Contents
Deprive a person – this is the combined name for a group of dermatological diseases with different etiologies, manifested in the appearance of itchy skin rashes. The course of lichen is always long, characterized by periods of exacerbations, with a high risk of developing a secondary infection of the skin. The patient suffers not only from a cosmetic and physical defect, but also from psychological discomfort.
There are several varieties of lichen in humans, they differ depending on the type of pathogen, on the nature of the rash, on the place of their localization and on the degree of contagiousness.
Symptoms of depriving a person
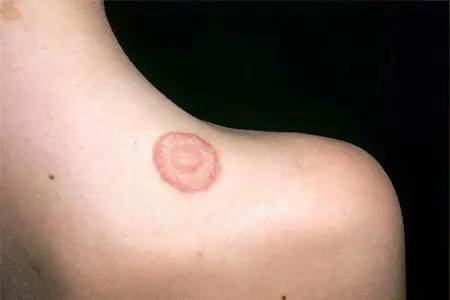
The symptoms of lichen in humans are very diverse and largely depend on the type of pathogen.
Nevertheless, it is possible to distinguish common signs of this group of dermatological pathologies:
The pigmentation of the skin changes;
There are spots on the skin that have a different color, size and shape;
The skin on the affected area begins to peel off;
There is itching;
There is a complete or partial loss of hair.
After discovering one or more symptoms of lichen in yourself, you need to consult a doctor and determine its type.
Dermatologists have identified the following symptoms of lichen in humans, depending on the type of pathogen:
Ringworm:
It affects the scalp, neck, shoulders and face.
It appears as a pink spot with clear contours. The spot peels off, the hair breaks and becomes short. Similar symptoms are characteristic of microsporia.
Trichophytosis appears as a pink ring. The hair breaks at the root, as its deep damage occurs.
Rosacea:
It affects the back, chest, shoulders, sides, abdomen, skin folds on the body.
Spots from pink to light brown, oval or round in shape.
The skin in the middle of the patch is dry and tends to peel.
The spots tend to grow, merge into small pink foci. They can reach several centimeters in diameter.
For pink lichen is also characterized by itchy skin.
Microsporia:
It is possible to spread this type of lichen not only on the scalp, but also on the body.
Characterized by the appearance of one or more large spots.
The color of the spots is pale pink, in their center there is a peeling area. The edges are edged with a darker roller.
Hair will break at a distance of 5-8 cm from the root.
Skin itching is not typical for microsporia.
Multicolored, pityriasis versicolor:
The spots have different shapes and different sizes. Large foci that have an oval or round shape predominate. Perhaps their merger with the formation of spots with uneven edges.
If a person’s skin has a tan, then multi-colored lichen stands out on it as a discolored spot. In winter, these areas darken.
The disease has been around for a long time. In this case, the color of the lesions may become greenish or brown.
There is peeling, but it is not pronounced.
Shingles:
On one side of the chest there is severe pain and itching.
The affected area after a short time is covered with blisters filled with liquid.
After a few days, the bubbles burst, a crust appears on their surface.
A person suffers from severe pain, as nerves and their endings are involved in the pathological process.
The most dangerous form of shingles is ophthalmic, as a person can permanently lose sight.
Lichen planus:
Human skin is covered with flat nodules that have a red or purple color.
When the mucous membranes are involved in the process, the nodules have a pale pink color.
If the nail plates are affected, then they begin to crumble and collapse.
With lichen planus, a person always suffers from severe itching.
New nodules form in places where the skin is damaged – in the area of scratches and scratches.
The variants of skin lesions with red lichen are as follows: in the form of rings, in the form of red soft bumps, in the form of warts with a bumpy surface, in the form of ulcers and erosions.
Causes of depriving a person
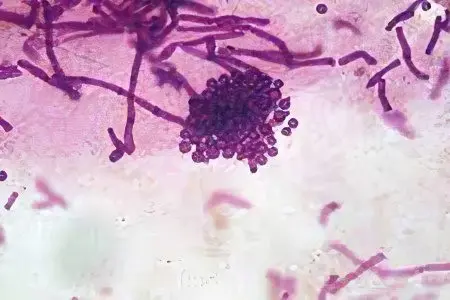
The causes of lichen in humans are infection with a viral or fungal flora.
At this point in time, the following causative agents of lichen are known to science:
zooanthropophilic fungithat can be transmitted from animal to human. The most common carriers of these fungi are cats or dogs.
Anthropophilic mushrooms, which can only affect human skin. They are transmitted from one patient to another through direct contact.
geophilic mushrooms, infection with these microorganisms is possible only through contact with the ground.
Virusesthat provoke pink and herpes zoster. Some of them can exist in the human body and lead to the development of the disease only if the immune system is disturbed.
Ringworm can be contracted through close contact with a person or animal that carries the infection.
Pink lichen has an infectious-allergic nature and is not a highly contagious disease. Most often, a person becomes infected when using common household items. In the presence of strong immunity, infection does not occur at all.
Microsporia is provoked by a fungus such as microsporium canis. It exists in the fur of animals, most commonly affecting cats. Therefore, the transmission of microsporia occurs from a sick animal to a person. Children are at risk.
Pityriasis versicolor is provoked by fungal microorganisms, the likelihood of the disease increases under the influence of a number of factors. The infection is transmitted most often by household means, through common household items, or by direct contact with its carrier.
Shingles has a herpetic nature. It can lead to infection upon contact with the herpes virus, or develop after the activation of a latent herpes infection that exists in the body.
The reasons for the development of lichen planus lie in the person’s allergic predisposition, chronic stress and viral infections. These are the main assumptions of experts regarding the etiology of the development of this variety of lichen.
The factors provocateurs that affect the risk of developing the disease are considered to be the following:
Genetic predisposition;
Various infectious diseases;
stress loads;
Violations in the functioning of the immune system;
Physical overexertion;
Autoimmune diseases;
Diseases of the digestive tract;
Tendency to allergic reactions;
Taking certain medications;
Increased work of sebaceous and sweat glands;
Non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, the use of other people’s household items for this purpose;
Contacts with animals, especially homeless ones;
Endocrine disorders;
Stress effects on the skin with ultraviolet rays;
High emotional load.
Types of lichen in humans
Types of depriving a person can be as follows:
Pink deprive (deprive Zhibera).
Ringworm, subdivided into microsporia, trichophytosis of smooth skin or ringworm.
Herpetic lichen planus.
Lichen color (pityriasis, multi-colored).
Lichen planus.
Stages of depriving a person

The stages of depriving a person will depend on the type of pathogen that provokes a skin disease.
Nevertheless, there are common features that make it possible to distinguish several successive stages in the development of this dermatological problem:
The causative agent of the disease gets on the skin, on the hairy part of the body or head, on the mucous membrane.
Depending on the type of fungus or virus, the pathological process starts either immediately or in the presence of favorable factors (falling immune defenses, taking medications, excessive sweating, etc.);
There is the appearance of one or more spots, nodules, or bubbles.
The spread of foci of infection throughout the body, or an increase in the size of a single formation. Accession of accompanying symptoms (peeling, itching, hyperemia).
Hair loss in the affected area, or breaking off and thinning.
The period of extinction of the disease and its subsequent relapse in the absence of treatment.
Possible accession of a secondary skin infection.
The danger and consequences of depriving a person
The dangers and consequences of depriving a person will also depend on the form of the disease.
Some skin infections go away on their own and do not pose any risk to human health, and some forms can pose a serious threat:
The dangers of ringworm. The development of inflammation and suppuration of the scalp, followed by loss of hair without the possibility of its restoration. As a result, even after recovery, a person who has had ringworm may have one or several bald spots for life.
Dangers of pink depriving. Pink lichen, as a rule, does not carry any serious health consequences and complications. This disease resolves on its own, after 2-12 weeks. In rare cases, it can take up to six months.
The dangers of shingles. If a person has been ill with herpes zoster at a young age, then most often he has a complete recovery, without consequences for his body. However, against the background of reduced immunity, the infection can lead to serious complications.
So, the herpes virus can begin to actively divide in the spinal cord and brain. This leads to extensive destruction of brain tissue and can result in paralysis of the limbs, facial nerve, breathing problems, and even death of the patient.
Sometimes the herpes virus spreads to the organs of vision. As a result, the eyes become very inflamed, the development of glaucoma is possible, which leads to severe damage to the cornea and complete blindness of a person.
In addition, the herpes virus is able to capture internal organs such as the liver and lungs. It also threatens with serious inflammation.
Dangers of pityriasis versicolor. Pityriasis versicolor does not pose a danger to human life and health. The traces on the skin disappear on their own after the end of the therapeutic course. However, if left untreated, pityriasis versicolor will steadily, albeit slowly, progress, capturing new areas of healthy skin.
Dangers of lichen planus. Lichen planus most often does not cause serious health problems. However, this does not always happen. Sometimes, areas of the skin that have been involved in the pathological process may temporarily become darker and stand out against the background of the whole body.
In addition, there is a risk of formation of scars, scars and depressions on the skin.
If lichen planus has been affected by the scalp, then this can lead to hair loss without their subsequent restoration.
If lichen planus was transferred in an erosive form and affected the mucous membranes of the genital organs, then adhesions, scars often occur in these places, narrowing of the vagina, or phimosis may occur.
If the infection has affected the area around the eyes, then there is a risk of loss of vision, or a significant narrowing of the lacrimal canal.
Lichen planus is also capable of severely deforming the nail plate.
Another serious danger of untreated red lichen is an increased risk of developing oral cancer.
Answers to popular questions
How is ringworm transmitted from person to person?

Pityriasis versicolor is caused by mycotic microorganisms, but it has been found that they can exist on the skin of many people without causing the onset of the disease. Therefore, it does not matter how a person got the fungus that causes this form of lichen. Of greater importance are the conditions that contributed to the development of the infection.
It is not transmitted from person to person lichen planus, pink lichen Zhibera.
Ringworm is a contagious disease and can be passed from person to person. Spores of fungal pathogens can exist for a long time on combs, sofas, bed linen, car seats, soft toys and other items. Infection occurs through contact with healthy skin.
Shingles is contagious. It is passed from a sick person to a child or adult who has not had chickenpox. A person is contagious only at the time of the formation of fresh bubbles. When crusts appear on them, the risk of infection disappears. The transmission of the virus occurs by airborne droplets and by direct contact with the patient.
What does lichen look like in humans?
The spots of pink lichen look like a circle or an oval with a bright red outline. On top, it has a thin shiny crust, scales or film. The size can vary from a few millimeters to 5 cm. The spots can provoke severe itching.
Lichen planus appears for the first time on the limbs in the area of the joints. They look like saturated red or purple seals. A few days later, nodules appear on other parts of the body: on the chest, in the inguinal zone, on the trunk. In 10% of cases, the nodules are grouped, subsequently forming a ring (annular form of lichen erythematosus). On the fingers, on the lower leg, on the ankle, lichen often takes the form of warts. On the mucous membranes, it appears in the form of vesicles and is called the vesicular form.
The appearance of ringworm depends on where it forms. On smooth skin, it has the form of a pink spot with a roller rising above its surface. The roller is represented by small vesicles. Often within one ring with irregular shapes, a second smaller ring is formed. On the scalp, ringworm looks like a rounded bald patch with clear boundaries. The foci can be quite large and reach 10 cm in diameter. The scalp inside the bald patch will be covered with a white coating. On the body, ringworm appears as a round red rash. It tends to merge and forms bright rings. The skin in the center of the plaque will eventually look like completely healthy.
Colored lichen has the appearance of spots that have a different size and shape. In summer, on tanned skin, they look light, in winter they darken. Peeling of the skin on the affected areas is insignificant.
Herpes zoster manifests itself in the form of rashes, blisters appear in place of the spots every other day, followed by their rupture and the formation of crusts. Bubbles appear in waves.
How long does it take to get rid of a person?
Pink lichen lasts from 2 weeks to 4 months. Sometimes the disease can last up to six months.
Severe cases of lichen planus are treated for 6 weeks.
Ringworm therapy takes up to 2 months.
Lichen color is treated for two weeks.
The average duration of treatment for herpes zoster is 7-10 days.
How to treat lichen in humans?

To determine how to treat lichen in humans, it is important to know the type of infection and the type of pathogen. After the diagnosis is made, the following therapy can be prescribed:
Pink deprive. Pink lichen does not pose a threat to human health. It goes away on its own, without any treatment and does not cause health problems. Therefore, if a dermatologist diagnoses pink lichen and does not prescribe any treatment, then these are well-founded actions of a competent specialist.
If a person is concerned about itching, then he may be recommended antihistamines, for example, Suprastin.
To speed up the recovery process of the skin, you can follow the following recommendations:
Try to wet the skin in the affected area as little as possible. It is worth knowing that the fungus spreads through the body with the help of water much faster. Therefore, after taking a shower, the body should get wet so that no moisture remains on it. But you can’t rub the skin. Do not rub the affected area with soap and washcloth.
Until the disease has passed, wearing synthetic underwear should be avoided.
Exposure to ultraviolet rays can worsen the condition. Therefore, too long exposure to the sun should be avoided.
To prevent excessive sweating, it is necessary to refrain from physical activity.
It is not recommended to follow a diet, but it is mandatory to refrain from foods that cause allergies. It is highly desirable to exclude alcoholic products.
It is strictly forbidden to apply hormonal ointments, as well as cosmetic creams and other products to the affected areas.
To eliminate the risk of attaching a secondary infection, you can wipe places with pink lichen with antiseptics.
Ringworm. Ringworm therapy is carried out with the help of antimycotic drugs, since the disease develops as a result of the vital activity of fungi. Reception of antifungal agents is prescribed orally, the treatment is supplemented by local therapy. Grisiofulvin is considered an effective drug. It must be taken orally. Such drugs as Itraconazole, Fluconazole, Terbmnafin have a pronounced antifungal effect. The dosage should be selected only by a doctor, self-administration of these medicines is strictly prohibited (more: What is the danger of ringworm? Treatment methods)
Local treatment is carried out with the help of ointments: Clotrimazole, Terbinafine, Mikoseptin, Ketoconazole.
As an antiseptic, it is recommended to apply iodine or sulfur-tar ointment to the affected areas.
Color deprive. Colored lichen is very well endured with the help of ultraviolet rays. Therefore, the general recommendation for all patients with colored lichen is to sunbathe in the summer.
In addition, doctors prescribe oral administration of such antimycotics as: Lamisil (Brmizil, Terbizil, Terbinox, etc.), Nizoral (Fungavis, Mycozoral), Orungal (Rumikoz, Irunin, Itrazol).
Local treatment is carried out using Mycospor, Bifosin and other creams and ointments based on clotrimazole or nizoral.
To order in a pharmacy, you can make Vidal’s milk. It contains boric acid, salicylic acid. Alcohol, camphor and other components that contribute to the speedy restoration and disinfection of the skin.
Another prescription remedy is Lassar paste, which has a drying and antiseptic effect.
Lichen planus. With this type of lichen, doctors prescribe antibacterial drugs for oral administration. These may be drugs from the group of tetracyclines, macrolides or aminoglycosides.
With neurotic reactions, sedatives are prescribed, for example, Valerian. In severe cases, tranquilizers are recommended.
If the itching bothers the patient a lot, then soothing ointments should be applied to the skin. Drugs with thymol, anestezin, menthol help. After that, antibacterial ointments and hormonal ointments are applied, for example: Oxycort, Lorinden C, Dermozolin, etc.
Herpetic lichen planus. If a person is healthy and his immune system is in order, then treatment is usually not required and herpes zoster resolves on its own. Pain can be relieved with Ibuprofen, Naproxen, or Paracetamol. With severe pain, a person is prescribed Oxycodone, Gabapentin (more details: treatment of herpes zoster, answers to popular questions).
Sometimes it is required to take antiherpetic drugs: Acyclovir, Valaciclovir, Penciclovir, Famciclovir. An effective modern remedy for local treatment is Epigen cream with glycyrrhizic acid.
When a bacterial infection is attached, antibiotics are prescribed. In no case should corticosteroid ointments be prescribed for herpes zoster. These drugs only exacerbate the disease.









