Contents

Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women. The tumor consists of undifferentiated malignant cells that replace glandular tissue. The urgency of the disease increased in the late seventies of the last century. The disease was characterized by a predominant lesion of women over the age of fifty. A feature of modern oncopathogenesis is a disease in childbearing age.
How long do people live with breast cancer?
This question is of interest to all patients admitted to the oncology dispensary. It is asked in order to find out the truth, even if it is terrible.
Any doctor knows that predictions of the outcome of the disease should be approached with caution. There are known examples of inhibition of carcinogenesis of advanced stages and accelerated development of breast cancer detected in the early stages.
However, a patient with an early operable form of oncology is more likely to recover, if we abstract from:
individual characteristics (age, the presence of concomitant diseases, support and understanding of relatives and friends, attitude to the struggle for life);
efficiency and timeliness of treatment.
There are known cases of preservation of the mammary gland in the detection of pathogenesis in the early stages of the disease. Oncologists sometimes decide to remove the breast. It’s annoying, but not fatal. The support of loved ones is important.
In pathogenesis with metastases to other parts of the body, the prognosis is cautious, it is necessary to fight, because it is possible to suppress the growth of pathological cells even at this stage.
The first signs of breast cancer
Women often face breast problems in the form of nodular or extensive seals and other signs that are frighteningly similar to oncology. Fortunately, not all formations are malignant.
Pain and tightness in the chest are accompanied by:
Mastitis is an inflammatory disease;
Mastopathy – small (nodular), extensive (diffuse) seals;
Fibroadenoma is a benign neoplasm.
Mastitis – inflammation of a functioning gland of an infectious or traumatic nature. In some cases, a connection is found with mastopathy that is not related to lactation.
General characteristics of mastitis. Usually women who give birth for the first time, rarely young women who have not given birth, suffer. The disease is associated with the entry of banal microflora (staphylococci, streptococci) through nipple cracks into the gland, hormonal disruptions, hypothermia, injuries, improper attachment of the baby. Risk group: nulliparous women.
Signs of mastitis:
Consolidation in the chest, diffuse at first;
Bursting pain, aggravated by feeding;
Increase in local and general temperature;
Perhaps the formation of a purulent cavity and nodular compaction;
Discharge from the nipple during lactation (liquid, viscous, purulent, bloody).
Mastitis differs from oncology by its rapid onset associated with the above reasons, which are determined during the patient’s interview and during the collection of anamnesis.
disease of the breast – this is not an inflammatory disease, it is associated with the pathological growth of the alveoli and ducts of the breast under the influence of hormonal imbalance – an increase in the level of estrogens, prolactin, a decrease in progesterone in the blood and tissues of the gland. There are nodular and diffuse forms of mastopathy. Due to the growth of tissues, this disease is called fibrocystic pathology. Risk group: women over 35 years old.
Signs of mastopathy:
When palpated, seals resembling grains (nodules) or strands (diffuse lesion).
Perhaps a combination of pathology with a violation of menstruation or with menopausal changes in the body;
The pain develops gradually as the seals increase;
With a long course, symptoms of mastitis may join.
Fibroadenoma – a benign formation of glandular tissue, which has an unclear etiology. There are mature fibroadenomas (the form is well contoured) and immature (the form is loose). Some formations are prone to rebirth. Risk group: women over 20 years old.
Fibroadenoma symptoms:
Single or multiple seals in the chest;
Pain and other signs are often absent.
It is advisable to contact a mammologist for consultations.
[Video] Dr. Berg – 6 Early Signs of Breast Cancer:
Caffeine
Caffeine is often indicated as a specific stimulant of estrogen-dependent carcinogenesis. Coffee is a common drink, so its effect on the body in cancer is interesting.
Caffeine is in:
natural coffee;
freshly brewed tea;
Cocoa;
Mate – a tonic drink from Argentina and some Latin American countries;
Guarana – Brazilian tonic drink.
Caffeine is an alkaloid from the group of methylxanthines. Preparations of this group are used to treat asthma, increase tone in lung diseases and diseases accompanied by edema, as diuretics. The well-known anticancer effect of theophylline and pentoxifylline are drugs from the group of methylxanthines.
A similar anti-cancer effect of caffeine was confirmed by Swedish scientists from the University of Lande and Malmö, who studied the CYP1A2 gene and its alleles – A / A, A / C, C / C. It was found that caffeine with different intensity inhibits the development of breast cancer in all groups of subjects. 15% of women who do not drink coffee have estrogen-independent cancer, which is difficult to treat.
Thus, caffeine is not related to estrogen-dependent forms of breast cancer.
Types of breast cancer
Nosological forms of cancer are divided into precancerous or non-invasive (in situ), invasive ductal and lobular. Breast cancer is associated with the level of estrogen and progesterone in breast tissues, as well as with the presence of a specific tumor protein HER2/neu.
Hormone dependent breast cancer
Due to the peculiarities of physiology, a woman’s body is under hormonal pressure much stronger than a man’s. Important functions are hormones produced primarily by the ovaries – estrogens, progesterone, pituitary – LH, FSH. At the same time, regular hormonal changes associated with natural physiological processes occur.
Against the background of modern life, the number of risks associated with the imbalance of hormonal status has increased many times over. First of all, this is the widespread use of methods of endocrine regulation of fertility. Some of the factors were mentioned at the beginning of the article.
It has been noticed that in many forms of breast hyperplasia, endocrine disorders are noted, as well as a very high level of estrogens, prolactin against the background of a decrease in progesterone levels. This ratio is maintained in the clinical manifestation of breast cancer. There are predominantly estrogen-dependent and predominantly progesterone-dependent forms of breast cancer.
Hormonal imbalance is treated with good effect in an average of one third of patients with both forms of cancer using endocrine therapy. Efficiency in the sensitive group reaches 75%.
Along with the long-term use of hormones – analogues of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, the regulation of ovarian function can be carried out by methods of physical (radiation exposure) and surgical castration.
Negative breast cancer
The most severe form of breast cancer. Clinically, it proceeds according to a pathogenesis similar to other forms of cancer. Differs in complexity of treatment. This type of cancer can only be determined by laboratory molecular genetic studies. The classification was put into practice after 2000. Usually this disease in medical practice is classified as triple-negative breast cancer. This form of cancer is detected in every third patient, from 27 to 39% of those examined. Ultrathin studies have established the presence of oncological diseases that have receptors for one of the three body proteins:
estrogen;
progesterone;
specific tumor protein.
Triple-negative cancer is characterized by the presence of cells that do not have receptors for all three proteins. As a result, carcinogenesis resembles a fight with a dragon, which constantly eludes its pursuer. In recent years, doctors have found effective ways to influence the body in this form of the disease.
Luminal breast cancer
It belongs to the group of estrogen-dependent breast cancers. There are two forms – type A and type B.
Luminal cancer type A
It occurs in women during menopause. At this age, it is found in 30-40% of the observed cases.
Cancer cell receptors:
well perceive estrogen and progesterone cells;
insensitive to the marker of cell growth of breast cancer cells Ki67;
cells absolutely do not perceive a specific tumor protein, its histochemical designation is HER2/neu.
Patients with type A luminal cancer respond well to hormone therapy with the estrogen antagonist tamoxifen, as well as aromatase inhibitors. Aromatase is an adrenal enzyme involved in the conversion of testosterone to estrogen. Register a high percentage of survival, low percentage of relapses.
Luminal cancer type B
Diagnosed among young women of childbearing age. Approximately 14-18% of estrogen-dependent cancer patients have type B.
Accompanied by metastases to the lymph nodes, a high frequency of relapses. The disease is usually difficult to respond to chemotherapy and hormone therapy. Only in some cases is it possible to stop cell growth with the help of a course of immunotherapy with transtuzumab. Transtuzumab is a human monoclonal antibody against the specific tumor protein HER2/neu. Thus, under certain indications, specific immunity is stimulated to the oncoantigen of the corresponding clone.
Stages of breast cancer
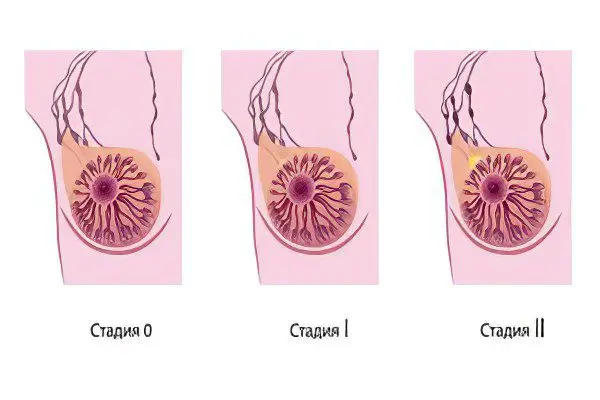
The division of breast cancer into stages depending on the severity of pathogenesis is rather arbitrary. Cancer is a multifactorial disease; the degree of damage and the volume of the tumor are not the main criteria for assessing the severity of the disease.
Meanwhile, the stages of breast cancer in the medical literature are indicated by:
tumor size T1, T2, T3, T4;
involvement in the pathogenesis of regional lymph nodes N 0, N1, N2, N3.
the presence of distant metastases – M0, (absent) M1 (available).
Designations are also available for early non-invasive neoplasms, we will not indicate them here.
stage 1 breast cancer
A breast tumor of the initial stage can be described as follows:
Т1 (size up to 2 cm);
N0 (metastases of regional lymph nodes are absent);
М0 (distant metastases are not detected).
stage 2 breast cancer
A breast tumor in the second stage of pathogenesis can be described as follows:
Т2 (size from 2 to 5 cm);
N1 reveal metastases in the lymph nodes I, II, the defeat of one or two lymph nodes on the one hand. The nodes are palpated as separate formations;
M0 or M1 single distant metastases are possible.
stage 3 breast cancer
A breast tumor in the third stage of pathogenesis can be described as follows:
Т3 (size more than 5 cm);
N2 metastases are detected in the lymph nodes of the armpit I, II level, on the one hand in the form of a single package, or the lymph nodes near the mammary gland increase to a detectable size (usually not determined), in the absence of changes in the axillary lymph node.
M0 or M1 absent or distant metastases.
stage 4 breast cancer
A breast tumor at the fourth stage of pathogenesis can be described as follows:
Т4 the size of the tumor does not matter, it is determined outside the mammary gland and on the skin of the chest, it is accompanied by ulcerations, nodules;
N3 – metastases on both sides of the chest of level III, palpable under the mammary gland, in the axillary and supraclavicular space.
M1 multiple distant metastases.
Variants of the specified digital designations are possible, as well as additional numbers to clarify the description.
Diagnosis of breast cancer
Minimally invasive diagnostic methods include mammography – a variant of X-ray examination, ultrasound diagnostics, elastography, magnetic resonance imaging. To invasive – biopsy and further histological and cytological examination of alveolar cells.
Mammogram
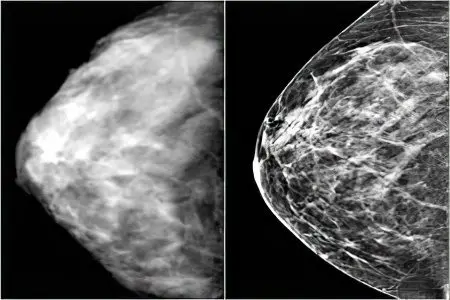
The most common method in our country is an x-ray (mammogram) in two projections. The study is recommended to be carried out in accordance with the individual menstrual cycle.
In recent years, with the introduction of new methods, doubts have arisen about the diagnostic value of mammography. This is due to additional X-ray radiation during regular examinations and questionable results with fibrous growths, the presence of breast implants, and small tumor sizes. In some cases, the diagnostic reliability of the results is reduced to 6-40%.
Meanwhile, primary, secondary and indirect symptoms of breast proliferation can be obtained with this method. The diagnostic value is based on the detection of calcifications (microcalcifications) – calcium salts, which are clearly visible against the background of the alveoli and ducts.
Primary (important) symptoms:
Contrasting area in the picture;
Irregular edges (rays, tubercles or calcifications and microcalcifications);
Limited location in the form of single formations or clusters;
Size from 0,5 mm and below.
There are three degrees of contouring in mastopathy, the third (severe) degree is transitional between benign and malignant:
First (light) degree. The picture shows the predominance of shadows characteristic of adipose tissue.
Second (middle) degree. The picture shows the same degree of shading of areas characteristic of adipose, glandular and connective tissue.
Third (severe) degree. Contours of predominantly glandular tissue are visible; shading characteristic of adipose tissue is absent. This should be alarming, perhaps the tumor in the picture does not contour.
Analysis of the level of gene expression
Analysis of the level of gene expression makes it possible to assess the likelihood of recurrence of the disease. This study should be carried out in order to resolve the issue of the need for chemotherapy. Relapse of the disease occurs on average in 10% of women, and chemotherapy is prescribed to the vast majority, which negatively affects the health of patients. This analysis will identify women who really need chemotherapy.
Other types of diagnostics
Physical studies include:
Breast ultrasound and elastography
breast MRI
Physical research
Screening examination









