Stomatitis is a disease of the oral cavity, which is accompanied by inflammation of its mucous membrane. It is the reaction of the immune system in response to a particular irritation. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in childhood. However, this does not mean that stomatitis cannot develop in adults.
Causes of stomatitis in adults
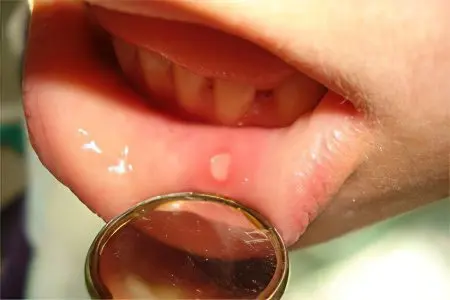
Among the main reasons that can cause the development of stomatitis, there are:
Infectious lesion of the oral mucosa. It can suffer due to the influence of viruses, bacteria or mycoplasma. In order for this pathogenic flora to actively multiply and lead to the development of stomatitis, additional factors are required. If they are not present, then the conditionally pathogenic flora does not lead to the development of the disease.
Nutritional errors. If a person receives less vitamins and microelements with food, this will lead to the development of stomatitis. In this regard, a deficiency of B vitamins, iron, folic acid and zinc is especially dangerous.
Received injuries of the oral cavity. The mucous membrane can be damaged by chemical, mechanical, thermal agents. People who have been injured most often indicate this to the doctor, which makes it easier to diagnose stomatitis. The epithelium of the oral cavity can be damaged by hard food, nuts, crackers, dried fish. A chemical burn develops due to the ingestion of acids or alkalis into the mouth. If the injuries are minor, then they go away on their own. However, when exposed to certain risk factors, a person develops stomatitis.
As it becomes clear, stomatitis manifests only if certain risk factors influence the human body.
These include:
Poor oral hygiene.
Eating dirty foods.
Poor hand hygiene before the upcoming meal.
Incorrectly fitted dentures. Low quality of such products.
Excessive oral hygiene, the use of toothpaste, which includes sodium lauryl sulfate. This component leads to the fact that the production of saliva decreases in a person. As a result, the epithelium of the oral cavity loses its main defense mechanism, begins to dry out, which becomes a favorable environment for the reproduction of bacteria.
Taking drugs that reduce saliva production. In particular, this applies to diuretics.
Alcohol abuse.
Tobacco smoking.
The presence of chronic or acute diseases.
Often it is thanks to stomatitis that it is possible to detect other diseases in a person that he had not previously suspected.
So, inflammation of the oral mucosa can occur in such cases as:
Oncopathology. Cancer tumors can be located in the nasopharynx, in the neck.
Undergoing cancer treatment.
Diseases of the digestive system: gastritis, colitis, infection with worms.
Deficiency of fluid in the body, which can occur after severe diarrhea, vomiting, bleeding. Sometimes dehydration occurs against the background of high body temperature, which persists in the patient for a long time.
Hormonal imbalance in the body. Stomatitis often becomes a companion of pregnant women, as well as patients who have entered menopause.
HIV-positive people may suffer from severe stomatitis.
Patients with diabetes.
People with Sjögren’s syndrome.
Patients with bronchial asthma. The likelihood of developing the disease in them will increase if they use aerosol hormonal agents for treatment.
Anemia.
Types of stomatitis
Depending on what exactly caused the development of stomatitis, the type of disease will differ:
Stomatitis is bacterial. Such permanent residents of the oropharyngeal tonsils as staphylococci and streptococci can provoke the disease. First, small pustules appear in a person’s mouth. They quickly open up and transform into erosion and ulcerative defects.
Viral. Herpes simplex or Epstein-Barr viruses can cause inflammation of the oral cavity. A person has small bubble rashes in the mouth, which are filled with transparent contents. If stomatitis is complicated by a bacterial infection, the fluid becomes cloudy. Then the bubbles burst, and areas of erosion appear in their place.
mycotic. The disease develops due to the reproduction of fungal flora. Often it is a consequence of prolonged use of antibiotics, or a pronounced decrease in immunity. Fungi of the genus Candida begin to multiply in the mouth, which is manifested by the formation of a white cheesy plaque, under which there will be an eroded oral mucosa.
Ray. The disease develops due to the influence of ionizing radiation on the body. A person has dense patches in the mouth.
Chemical. The disease develops due to burns of the oral mucosa. After the wounds heal, scars will remain in the mouth.
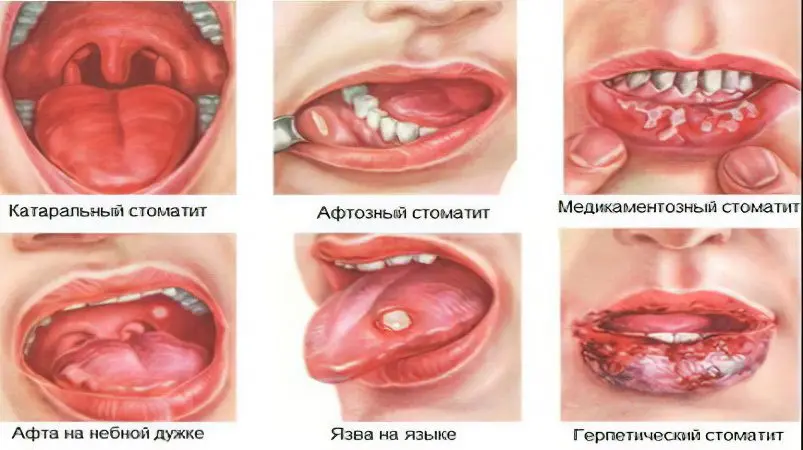
Symptoms of stomatitis

Stomatitis, regardless of its variety, is always accompanied by an inflammatory process in the oral cavity. Unlike children, in adults, the disease is rarely accompanied by a high body temperature. It does not lead to a pronounced deterioration in well-being, although it still causes some discomfort.
The main manifestations of the disease include:
Redness of a certain area of the oral mucosa. It becomes edematous, gives pain. These signs indicate that the disease is just beginning to develop.
A day later, an ulcer will appear at the site of inflammation, which may be in the form of an oval or circle. A reddish border forms around it, and in the center there is a film that may have a yellowish or white color. These symptoms indicate that a person is developing a bacterial form of the disease.
The work of the salivary glands intensifies, an unpleasant odor begins to come from the mouth, the gums may bleed.
Pain with stomatitis can be quite intense. Because of it, it will be difficult for a person to eat the usual food. Pain responds to movements of the lips and tongue.
If the disease has an acute course, then the body temperature rises to 39 ° C. Lymph nodes may increase in size.
Most often, ulcers are located on the lips from the inside, on the cheeks, on the palate and on the tonsils. Less commonly, the disease affects the tongue and the area under the tongue.
Treatment
Sometimes a person develops catarrhal stomatitis. It is the result of poor oral hygiene. This disease is mild and disappears in a week. At the same time, you need to treat your mouth with disinfecting compounds, eat right, removing spicy, salty, sour, hot and cold dishes from the menu.
If you can not cope with the disease on your own, then you need to contact the doctor. A dentist or general practitioner can advise a person. With developing aphthous, herpetic or ulcerative stomatitis, an integrated approach is required.
If stomatitis is caused by the herpes virus, then the use of antiviral drugs will be required. When the disease is the result of the reproduction of fungal flora, it is necessary to use antifungal agents. Allergic stomatitis is treated with antihistamines. But what kind of stomatitis you have, the doctor will be able to tell you, and prescribe the exact treatment.









