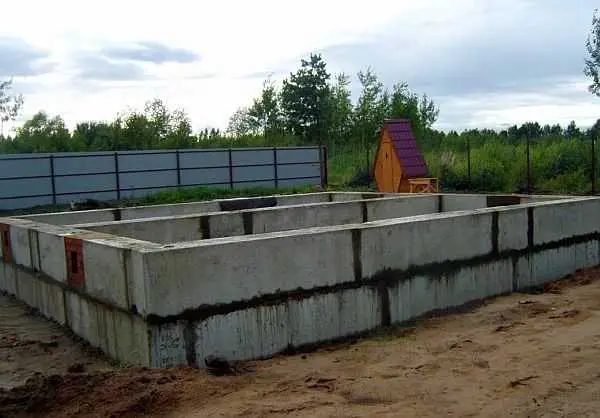
The most popular foundation in private construction is tape. This is one of the most flexible foundations that can be designed for any building and for any soil. It is laid along the perimeter of the building and under all load-bearing partitions, which is why it looks like a tape. In cross section, it most often looks like a rectangular parallelepiped, sometimes with a wider base, sometimes without. The width of the tape in any place should be the same. The depth of the foundation is determined based on the type of foundation chosen, climatic factors, the type and mass of the building, the geological structure on the site and the level of groundwater. All these factors together determine the parameters of the strip foundation of the foundation.
It should not be done on unstable and water-saturated, highly heaving soils with a large freezing depth (more than 2 meters). It can be designed, but it will cost a lot. They are not suitable for peat bogs or loess soils. Usually, in such conditions, other types of foundations are optimal. Also, tapes are not always used for light buildings – frame or wooden: for them there is a cheaper, but no less reliable type – columnar or pile (pile-grillage). In all other cases, it is the strip foundation – most often – the best option.
It is used not only in the construction of houses. It is made during the construction of a fence, garage, capital outbuildings.

Project: to order or not
Building a house requires a lot of money. Naturally, there is a desire to save money. But the foundation is not the stage at which it is worth saving, because its incorrect construction will lead to problems, the elimination of which will require much more money. Therefore, it is desirable to order a project, as well as a geological study.
You can do without this stage except when building small houses, baths, temporary or outbuildings. If a capital house is being built, and from heavy materials, then the risks are too great. But it’s up to you.
Actually, there is enough information for independent design of foundations, especially tape ones. But the lack of knowledge and experience often leads to two opposite results:
- The foundation was made with an excessive margin of safety for these conditions. This is good from an operational point of view, but leads to increased costs, often exceeding the cost of design.
- Insufficient margin of safety or incorrect design, which led to uneven settlement of the soil. The result is cracks in the walls of the house.
As you can see, both options lead to cost overruns: during the construction phase or for restoration and repair. And it’s not a fact that design work will cost more. Rather, on the contrary. The calculation of the foundation can cost about $100-250, but it requires data on the geology at the site, and these studies cost in the region of $1000. Under a small building, you can conduct research on your own, but under a solid one, it’s probably better to trust professionals.
Types of strip foundations and their use
During the construction of a strip foundation, several types of materials can be used, the name changes accordingly, there are differences in technology. What remains unchanged: digging a foundation pit and preparing the foundation. The rest of the steps are subject to change. Briefly, the types can be described as follows:
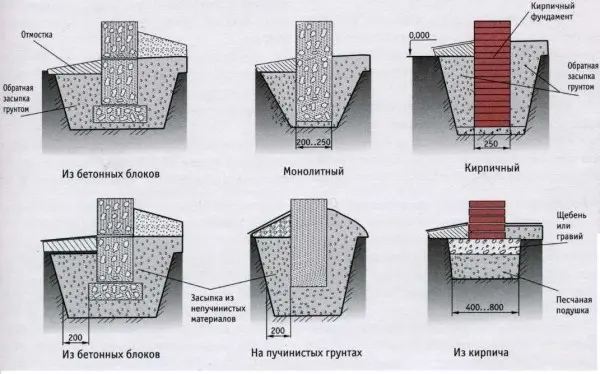
- When using concrete mortar and reinforcement, the strip foundation is called monolithic. All work takes place at the construction site. First, a formwork is installed in a dug pit – a prefabricated structure that gives shape to the concrete solution. Then the reinforcement is laid and tied, then poured with concrete mortar. Subject to the technology, the service life of a monolithic strip foundation is about 100-150 years. Therefore, it makes sense to use them for structures made of materials whose service life is comparable to the named interval. It takes a lot of time for all the work: to assemble the formwork, tie the reinforcement, pour and process the solution. This all takes weeks.

If concrete is poured directly on the construction site, we get a monolithic foundation - Prefabricated concrete strip foundation. It consists of reinforced concrete blocks cast at the factory. They are of two types. Trapezoidal (also called a pillow) are laid down, wall foundation blocks (FBS) are installed on them in one or more rows. Between themselves, they are connected by reinforcement, the gaps are filled with mortar. The service life of a FBS foundation is about 50-70 years, which is comparable to the service life of frame houses. With this option, the work is much less (several days), but in most cases it is required to rent lifting equipment – a winch for small buildings or a crane for more serious projects. At the same time, it must be remembered that the strength of the prefabricated foundation is 20-30% lower than that of a monolithic one, which is why they are not used on heaving or subsidence soils.

To make construction go faster, at a low level of groundwater, the tape is assembled from ready-made concrete blocks - Rubble strip foundation. It is built from natural rubble stone. Sometimes with concrete, sometimes without. When using concrete, they talk about a buto-concrete foundation. Construction requires a lot of experience and high qualifications of workers: the stones must be laid correctly, because they are bound only by mortar. Such foundations can be used on stable, non-porous bases, otherwise there is a high probability of cracking or complete destruction. Service life – as in prefabricated 50-70 years.

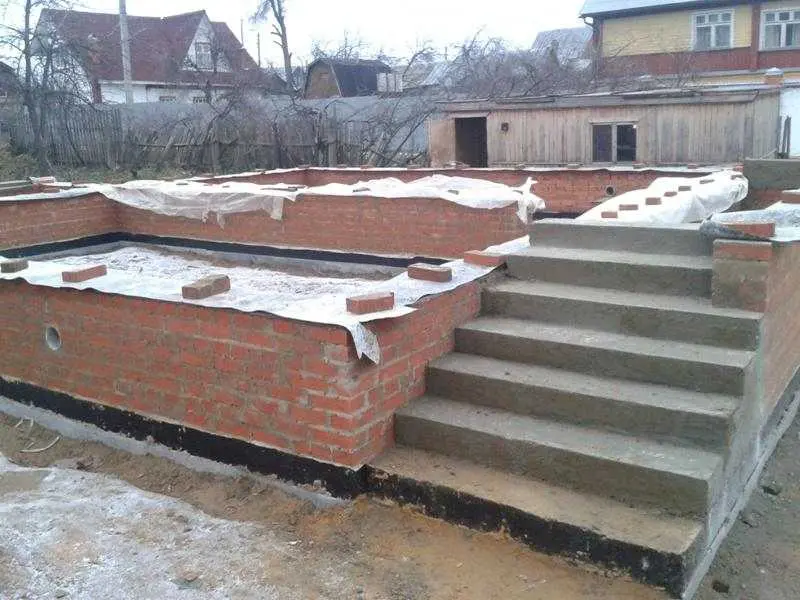
Rubble foundations require high skill: the stone must be laid so that the house does not deteriorate later - Brick strip foundation. This is a private version of the prefabricated foundation. In this case, most often, a monolithic tape with an armored belt is first poured along the perimeter of the foundation, and a brick wall is laid on top. Sometimes building blocks are used instead of bricks. It is worth sitting down that both brick and building blocks are hygrocosmic and do not have the longest service life. In terms of reliability, these are the most problematic and short-lived foundations: their service life is 30-50 years, and this is with proper design and execution.

The brick foundation is not very popular today: high labor intensity and short service life are the main reasons
Most often there is a monolithic strip foundation. Although it has the greatest labor intensity, it is a single design that is capable of redistributing loads. Therefore, it is often used on heaving soils. If the soils are dry and reliable, a reinforced concrete prefabricated foundation can be installed. It often has a high cost, but it takes less time to build, which is sometimes also important.
Rubble and rubble concrete foundations are mainly used in regions with a sufficient amount of suitable material – in mountains or close to them. There, firstly, the grounds for them are ideal, and secondly, there are good specialists who can competently perform the work. In the flat areas, the delivery of stone is unprofitable, and you won’t find a master either.
Brick foundations have rarely been made recently. Despite the general availability of the material, it has far from the best characteristics and requires significant costs for the organization of waterproofing, as well as insulation. As a result, its cost increases significantly. With a short service life, this is completely unprofitable even on stable soils.













