Contents
Excess moisture in the area of a country house can cause many problems. Persistent dirt, crumbling foundations, flooded basements, and crop disease are all the result of high humidity. Drainage of the site, made in accordance with all the rules, will help get rid of excess water and protect buildings from destruction.

When to Drain
Puddles on the site after rain and snow melting is not yet a reason to make a drainage system. It is necessary to understand when the soil itself is able to absorb water, and when it needs help. A drainage device on the site is necessary in the following cases:
- permanently flooded basement;
- soil leaching, as evidenced by dips on the surface of the site;
- with clay soils, resulting in swamping of the territory;
- if there is a slope nearby from which water flows;
- the site does not have a slope;
- heaving of the soil, which leads to the appearance of cracks in buildings, skewed door and window openings.
Varieties of drainage systems
Before making drainage on the site, it is necessary to determine the type of drainage system. There are two main drainage systems that perform the same function, but are used in different situations:
- Superficial – designed to drain water that appeared after rains or melting snow.
- Deep – is arranged in areas with a high level of deep waters.
The surface drainage system is mainly arranged on clay soils and is divided into linear and point. Linear is a system of ditches and trays located with a slight slope to the place of water collection. To give an aesthetic appearance to the drainage system, the trays are closed with decorative gratings.
In a point drainage system, water is collected by water collectors located in places of the greatest accumulation of moisture – under the stack of downpipes, low areas of the site, near the water supply located on the street. The water collectors are interconnected by pipes through which water is discharged into a drainage well.
Surface drainage construction
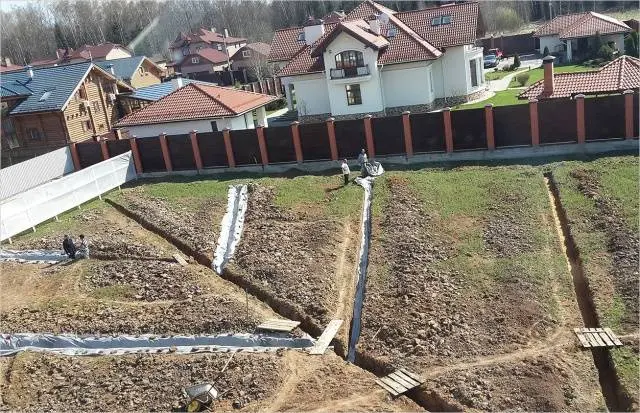
Do-it-yourself surface linear drainage on clay soils must be started after drawing up a plan that indicates the location and dimensions of trenches and other elements of the drainage system.
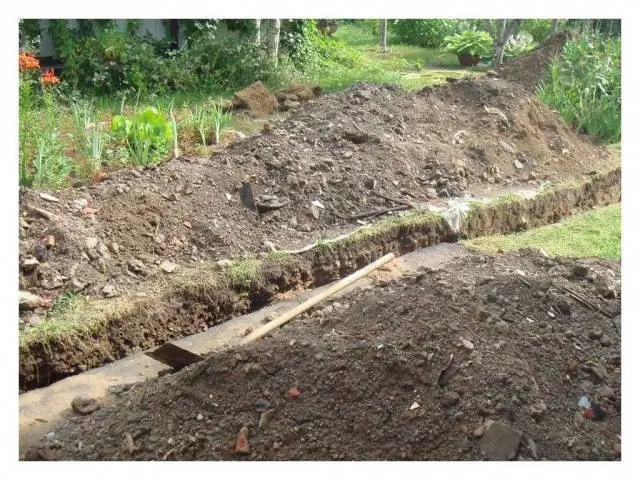

According to this plan, trenches are dug 0,7 m deep, 0,5 m wide and 30 degrees inclination of the walls, which will prevent them from crumbling. All trenches are connected to one common one, which runs along the perimeter of the site and ends with a drainage well. The main advantage of the open drainage method is the simplicity of the system, which does not require large financial costs. Among the shortcomings, the fragility of the structure can be noted – over time, unreinforced walls crumble, and the drainage system ceases to function. In addition, the trenches have an unaesthetic appearance, which spoils the appearance of the site.
The problem of shedding can be solved by backfilling with crushed stone. The bottom of the trench is covered with a layer of stone of a large fraction, and on top of it a smaller one. To avoid blurring, crushed stone backfill is covered with geotextile, on top of which a layer of turf is laid. This method impairs the throughput of surface linear drainage, but prevents shedding of the walls, which significantly increases the service life of the system.
There is a more modern way of arranging linear drainage – a closed drainage system. The difference of this method lies in the fact that the walls and bottom of the ditch are concreted and special trays are laid inside, closed with decorative gratings. Trays reliably protect the soil from slipping, and gratings protect the channel from debris. The trays are laid with a slope necessary for the unhindered passage of water. In places where water is discharged, sand traps are installed to collect small debris. It is more difficult to make such a drainage system than a trayless one, but its service life is much longer.
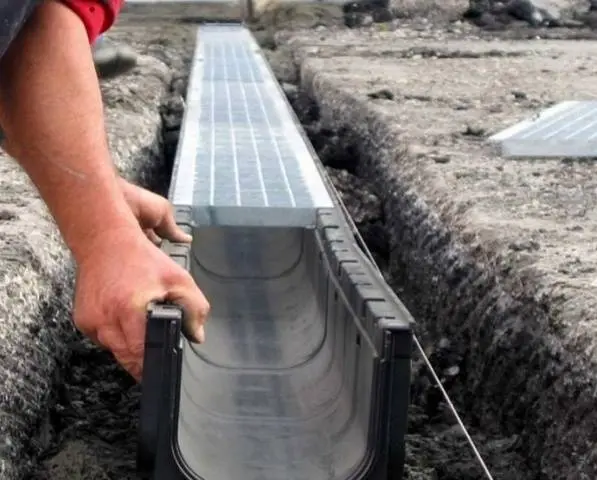

On sale there is a wide choice of accessories for the closed drainage system made of various materials: concrete, polymer concrete, plastic. The latter is the most popular due to its durability and light weight, which ensures maximum ease of installation.
Deep drainage device
The deep drainage system differs significantly from the surface one not only in its design, but also in its purpose. You can’t do without it in areas with a high level of groundwater and located in a lowland. For the effective operation of such a system, it is necessary that it be located below the aquifer. Determining the depth on your own is quite a difficult task – this will require the help of a surveyor, who will draw up a detailed diagram of the site with all groundwater levels.
The design of the deep system is a network of drainage pipes located in the ground and diverting excess water from the soil into a drainage well. Moisture seepage inside occurs due to the many holes located along the entire length of the pipe. Holes can be made with your own hands or you can buy products with finished perforations. For deep drainage, the following types of pipes are used:
- asbestos-cement – obsolete material, gradually becoming a thing of the past;
- ceramic – have a long service life and high price;
- plastic – by far the most popular because of their cheapness and ease of working with them.
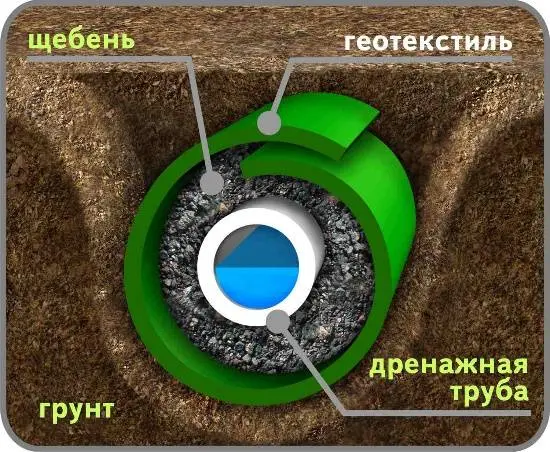
The sequence of laying deep drainage:
- Using a geodetic level, mark the site. If this is not available, then during rain, follow the direction of water flows and, according to observations, draw up a plan for the location of drainage channels.
- According to the plan, dig a system of trenches. To check the correctness of their location, wait for rain and make sure that the water does not stagnate anywhere. After making sure that everything is done correctly, you can continue to work.
- Lay geotextile tape along the entire length of the trench bottom.
- Observing the slope, pour a layer of crushed stone on top of the geotextile.
- Lay drainage pipes on top of the crushed stone pillow. The connection of individual pipes into a single system is carried out using tees, crosses and manholes.
- The end of the pipe, located at the lowest point of the site, is led into a drainage well.
- Cover the sides and top of the drainage pipe with a layer of crushed stone. Do not use crushed limestone for backfilling. As a result of exposure to moisture, it turns into a monolithic composition through which moisture cannot seep through.
- Wrap the pipe together with a layer of crushed stone in a geotextile tape – this will prevent clay and sand from getting inside the structure.
- Cover with rubble or coarse sand 20 cm below ground level.
- The remaining space is covered with soil located on the site.

To control the operation of the drainage system and clean it in case of clogging, it is necessary to install manholes at a distance of 35-50 m. If the system has many bends, then through one turn. Wells are constructed from reinforced concrete rings or polymeric corrugated pipes of the required diameter and are closed with decorative covers.
Properly designed and laid according to all requirements, a deep drainage system can last more than half a century.
Maintenance of the drainage system
In order for the soil drainage system to function for a long time and properly, it requires regular maintenance:
- Routine maintenance involves periodic cleaning of wells. The frequency of this procedure depends on the conditions in which the system is operated.
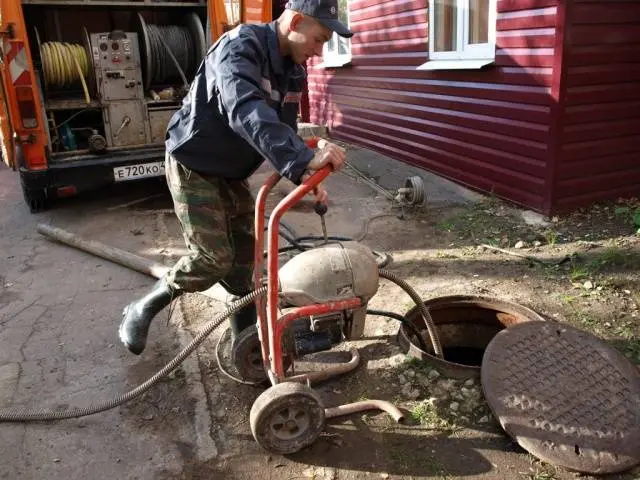
- Mechanical drain cleaning. Cleaning the surface drainage system is not particularly difficult and can be done independently. In the case of deep drainage, the situation is more complicated – a special pneumatic installation is required, which has nozzles for removing deposits and crushing large elements. Such cleaning is recommended to be done once every 1 years.
- Hydrodynamic cleaning of drainage. This method consists in flushing pipes with a mixture of air and water supplied under pressure. The mixture is fed alternately first to one end of the pipe, located in the drainage well, then the second, which is brought to the surface at the stage of installation of the drainage system. Flushing is carried out by a pump and a compressor supplying air under high pressure. Under the action of the mixture, the deposits are crushed and washed out. The frequency of hydrodynamic cleaning is 1 time in 10 years.

Savings on cleaning can lead to system malfunction and the need to replace some elements, which will ultimately lead to additional costs for materials and work. Proper operation will help keep the system in working order and extend its life.










