Contents
Quite often, users are faced with the task of squaring a certain number, or, in other words, to the second power. This may be required to solve engineering, mathematical and other problems.
Despite the widespread use of this mathematical function, including in Excel, there is no special formula that allows you to square a number. However, there is a general formula for raising a numerical value to a power, with which you can easily calculate the square.
Content
How is the square of a number calculated?
As we remember from the school curriculum, the square of a number is a number multiplied by itself. Excel uses the same principle to square a number, of course. And to solve this problem, you can go in two ways: use a formula that includes a special degree symbol “^”, or use the DEGREE function.
Let’s look at both methods in practice to understand how they are implemented and which one is easier and more convenient.
Formula for calculating the square of a number
This method is perhaps the easiest and most commonly used to obtain the square power of a number in Excel. For the calculation, a formula with a special sign “^” is used.
The formula itself looks like this: =n^2.
where n is the number whose square power is to be calculated. The value of this argument can be specified in different ways: as a specific number, or by specifying the address of the cell that contains the desired numeric value.
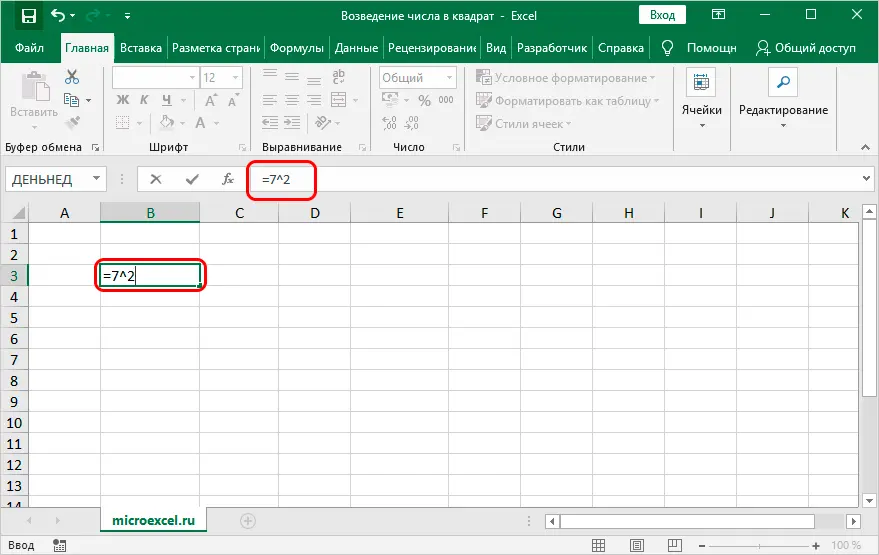
Now let’s try to put the formula into practice. In the first variant, we will directly write in the formula the number itself, the square power of which must be calculated.
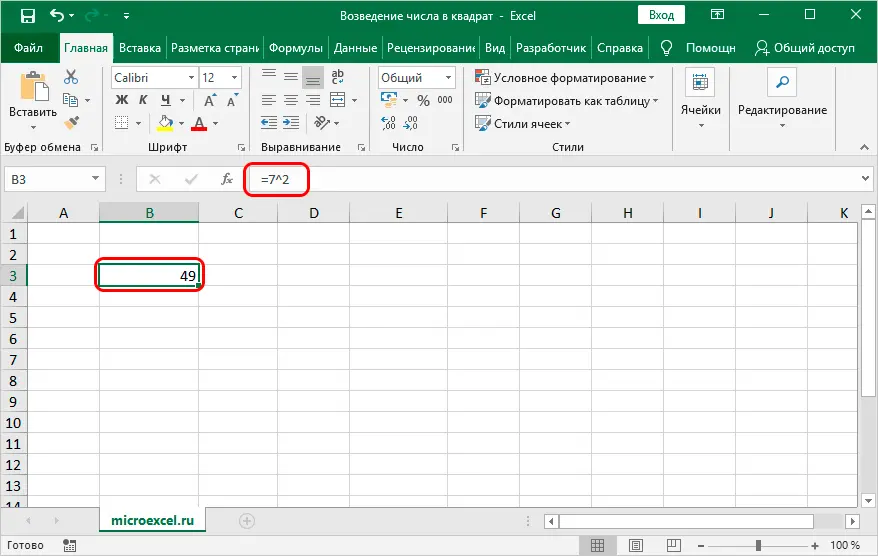
- To begin with, we determine the cell of the book in which the result of the calculations will be displayed, and mark it with the left mouse button. Then we write a formula in it, not forgetting to put the sign “equal” (“=”) at the very beginning. For example, the formula “=7^2″ means that we want to square the number 7. By the way, the formula can also be written in the formula bar, after selecting the desired cell.

- After the formula is typed, click the Enter key on the keyboard to get the desired result.

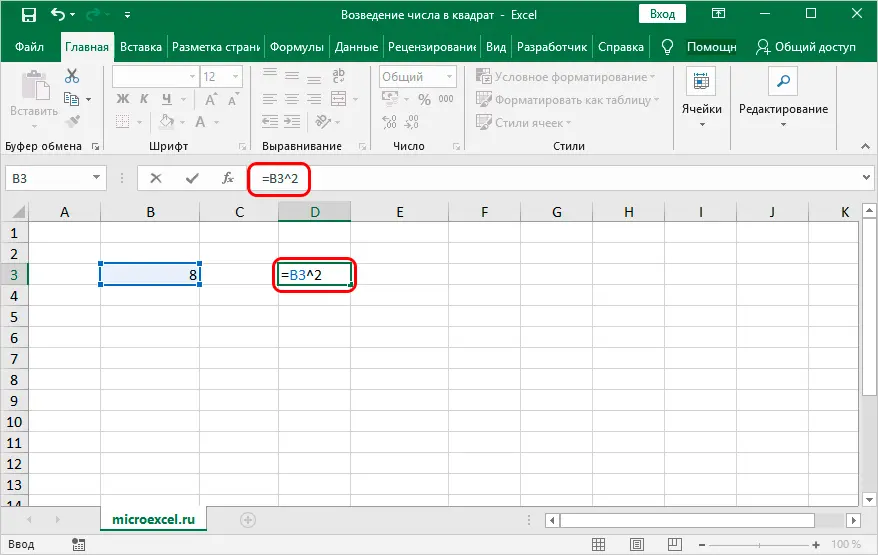
Now let’s look at the second option, in which instead of a specific number in the formula, we indicate the address of the cell containing the desired number.
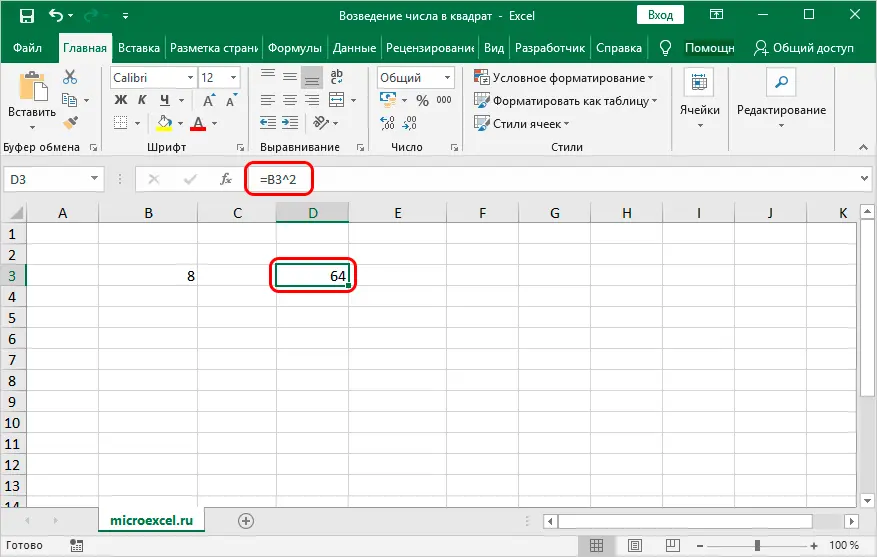
- Select the cell where the result will be displayed, and write the formula in it. As usual, we put “=” at the beginning. Then we click on the cell containing the number whose square we want to get (in our case, this is cell B3). Next, add the degree symbol and the number 2, which means raising to the second power. As a result, the formula looks like this:=B3^2“.

- After that, press Enter to display the result in the selected cell with the formula.

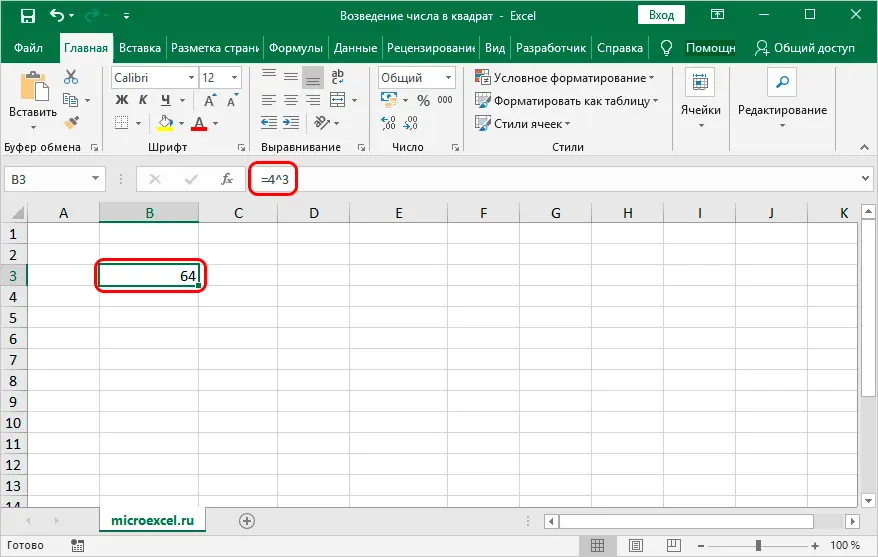
Note: this formula is applicable not only to squaring a number, but also to other powers. In this case, instead of the number 2, we write another desired number. For example, the formula “=4^3” will raise the number 4 to the third power, or, in other words, to the cube.
POWER function for squaring a number
In this case, to find the square of a number, a special function called POWER. This function belongs to the category of mathematical operators and performs the task of raising a specified number to a given power.
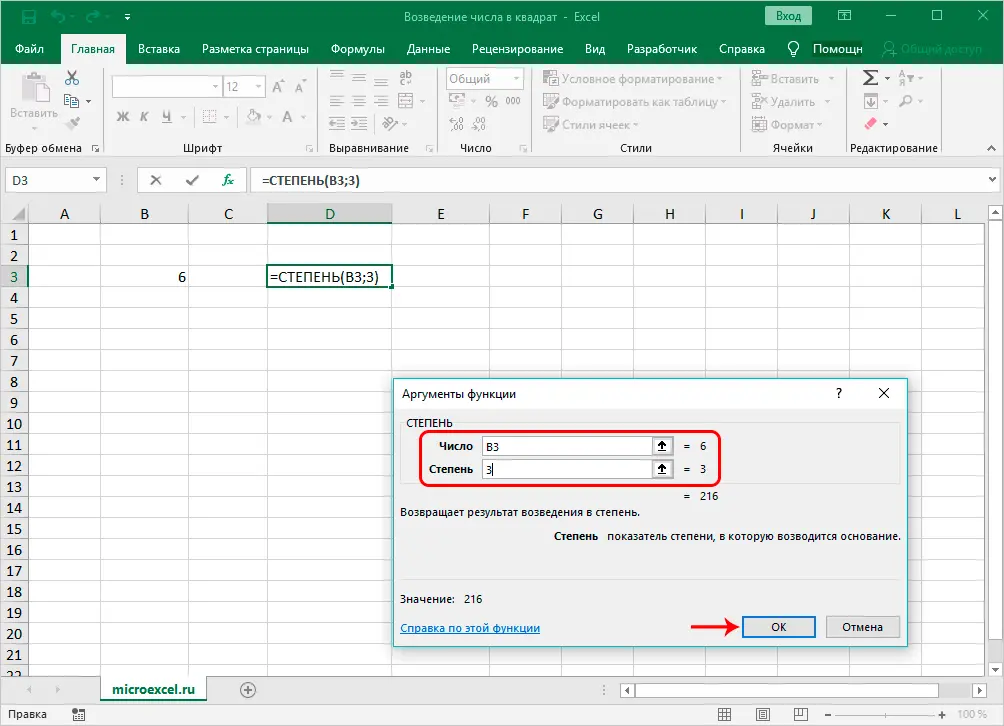
The formula for this operator looks like this: =POWER(number, power).
As we can see, there are two arguments in this formula: number and degree.
- “Number” is an argument that can be represented in two ways. You can write a specific number that you want to raise to a power, or specify the address of the cell with the required number.
- “Power” is an argument indicating the power to which our number will be raised. Since we are considering squaring a number, we indicate the value of the argument equal to the number 2.
Let’s see how to use the function POWER on examples:
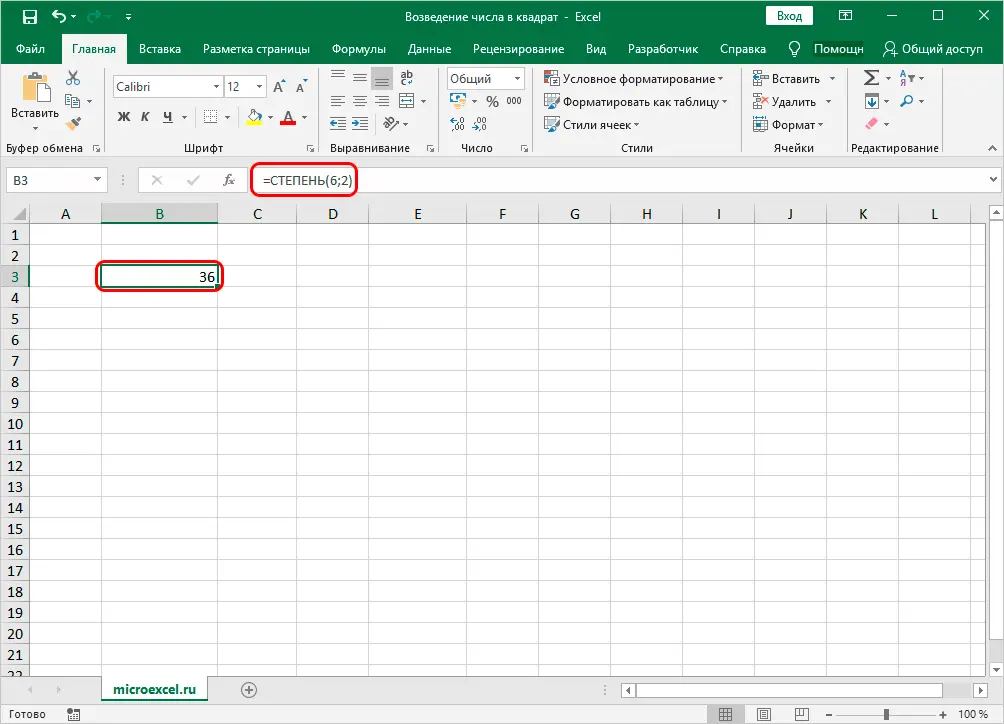
Method 1. Specify a specific number as the value of the “Number” argument
- Select the cell in which we will make calculations. Then click on the “Insert Function” button (on the left side of the formula bar).

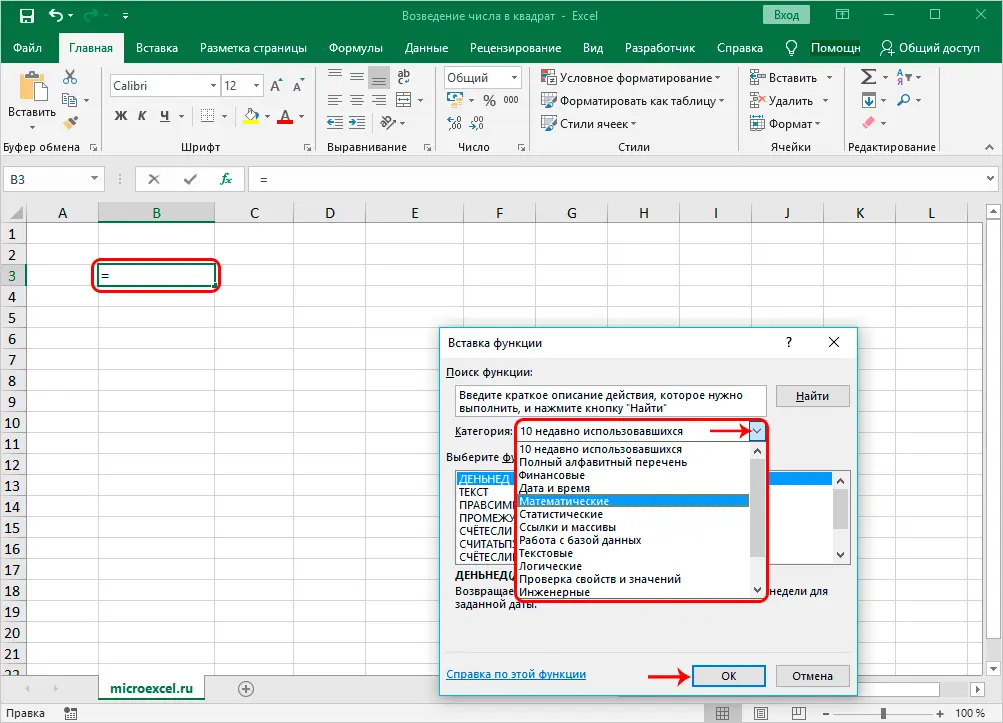
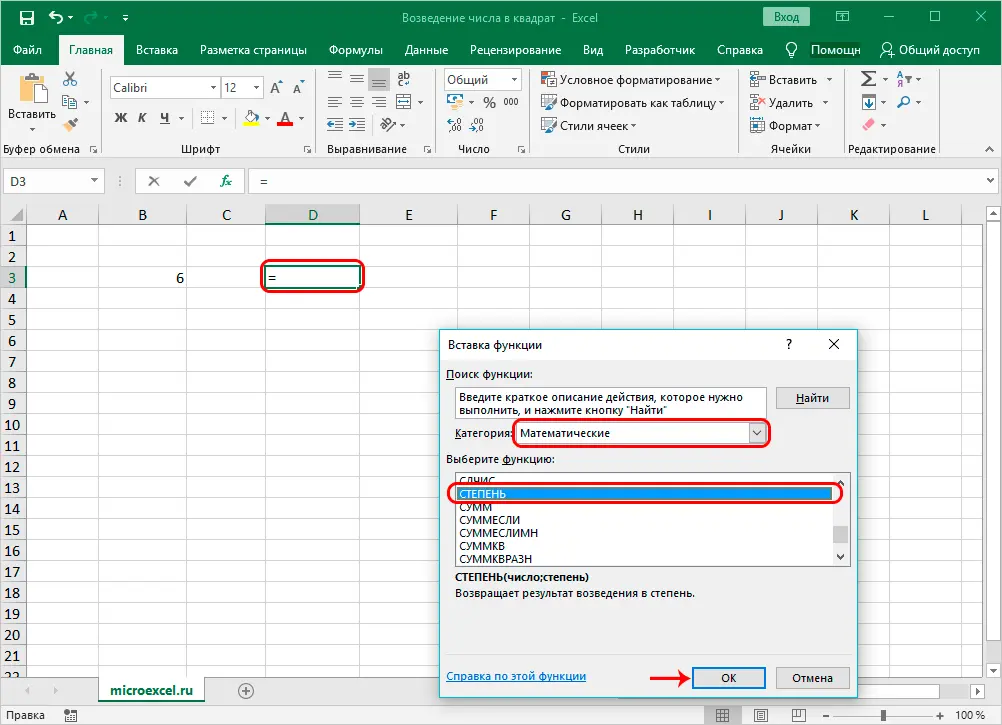
- The Function Wizard window opens. We click on the current category and select the line “Mathematics” in the list that opens.

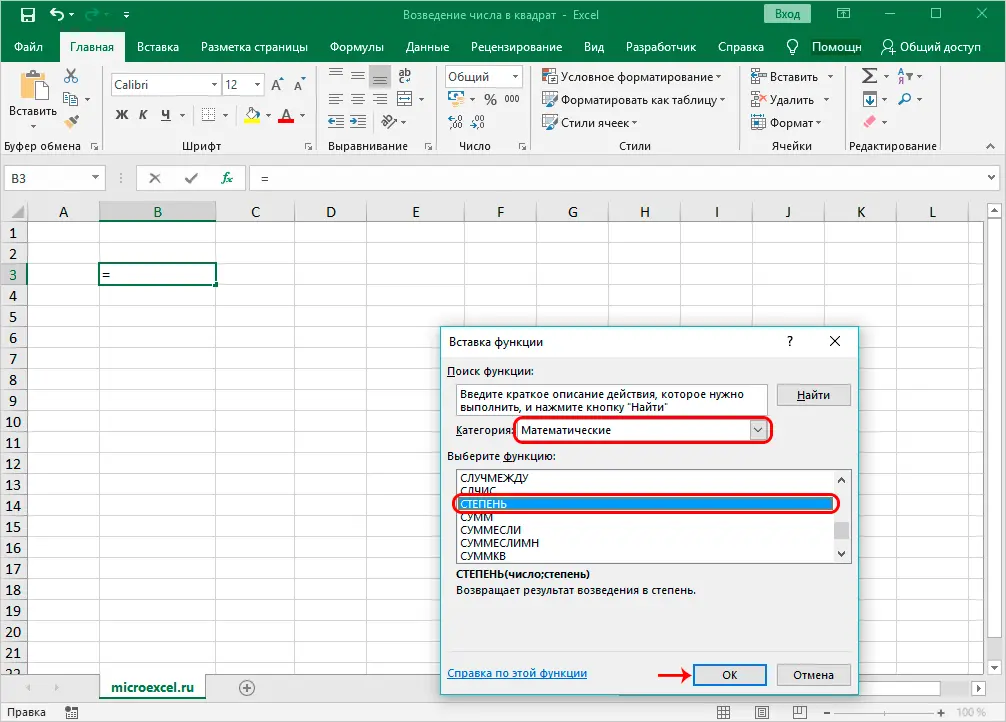
- Now we need to find and click on the operator “POWER” in the proposed list of functions. Next, confirm the action by clicking OK.

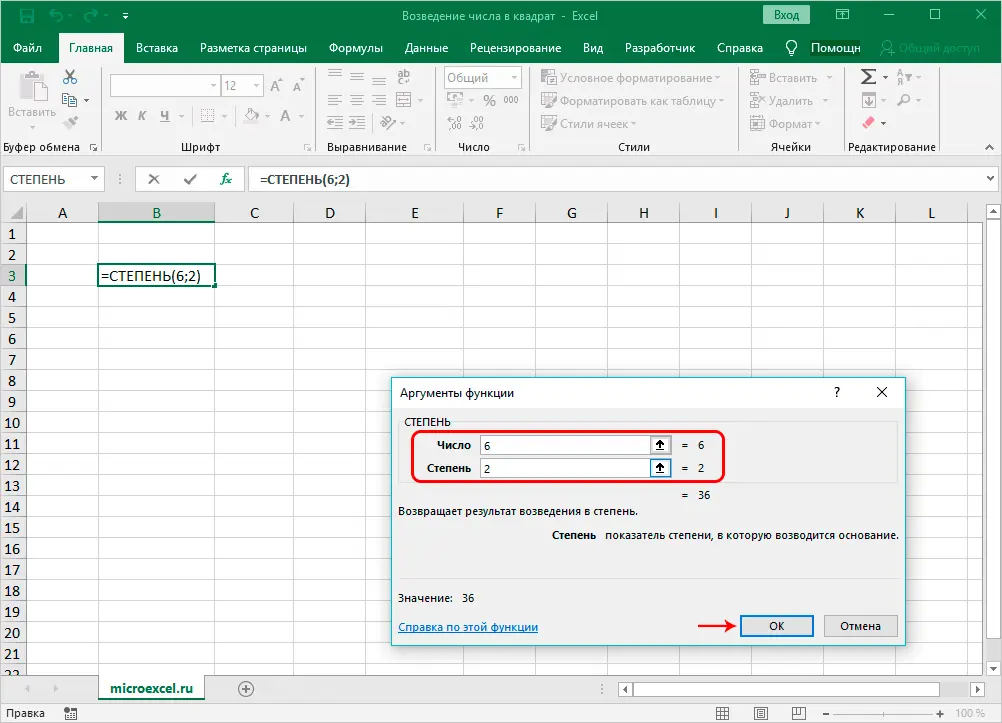
- We will see a window with settings for two function arguments, which contains, respectively, two fields for entering information, after filling which we press the OK button.
- in the “Number” field, write the numerical value that you want to raise to a power
- in the field “Degree” we indicate the degree we need, in our case – 2.

- As a result of the actions taken, we will get the square of the given number in the selected cell.

Method 2. Specify the address of the cell with the number as the value of the “Number” argument
- Now we already have a specific numerical value in a separate cell (in our case, B3). Just as in the first method, select the cell where the result will be displayed, click on the “Insert Function” button and select the “POWER” operator in the “Math” category.

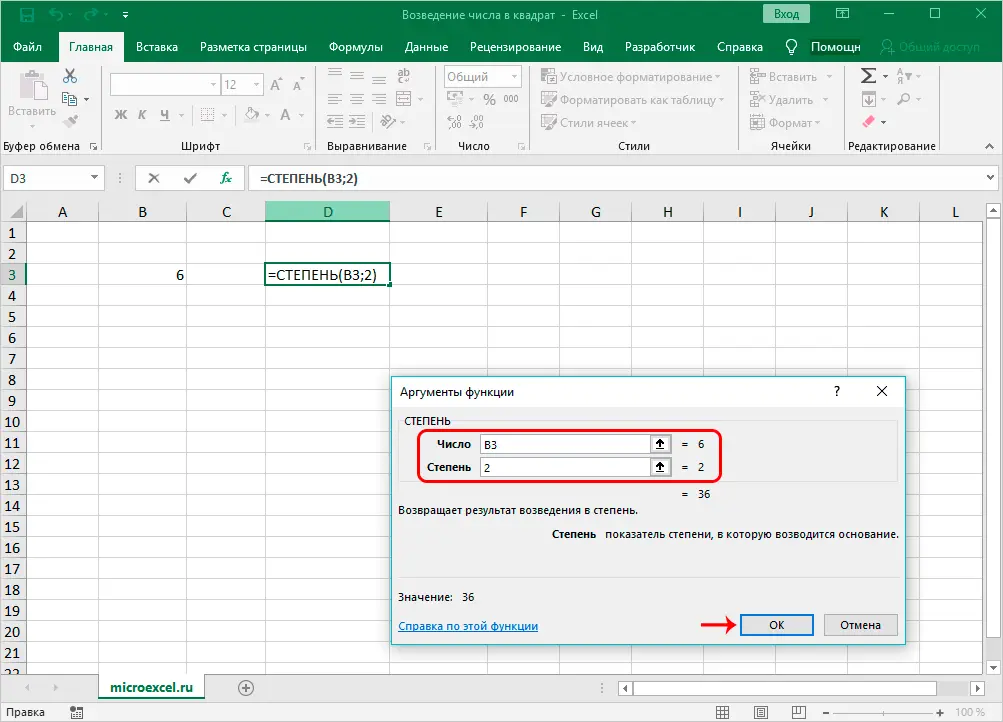
- Unlike the first method, now instead of specifying a specific number in the “Number” field, we indicate the address of the cell containing the desired number. To do this, first click on the argument field, then on the desired cell. The value of the “Degree” field is also equal to 2.

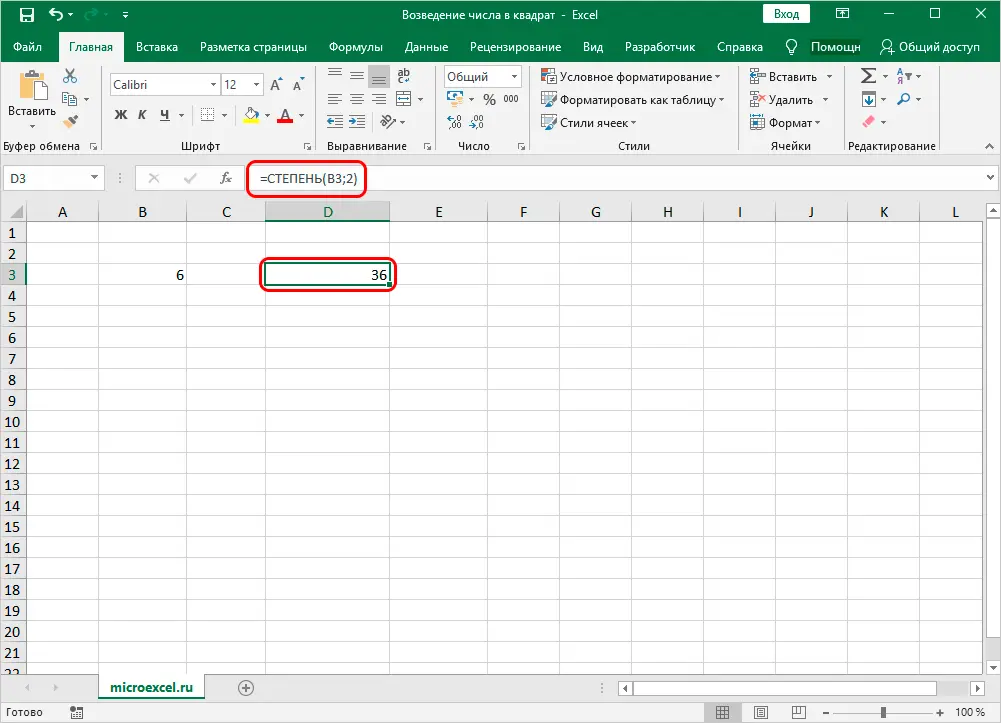
- Next, press the OK button and get the result, as in the first method, in the cell with the formula.

Note: Just as in the case of using a formula for calculating the square of a number, the POWER function can be used to raise a number to any power by specifying the desired number in the value of the “Power” argument. For example, to raise a number to a cube, we write the number 3.
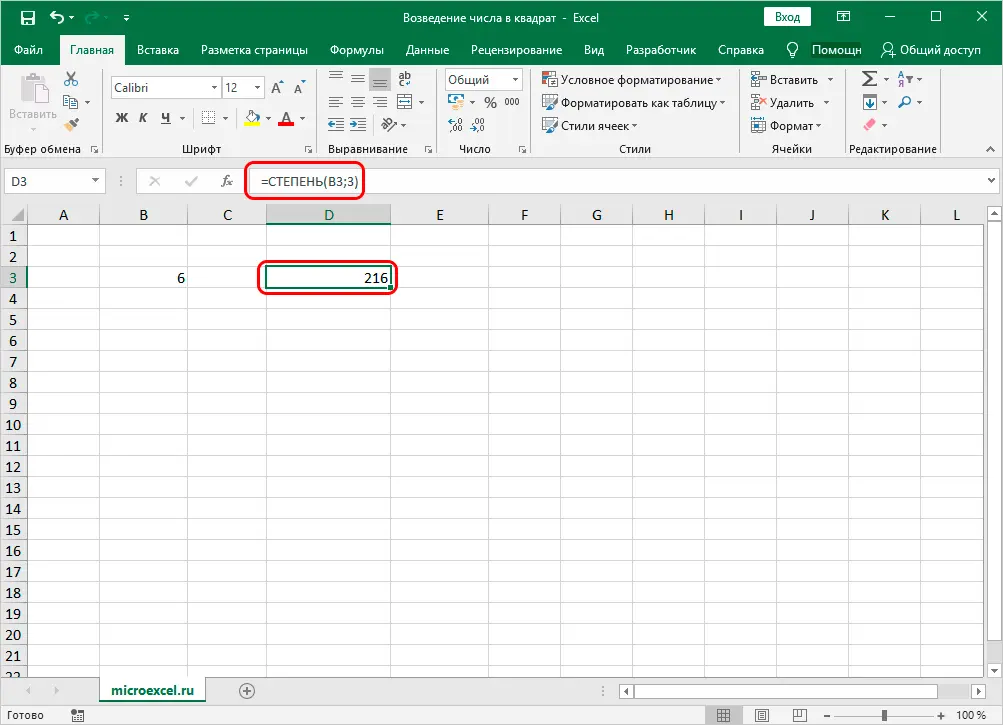
Next, press Enter and the value of the cube of the specified number will appear in the cell with the function.
Conclusion
Squaring a number is perhaps the most popular mathematical operation among all calculations related to the calculations of various degrees of numerical values. In Microsoft Excel, this action can be performed in two ways: using a special formula or using an operator called POWER.