It grows well on moist, loose, fertile soils; heavy clay areas are not suitable for it. It is preferable to plant it in well-lit places, especially if the planting is done in order to decorate the backyard. Mint Variegata also grows well in the shade, but the light border on the leaves, which gives the plant a decorative look, fades greatly in low light conditions.

It is better to prepare the beds for sowing in the fall by digging them with the addition of compost. The best time for planting Variegata mint in open ground is the second half of spring, when the temperature at night no longer drops below + 5 ° C. Before planting, the seeds must be rejected, selecting the largest and densest for planting, and disinfected in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 25-30 minutes. Then they are rinsed with clean water and dried in the air.

Planting the mint variegata is very easy. Seeds are laid out on the surface of the soil at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other and slightly sunk into the ground. Then the bed is watered and covered with plastic wrap until the first shoots appear. If the weather is warm outside, then it is not necessary to close the crops.
Peculiarities of growing
In order for the mint Variegata to grow well, it requires some care. During the season, the following events are held:
- watering;
- weeding;
- loosening the soil.
In dry weather, beds with growing mint Variegata must be watered daily. This should be done in the evening so that the bright rays of the sun, concentrated by drops of water, do not burn the foliage of plants. Water should be warm and settled, so you need to collect it in containers in advance. If the weather is cloudy and cool, the frequency of watering should be reduced and guided by soil moisture and natural precipitation.

It is imperative to remove weeds from the bed with mint. They not only shade the plants, preventing the process of photosynthesis, but also absorb nutrients from the soil in large quantities, which inhibits the growth of cultivated plants. Simultaneously with the destruction of weeds, loosening of the soil is also carried out, but this must be done very carefully. The roots of mint Variegata are horizontal and close to the surface.
If the weather conditions allow growing Variegata mint in a long-term cycle, then the plants must be covered for the winter, this is especially important in the first year after planting. It is best to do this in several layers: first, sprinkle the root zone with fallen leaves, then put spruce branches, and with the onset of winter, build an additional snow blanket.
Pests and diseases
With proper crop rotation of the disease, pests are quite rare on Variegata mint. Problems arise with violations in care, as well as in case of adverse weather conditions. Here are the main diseases of mint Variegata:
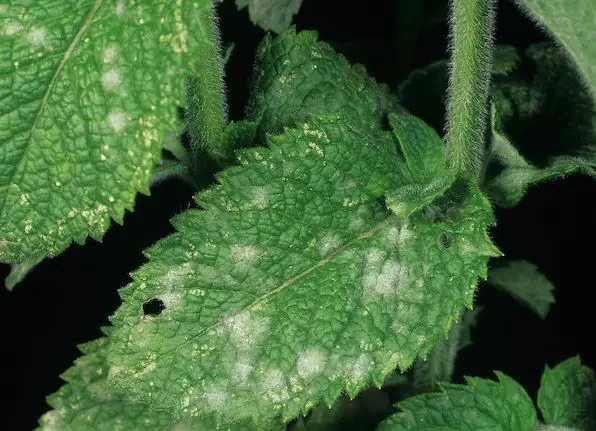
- Powdery mildew. One of the most common fungal diseases affecting various garden crops. It often manifests itself with a sharp change in weather, a decrease in air temperature and in conditions of high humidity. Outwardly, it looks like a white powdery coating on the leaves, which then turn black and die off very quickly. For the prevention of powdery mildew disease, it is recommended to carry out deep plowing of the beds in the fall, and during the growing season to treat the plantations with ground sulfur or its colloidal solution.

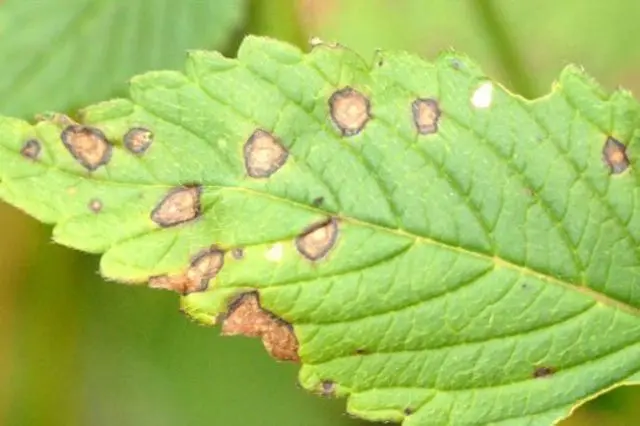
- Anthracnose. A fungal disease that manifests itself in the form of brown spots on the leaves. To prevent disease, plants are treated several times during the season with a solution of Bordeaux liquid 1%.

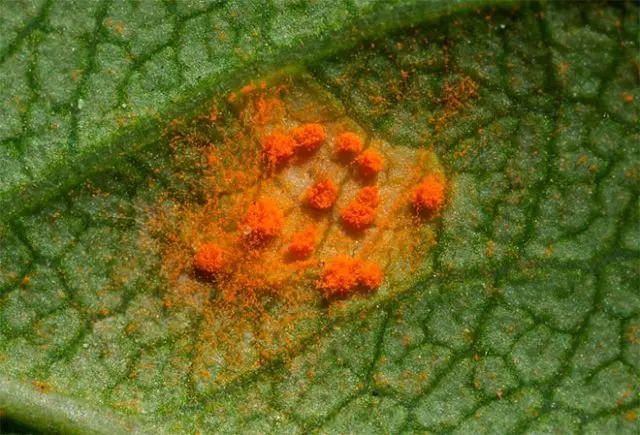
- Rust. This fungal disease often manifests itself at low temperatures and high ambient humidity. Risk factors for rust are also an excess of soil nitrogen and the cultivation of mint in a perennial cycle. In the leaves affected by the disease, spore pads of a characteristic reddish-brown color appear on the reverse side, over time they grow, the leaves turn black and die. They fight rust with the help of preventive treatments of plantings with fungicides.

- Verticillium wilt, or wilt. A dangerous disease that causes the death of a mint bush. The plant affected by the disease begins to dry out from above, while the tip withers, and the leaves curl, turn black and die. It is not possible to cure wilt with modern means. The affected plant is dug up and burned. Re-planting mint in such a plot is allowed no earlier than after 9-10 years.

No less dangerous for mint Variegata are insect pests. In this case, all parts of the plant, both aboveground and in the soil, can suffer. Here are the most dangerous mint pests Variegata:
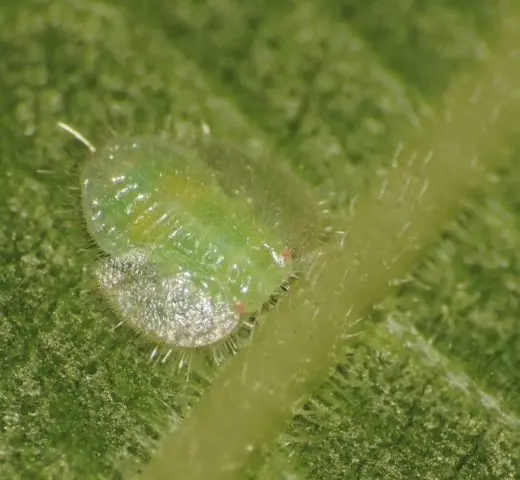
- Mint mite. It is found mainly in the southern regions. It feeds on the juice of the apical shoots. To combat the mint mite, various acaricides are used, and at the end of the season, the soil on the site is deeply plowed. If these insects are found, it is recommended not to plant Variegata mint in this place for the next 3 years.

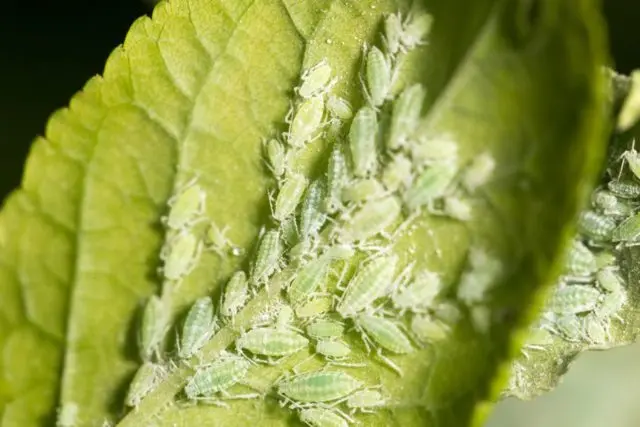
- Aphid ordinary. A microscopic sucking insect that feeds on plant sap. Aphid colonies are located mainly on the stems and on the reverse side of the leaf blades. If there are few insects, sometimes they can be washed off with plain water. As folk remedies against aphids, you can use an infusion of ash, hot pepper or tobacco dust. This is not always justified, since the products used can greatly spoil the taste of mint leaves.

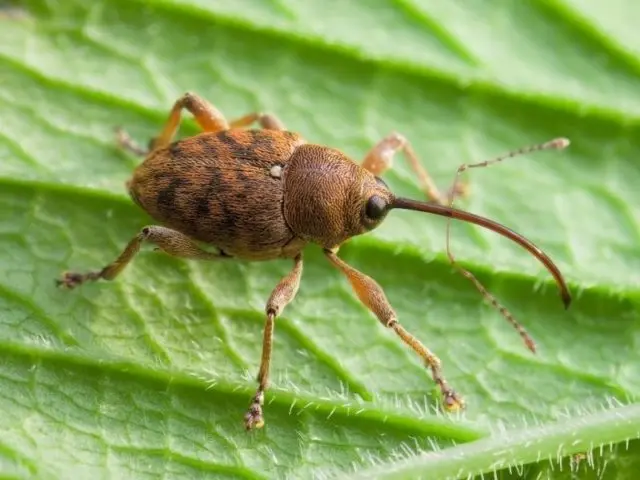
- Long-nosed. Adults feed on the young greens of the plant. They are best collected by hand or shaken on a cloth or newspaper. Weevil populations are rarely significant, and they do not appear every year.

- Wireworm. The pest is a larva of the click beetle and is a worm a few centimeters long with a dark head and a hard body that is light yellow or light orange in color. The wireworm feeds on the roots of plants, gnawing long winding passages in them and nibbling the tips. If this pest is present, it is better to change the area for planting mint.

When and how to harvest Variegata mint
You can start harvesting Variegata mint from mid-July. At this time, inflorescences appear in the bushes, and a sufficient amount of aromatic substances has already been accumulated in the leaves. For harvesting for future use, the bushes are cut off entirely. They are washed under clean running water, dried and tied into bundles. At the same time, culling is carried out, removing damaged or blackened leaves.

How to dry mint Variegata
Dried bundles of bound mint Variegata are hung in the attic of the house, on the veranda or terrace. It is better if they are not exposed to direct sunlight, this negatively affects the aroma. The degree of dryness of Variegata mint can be determined by the characteristic rustling of the leaves. If they become brittle and easily break off from the stem, then drying can be stopped. Store dry mint in hermetically sealed earthenware or glassware. It is allowed to use clean canvas bags for storage, but keep them away from other strong-smelling substances.

Conclusion
Mint Variegata is a beautiful ornamental plant that combines many useful properties. Planting it is quite simple, it takes very little space for it in the beds, and care is not difficult. It can be grown both in an annual and in a multi-year cycle, while the measures to prepare the plant for winter will not take much time and money.