Contents
The styloid process is a specific fragment found in three bones of the human body. It is an anatomical part of the radius bone, temporal bone and ulna. These structures are exposed to mechanical injuries and various disease states. Below we present the most important information about the anatomy and disease states of individual styloid processes.
Styloid process in the ulna
The ulna is classified as a long bones and it forms the skeleton of the upper limbs in the human body. The bone ends on one side with an ulna and a pointed process. They are felt through the skin at the point where the arm bends – the elbow. On the other hand, the ulna ends with the so-called head of the ulna, passing into the styloid process.
When there is a strong mechanical trauma on the surface of the upper limbs, the styloid process in the ulna may fracture. Unlike many limb fractures, treatment of a styloid fracture at the ulna is not long-term treatment. This is due to the fact that the styloid process of this bone does not connect directly to the tissues of the joint where the forearm meets the hand. For this reason, the correct fusion of the broken styloid process does not require the arm to be stiffened with a plaster cast for a long time. Most often, immobilization of a broken place takes about two weeks, and to carry it out, plaster is not used, but more delicate materials, such as an elastic bandage. After a period of 2 weeks of stiffening, the elastic bandage is removed and the hand is suitable for most of the daily manual activities. However, avoid overloading the hand in which the styloid has fractured. Above all, you should give up lifting weights and performing other exercises that burden your arm. In addition, we may feel slight discomfort in the elbow, such as a stabbing pain when suddenly moving. These symptoms are normal and should go away on their own after a few more weeks.
Styloid process of the radius
The radius is a long bone, one of the two parts of the forearm. On one side, it ends with a bone neck topped with the head of the radial bone, through which it connects to the bone head of the humerus. Thus, they form the elbow joint. On the other hand, the end is more thickened and has an elbow notch and a styloid. The styloid process of the radius can be felt through the skin. It is enough to gently press your finger on the skin in the so-called anatomical snuffbox (dimple on the hand, below the thumb, with a slightly triangular shape).
As in the case of the ulna, the process of the radius can fracture under the influence of mechanical trauma, such as a strong impact or falling in an unfortunate position on the arm. Unfortunately, such a fracture is more difficult to treat than a styloid fracture of the ulna. A complete diagnosis of the fracture is made by taking an X-ray. It allows you to assess whether there is a need to adjust the pond. If the structures that make up the joint are intact, the hand immobilization alone is sufficient. It usually takes a longer period of time, from 4 to about 6 weeks. In addition, removing the dressing from your hand does not complete the healing process. Often there is a need to participate in rehabilitation aimed at improving the broken place and returning it to its previous condition.
In the case of styloid fractures, immobilization is used both in the ulna and in the radius. You can also apply appropriate analgesic and anti-swelling ointments that reduce the level of swelling in damaged tissues.
Other health problems with styloid
The styloid process is exposed not only to mechanical damage, but also to other threats that may disrupt its structure or cause pain. These include:
- De Quervian’s disease, involving the alteration of the tendon attachments. This disease causes a feeling of pain and severely limits the manual skills of the hands.
- Inflammation of the tissues of the wrist that may occur as a result of prolonged stress. Importantly, inflammation can occur not only as a result of excessive physical effort, but also, for example, as a result of manual work that strains hands and wrists.
- Rheumatoid arthritis can also lead to inflammation of the styloid process.
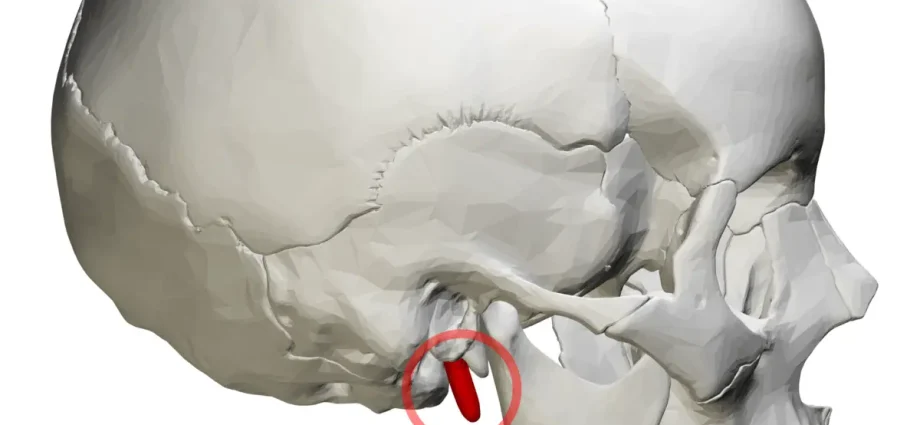
Styloid process in the temporal bone
The styloid process also occurs in the temporal bone, where it is the site of attachment of several important muscle tissues and ligaments. This process may be slightly elongated – then we are dealing with a disease called Eagle’s syndrome. Its genesis is not fully elucidated, but in many cases it results from the pressure on the nerve tissues that make up the muscles: the stylus-lingual, stylopharyngeal or stylohyoid muscles, or on the trigeminal nerve.