Contents
A wound is any violation of the integrity of tissues resulting from the mechanical impact of certain external objects. The degree of damage to body tissues depends on the size, shape, weight of the object causing injury, as well as on the strength and speed with which this action is performed. According to this, wounds can be cut, chopped, stab, bruised, crushed, lacerated, bitten and gunshot.
Cut, chopped and stab wounds cause less tissue destruction than other types, since these are wounds with a small area of damage. Torn, bruised, bitten and crushed wounds have a large area of damage. Gunshot wounds can have a different zone of damage. Random wounds are always infected.
Treatment of open wounds is reduced to restoring the integrity of the skin. Dermal cells have the ability to divide and regenerate. However, their full recovery is possible only with timely and high-quality cleansing of the damaged area.
Stages of treatment of open wounds
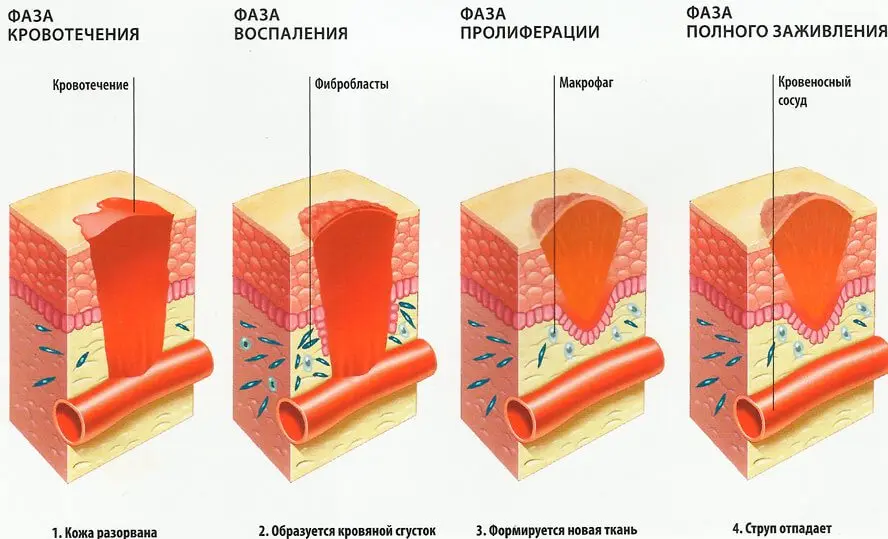
The healing of any open wound involves the passage of 3 stages:
Primary self cleaning.
Inflammation.
Granulation tissue repair.
Primary self-cleaning
Immediately after the injury, bleeding develops. The vessels narrow sharply, due to which a blood clot is formed and it stops. After that, the vessels expand, the permeability of their walls increases, which leads to the formation of edema in the affected area.
This reaction of the body helps the soft tissues to be cleansed on their own, without the use of any disinfectants.
Inflammation
The second stage is accompanied by an increase in tissue swelling. The skin becomes red. A significant amount of leukocytes accumulates in the damaged area.
Granulation tissue repair
Granulation tissue repair can begin against the background of existing inflammation. This is absolutely normal. The granulation process captures the entire wound surface, including its edges and surrounding tissues.
The granulation tissue then transforms into connective fibers. The process ends with the formation of a scar.
The wound can heal with primary and secondary intention. If a small area was injured, the divorced edges are close to each other, and the inflammation is insignificant, then the tension will be primary. In all other cases, healing is characterized by secondary intention.
Features of the treatment of an open wound directly depend on how intense the inflammatory reaction is and how severely the tissues were injured. An important condition is the stimulation and control of all stages of their recovery.
Primary wound care
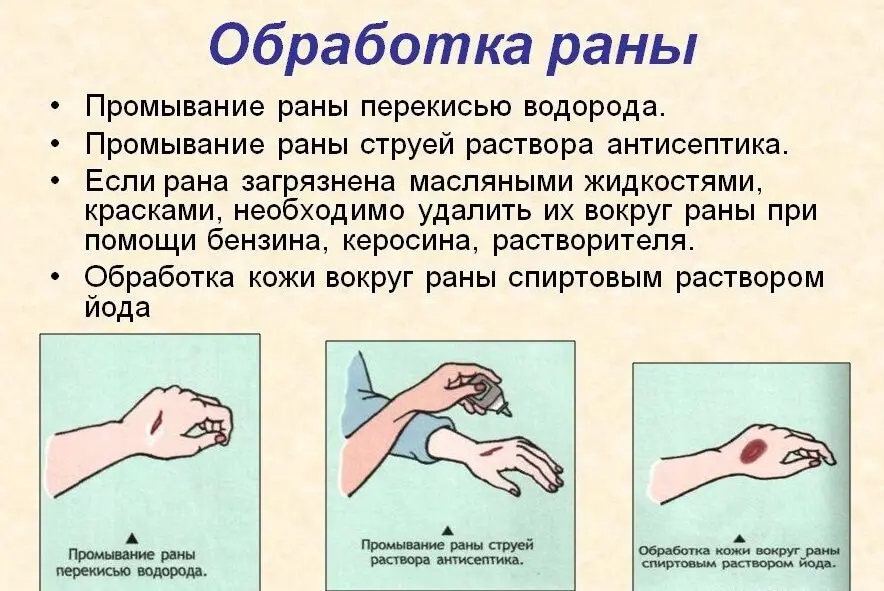
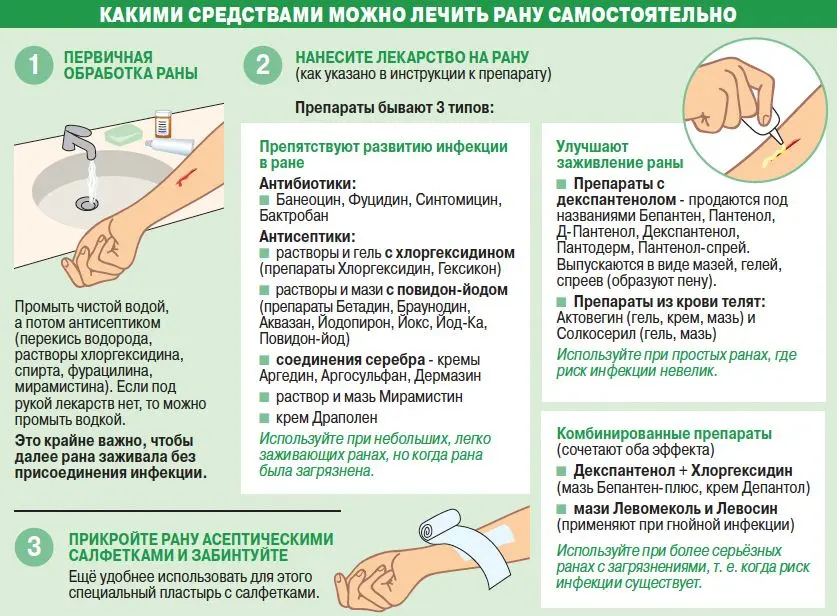
Primary treatment of wounds is a prerequisite. If the incision is small and was obtained at home, all contamination must be removed from it. To do this, you can use the pointed tip of a sterile bandage, or tweezers (it must be treated with an alcohol-containing liquid).
When the contamination from the wound is removed, it must be washed with an antiseptic solution. You can use 3% hydrogen peroxide, iodinol, chlorhexidine, etc. Hydrogen peroxide helps push out the smallest contaminants, since bubbles form after it is applied to the wound. In parallel, it destroys the pathogenic flora. If there are no medicines at hand, then you can use a 2% solution of soda, a solution of concentrated salt, vodka or chamomile infusion. It must be understood that microbes will always be present in the wound, unless the incision was made with a sterile instrument.
Household wounds are susceptible to infection. Sometimes microbes begin to multiply even in postoperative wounds. Therefore, after injury, the damaged area must be closed. To do this, it is bandaged or sealed with a plaster. Only small scratches and shallow cuts can be left open.
deep wound care

If you receive a deep wound, you need to seek medical help. Cuts larger than 2 cm will take a long time to heal on their own. They hurt, cause discomfort and are often complicated by suppuration. Therefore, it is highly recommended to visit a specialist.
You should not try to heal wounds that are accompanied by severe pain on your own. In this case, you need to make sure that the nerve has not been damaged. Medical attention is required if there is a bleeding wound.
Sometimes the cut is sutured. So the tissue will recover faster. The doctor will treat the affected area, trim the torn edges, stop the bleeding, and put in stitches. In some cases, the wound is sutured later, after the acute inflammation subsides. The bandage should be changed daily.
In the first 7 days, a wet-drying bandage is used. It contains antiseptic preparations. Then gauze ointment bandages are recommended. They must be impregnated with agents to destroy microbes and to accelerate tissue regeneration. These can be drugs such as: Levomekol ointment, Levosin, Methyluracil.
If necessary, the doctor will prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics for oral administration.
How to treat a weeping wound?
If a lot of fluid is released from the wound, then its treatment is somewhat different. Abundant discharge is not a pathological sign. On the contrary, they stimulate healing, as they contribute to the cleansing of the injured surface. However, excess exudate requires special measures, as it worsens blood microcirculation in the affected area.
Change sterile dressings more often if the wound is weeping. To disinfect surfaces, it is necessary to use a solution of Furacilin or sodium hydrochloride. You can irrigate the wound with Miramistin or Okomistin.
It is possible to reduce the amount of liquid separated by using a 10% sodium chloride solution. Change the bandage every 4 hours.
Antibacterial ointments are used for disinfection: Streptocid, Mafenide, Streptonitol, Fuzidin. They are applied under a sterile dressing. Alternatively, you can apply the ointment to a swab and use it to treat the wound surface.
Xeroform or Baneocin powder is used to dry the wound. These drugs kill germs and also help reduce inflammation.
Treatment of an open purulent wound
A purulent open wound is the most difficult to recover. It is important to stop the process of reproduction of pyogenic bacteria and prevent damage to healthy tissues. To do this, with each change of the bandage, it is necessary to clean the wound surface, removing pus from it. Drainage can be used for this purpose. It allows you to ensure a constant outflow of purulent masses.
Be sure to treat the wound with antibiotics during dressing, for example, Dimexide. You can remove dead tissue and pus with Trypsin or Chymotrypsin powder. The selected agent is diluted with Novocain or Sodium Chloride, sterile wipes are impregnated with the resulting composition and injected into a festering wound. The bandage is left for 1-2 days. It is possible to apply powders directly to the wound if it is wide and deep.
A purulent wound requires mandatory oral antibiotics. Sometimes they are given in an injectable form.
Features of the treatment of a festering open wound:
After removing the pus from the wound, Levosin ointment is injected into it. It has antimicrobial and analgesic effects.
Dressings that are applied to a purulent wound are lubricated with Levomekol or Synthomycin ointment.
If purulent inflammation develops due to the multiplication of Staphylococcus aureus in the wound, it is recommended to treat the wound with Baneocin.
Anaerobic infections respond better to Nitacid.
Specialists call Dioxidin ointment a universal drug. It is detrimental to most representatives of the bacterial flora. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and even microbes that provoke gangrene are sensitive to it.
It is possible to treat the wound surface with ointments containing polyethylene oxide. In past years, products containing petroleum jelly or lanolin were used, but modern surgery refuses them.
Vishnevsky’s ointment helps to quickly reduce the swelling of tissues, improves their nutrition by activating blood flow. Apply the drug to the wounds 1-2 times a day.
If a person with an open and festering wound enters the hospital, then he is shown therapy aimed at removing intoxication from the body and increasing immune forces. Ultrasound therapy and liquid nitrogen treatment help to speed up the process of tissue repair.
Ointments and creams for wound treatment
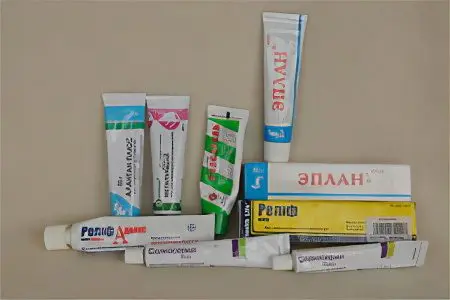
When the wound is shallow, you can deal with it at home.
For the speedy regeneration of tissues, you can use such means as:
Salicylic ointmentwith antibacterial effect. It is applied to the wound after pre-treatment with hydrogen peroxide. Cover the affected area with a sterile dressing. Alternatively, you can use Ichthyol ointment.
Streptocide. If tablets are at hand, they are crushed into powder and sprinkled on the affected area. Some people treat wounds with BF glue. However, it should not be applied to a contaminated wound surface. First you need to disinfect it with streptocide.
Balm Rescuer. It forms a thin film on the wound. Therefore, before applying the balm, the damaged area must be treated with hydrogen peroxide.
Solcoseryl. This ointment is applied to an open dry wound. If the damaged surface becomes wet, then the drug is used in the form of a jelly.
Heparin ointment, Troxevasin ointment, Dolobene gel. The listed drugs are applied to the skin if a hematoma has formed on it. These drugs help get rid of the bruise and reduce tissue swelling.
Cream Eplan. The basis of the drug is polyethylene glycol. It will allow you to qualitatively disinfect wound surfaces. Therefore, the risk of infection entering the wound is reduced.









