Contents
The skin is the largest and very important organ of the human body. It not only protects the body from the damaging effects of the environment, but also signals one of the first internal troubles. Many diseases and pathologies manifest themselves as a local change in the color and structure of the skin of the lower extremities – in other words, the formation of dark, light, pink, red, blue, yellow or brown spots with various shades.
This process may be accompanied by inflammation, swelling, pain, itching and peeling, or it may not bother a person at all. Therefore, it can be very difficult to understand the variety of symptoms and determine the cause of rashes on the legs.
We will tell you why such skin defects occur, compile a list of the most likely diagnoses and briefly write down the main symptoms, and also, for your convenience, sort the rashes by color and provide a photo of what the spots on the legs look like with various pathologies so that you can most accurately determine the cause of the problem. . However, we recall that self-medication is not an option, especially since many serious diseases are manifested by seemingly harmless spots on the skin. Therefore, at the end of the article, we will tell you which doctor is best to contact, depending on the clinical signs.
Why do spots appear on the body?
The main reasons are as follows:
allergic reactions;
Insect bites;
Traumatic skin injuries – burns, cuts, scratches, wearing tight clothes and shoes;
Infectious diseases of fungal, viral, bacterial, parasitic etiology – mycoses, lichen, pyoderma and other dermatoses;
Congenital or acquired skin pigmentation defects;
Vascular pathologies – varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, venous congestion, atherosclerosis and deep vein thrombosis;
Endocrine diseases – diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, dysfunction of the adrenal cortex or gonads;
Severe pathologies of internal organs – hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, endocarditis;
Malignant and benign neoplasms of the skin;
Blood diseases – thrombocytopenia, idiopathic purpura;
Systemic autoimmune diseases – scleroderma, vasculitis, lupus erythematosus;
Venereal diseases, AIDS;
Poisoning of the body, work in hazardous industries;
Malnutrition, vitamin deficiency;
Frequent stress.
If you notice a suspicious spot or rash on your leg, you first need to think about what it can be most likely to cause: for example, an insect bite if you have recently been out in nature, or an allergy if you have purchased new trousers made of synthetic fabric or washed things with other powder, and so on. If there is no obvious answer, pay attention to additional symptoms and the nature of the rash: whether there is itching, pain, suppuration, and peeling, whether the rash has spread further, whether it is present elsewhere.
Types of spots on the body
By the term “spot” we mean the whole range of possible dermatological manifestations, ranging from small dots to large areas of skin with altered structure and color. Consider also the rash on the legs, which comes in several forms: papule (a raised, rounded area), pustule (vesicle with purulent contents), and vesicle (sack of exudate). Spots can take the form of bruises and spider veins, scaly plaques with clear outlines, redness without a sharp transition, completely discolored or very dark areas of irregular shape – we will discuss all of them, give photo examples and list the symptoms.
So, according to the etiology, spots on the legs are divided into the following categories:
Pigment – occur due to insufficient or excessive production of the pigment melanin, which is responsible for the color of the skin. Such defects are congenital, such as moles, and they are also acquired, and it is not always possible to establish the exact cause of the disease, as is the case with vitiligo. Hyperpigmented areas of the skin often appear at the site of an injury, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, hormonal fluctuations, or simply from old age. White, beige, brown, dark and black spots on the legs of pigment origin are among the most harmless, since this is an exclusively cosmetic defect. However, in rare cases, moles can degenerate into a malignant tumor;
Inflammatory – represent the reaction of the body to traumatic injury, exposure to an allergen or toxin, pathological activity of infectious pathogens. The skin manifestations of this group are usually colored from pink to scarlet and dark red, yellow and orange rashes occur. Such shades are explained by the flow of blood to the sore spot, the destruction of tissues at the cellular level. Spots of an inflammatory nature are often characterized by edema, local fever, pain, burning, itching, suppuration and flaking, which causes serious inconvenience to a person. It should be borne in mind that the disease accompanied by such a rash can be very contagious;
Vascular – are the result of proximity, temporary or permanent expansion of the lumen of the vessels, as well as their growth, tortuosity and the formation of nodes. This category also includes congestion – thrombosis and atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, when the blood flow slows down or stops due to an internal obstacle. Vascular spots on the legs, as a rule, are painted in shades of red and blue: purple, lilac, burgundy. Varicose veins not only look ugly, but also hurt and itch. Spider veins and asterisks on the legs are a painless, but extremely unpleasant and common skin defect, especially among women of mature age. In addition, varicose veins are accompanied by fatigue and heaviness in the legs, which significantly reduces the quality of life;
Hemorrhagic – are the result of damage to blood vessels and outflow of blood into soft tissues, subcutaneous fat and the upper layer of the epidermis. The most common type of hemorrhagic defect is a banal bruise or hematoma as a result of an injury. But there are also more complex pathologies caused by vascular fragility, autoimmune inflammation of connective tissues, blood clotting disorders, lack of platelets – for example, hemorrhagic vasculitis or idiopathic purpura. It is very difficult to diagnose such diseases, they are accompanied by a mass of other disparate symptoms and often have an inexplicable nature. The color of the spots in this category is dark red, blue, purple, and in the final stage sometimes yellow or even green.
Dark (black) spots
Most skin defects of this shade are due to excessive accumulation of melanin, however, there are cases when the spot is vascular or even oncological in nature. It is necessary to carefully monitor the behavior of such dermatological manifestations – whether they increase in size, whether they darken even more, whether they capture new areas of the skin, or whether they are accompanied by a deterioration in general well-being. Consider the most common diagnoses.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
PVG is perhaps the most common explanation for spots on the skin of the legs. Any injuries, especially serious ones – burns, wounds, ulcers, acne that does not heal for a long time and itchy, insect bites – after healing, for some time, they can remind themselves of a dark spot. This is due to the fact that melanocyte cells located in such a skin area produce melanin more intensively, trying to additionally “protect” the sore spot.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation does not cause any inconvenience, in addition to a cosmetic defect, which disappears on its own after a few months, sometimes years.
You can speed up this process with special salon procedures, creams with a brightening effect or folk remedies. A 2018 published systematic review of clinical studies using natural products to treat dark spots on the skin: niacinamide (a form of vitamin B-3), soy, licorice extract and mulberry. These natural treatments have shown promising results in relieving hyperpigmentation. [1]
Results from a small 2017 study show that applying aloe vera gel to the skin can help reduce melasma during pregnancy, after 5 weeks. [2]
It is much easier to prevent the occurrence of PVH, that is, to take precautions, and if a problem has arisen, to qualitatively treat skin lesions and try not to scratch them.
Warts
Plantar warts in the mature stages of their development acquire a dark or even black color. This is due to the fact that a person constantly presses with the whole weight of his body on a sore foot while walking, the capillaries inside the defect burst and close with blood clots. Plantar warts, like any other, are caused by the human papillomavirus, which is carried by about 70% of people. Therefore, such skin lesions are very common. As a rule, they manifest at the age of 20-30 years, in young people who lead an active lifestyle, wear beautiful but tight shoes, visit public places where HPV can be contracted – saunas, fitness clubs, swimming pools.
It is quite simple to distinguish a wart from other spots on the legs: first, a light rounded plaque with a diameter of 0,5-3 cm is formed, it gradually hardens, becomes horny and rises above the surface of the skin, turns yellow, then darkens. There is the concept of a “maternal” wart, which appears first, and around it, others form over time or even merge with it into a single large irregularly shaped spot. Plantar warts cause serious discomfort, but it is not they themselves that hurt, but the surrounding tissues, which are subjected to constant pressure and trauma. Such skin defects in half of the cases disappear on their own, but it is better to contact a dermatologist and remove them.
Toxic reticular melanosis
This disease develops mainly in people employed in the oil refining and coal mining industries, or working in other potentially harmful industries. Almost all patients also have increased sensitivity to sunlight and problems with the digestive tract, which makes it difficult to evacuate toxins from the body. The disease begins with the appearance of extensive red spots on open areas of the body: face, shoulders, arms, legs. Then there is a net or diffuse gray-brown pigmentation, often additionally develops follicular keratosis – the mouths of the hair follicles are clogged with keratinized epidermis, due to which the sore spots are covered with punctate dark tubercles.
It is possible to distinguish toxic reticular melanosis from other possible diagnoses by several signs: dark spots are present not only on the legs, they do not hurt or itch, but quickly spread throughout the body and peel off. The skin becomes dry, thinned and wrinkled in places, the general state of health is disturbed: weakness, dizziness, sometimes nausea, weight loss and appetite. Symptomatic treatment: vitamin therapy, detoxification procedures, moisturizing and softening ointments. The main thing that needs to be done is to eliminate the source of toxic damage to the body as soon as possible. In this case, the prognosis of the disease is favorable.
Poikiloderma
This is a complex of dystrophic and atrophic changes in the skin, which does not have a clear etiology and is both congenital and acquired. In sick people, the skin becomes thinner, melanin unevenly accumulates under it, capillaries look out. Outwardly, poikiloderma looks like extensive fine-mesh hyperpigmentation, sometimes in combination with spider veins. Dark gray-brown spots cover the lower part of the face, neck, limbs, buttocks, inguinal region.
Poikiloderma can also be part of the symptom complex of some genetic diseases, such as Thomson’s or Bloom’s syndromes. But then small dark spots on the skin will be observed almost from birth and be accompanied by additional pathological signs – degeneration of teeth and hair, underdevelopment of the skeleton. If such net rashes appear on the body and legs in adulthood, they are treated with photoprotective agents, vitamins and hormones.
Dubray’s melanosis
Dubreu’s precancerous melanosis, or malignant lentigo, or melanocytic dysplasia is a dark brown or black spot of irregular shape, often unevenly colored, 2 to 6 cm in diameter, coarser and denser in comparison with surrounding tissues. Similar spots are formed on the legs, arms, chest, but especially often on the face. Most of the patients are postmenopausal women. It is believed that an additional risk factor is a light skin tone and increased photosensitivity.
The greatest difficulty is the differential diagnosis of Dubrey’s melanosis from senile keratoma and melanoma (skin cancer), especially considering the fact that in 40% of cases the formation is still malignant. Therefore, if you find a dark spot on your leg or in another place that looks like a blot, does not bother you (does not hurt, does not itch, does not peel off) – see a doctor as soon as possible, do not guess what kind of misfortune it is , and do not wait until the stain begins to grow to an alarming size. Treatment of Dubrey’s melanosis is exclusively surgical.
Nevus Becker
Pathology is otherwise called Becker’s melanosis or pigmented hair hemarthoma. It develops in men five times more often than in women. Manifests usually at the age of 25-30 years. An irregularly shaped brown spot appears on the trunk, shoulders, back or limbs, the area of u10bu50bwhich varies from 60 to XNUMX square centimeters. As the disease progresses, the affected area darkens and in XNUMX% of cases is covered with thick hair.
The formed Becker nevus exists unchanged throughout the rest of a person’s life. It is impossible to cure this skin formation with therapeutic methods, only invasive cosmetic procedures will help – laser resurfacing, dermabrasion. After such treatment, the skin will be red and painful for some time. By itself, Becker’s melanosis is not dangerous to health, does not cause any inconvenience, except for a cosmetic defect, and does not degenerate into cancer.
Black acanthosis
This pathology is characterized by the appearance of dark brown and black spots in places of natural skin folds: under the knees, in the elbows, on the back of the head and neck, in the armpits and in the groin. The reasons for the development of acanthosis nigricans are numerous: these are heredity, obesity, endocrine pathologies (hypothyroidism, polycystic ovaries, acromegaly, hypogonadism, Cushing’s disease, type 40 diabetes, and many others). Acanthosis, as a rule, first manifests itself at a young age – up to XNUMX years.
Outwardly, such dark spots on the legs under the knees resemble dirty stripes – you want to rub them and wash them off. The skin on the affected areas is rougher and drier, it rarely itches, but it can peel off, and is sometimes covered with a small papillomatous rash. If black acanthosis is associated with excess weight and constant friction, then the spots may disappear on their own when a person loses weight. Treatment of acanthosis is symptomatic and hormonal.
Follicular keratosis
In the people, this disease is called “chicks”. The essence of the pathogenesis is that the epithelial cells are filled with keratin before they mature, the old stratum corneum is not rejected, but clogs the mouths of the hair follicles, as a result of which the hairs on the body cannot grow outward and fold into a knot. Small dark spots then remain in place of these nodules, especially often on the legs, but there are pimples on the arms, and on the back, and even on the face.
Follicular keratosis usually develops during adolescence. It is believed that there is a hereditary predisposition to it. However, the disease can be triggered by a wide range of factors, including infections, trauma, hormonal problems, and beriberi. Dark spots on the legs and other parts of the body caused by follicular keratosis are purely cosmetic and do not pose any danger. However, sometimes chicks are accompanied by itching and flaking, which therapeutic ointments help to cope with.
Keratoma
This is a benign skin neoplasm that occurs due to the accumulation of keratin in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. There are several types of such tumors, the most common is senile or simply senile keratoma. It looks like a dark brown, brown or black convex spot on the leg, arm, head, in the auricle – that is, on open areas of the body that are regularly exposed to solar radiation. In addition to ultraviolet radiation and age-related changes, doctors cite hormonal disruptions, hereditary predisposition, and chemical damage to the skin as the causes of keratomas.
A keratoma is a tuberous outgrowth of a round or irregular shape with a soft, scaly structure and a diameter of 3-5 mm to 6 cm. The tumor can be slightly painful, the upper layers peel off from it at the slightest damage, which often leads to bleeding. In case of penetration of pathogens, such a spot on the leg can become inflamed and fester. Some types of keratomas (follicular, seborrheic, angiokeratoma) are harmless in terms of the risk of malignancy, but the solar one, which appears mainly on the face and at first looks like a scaly bright pink plaque with clear edges, can spontaneously degenerate into a malignant tumor, about which read below .
Melanoma
This malignant tumor was previously called melanoblastoma, it comes from cells that synthesize the pigment melanin, that is, from melanocytes. Melanoma affects mainly the skin, less often the mucous membranes and the retina of the eyes. Such a tumor is one of the most dangerous types of cancer, because it grows rapidly, metastasizes through the lymphatic network to other organs and tissues, and often recurs even with timely detection and removal.
Melanoma on the leg looks like a small dark spot of irregular shape with rounded outlines and a rougher structure than the surrounding skin areas. The color of the neoplasm varies from light brown and reddish brown to black, and the pigmentation is almost always uneven. Melanoma often occurs at the site of a mole, this is preceded by a feeling of soreness, a change in skin tone, hair loss and the appearance of bleeding in the defect area. If you experience any of these symptoms, see your doctor as soon as possible!
Pink and red spots
When it comes to pink or red rashes, one can almost certainly suspect an inflammatory etiology – the body reacts in this way to the pathological effects of allergens, toxins, infectious agents and their waste products. In addition, red spots on the legs may be the result of a chemical or thermal burn. Many diseases that cause skin rashes are contagious and require appropriate precautions. But we will begin our consideration of this group of defects with the most common – that is, with the bite of various insects.
Insect bites
It would seem that if someone bit you, then the reasons for the spots on your legs are obvious. But not always a person has time to notice the culprit of the bite, especially if everything happens during outdoor activities or, conversely, a good night’s sleep. In addition, some insects are so small and secretive that the affected person can only guess who bitten all the legs, and how to get rid of the unbearable itch. Let’s briefly review the symptoms of bites of the most common insects.
Mosquitoes
If you do not suffer from hypersensitivity to mosquito saliva, the bite site will look like a pink rounded spot with a diameter of 3-5 mm, almost not rising above the surface of the skin. A slight itching is possible, which will subside no later than 12 hours after the attack. You can probably suspect a mosquito by the nature of the bites – usually there are several of them, they are located nearby on an open area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe body (head, arm or leg, if you have a habit of sticking it out from under the covers during sleep).
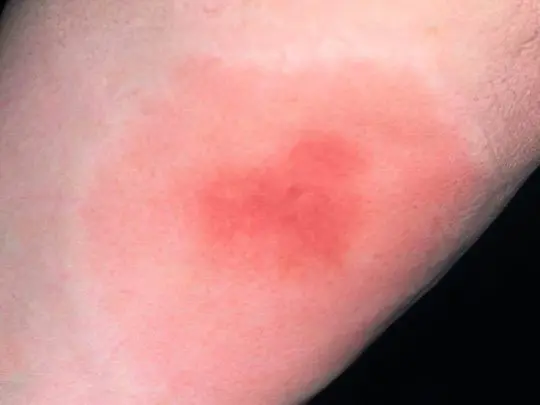
Mosquito bites cause significant inconvenience to hypersensitive people – they have blisters up to one and a half centimeters in diameter, which are very itchy and even hurt, sometimes the body temperature rises. In this case, you need to take an antihistamine (Cetrin, Loratadine) and apply a special soothing ointment (Fenistil, Bepanten) to the affected area.
Moss
Mosquito bites are potentially more dangerous than mosquito bites. The midge attacks a person in the morning and daytime, waiting for the victim near water bodies, in thickets of tall grass, on the edge of the forest. A whole flock of tiny insects sticks around the open area of the body, pointwise “cutting off” the surface layer of the skin and sucking out lymph and blood from the formed wounds. The victim at this moment does not feel anything, because the saliva of midges acts as an anesthetic. New flocks of midges flock to the smell of blood, and if they are not noticed and not driven away, the consequences will be worse.
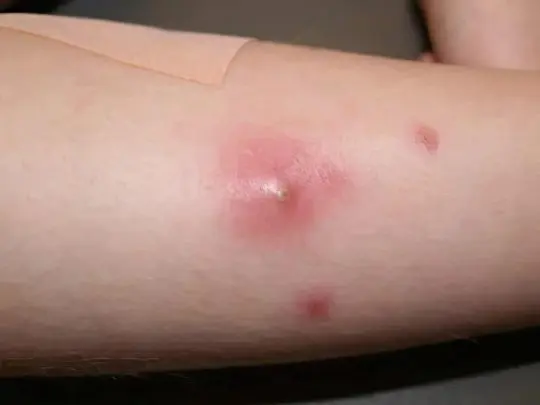
After 30-60 minutes, the bitten place swells and begins to itch terribly. Against the background of solid redness, individual points are distinguishable – bite marks. Noticing such red spots on the leg or other part of the body, it is necessary to clean and dry the skin, apply a healing ointment and bandage the damaged area so as not to comb it and not introduce an infection.
Fleas
For fleas, a person is an “intermediate” victim; it is much more convenient for them to parasitize domestic animals, hiding in their thick fur and biting through the thinner epidermis. But a flea attack on a person happens often, moreover, small red spots from bites appear on the legs, because it is easiest to jump to them. Fleas do not produce an anesthetic, but bite into the skin very strongly, so it is difficult not to notice the pain from a bite. However, it is extremely difficult to catch and identify a nimble insect.
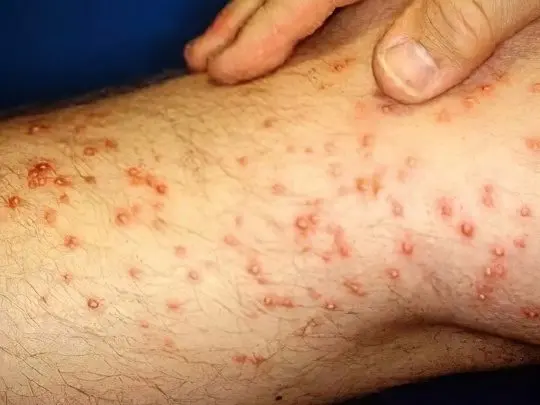
The places bitten by fleas are very itchy, you want to comb them until they bleed. This cannot be done – it is better to disinfect and seal the red spot with a band-aid, and most importantly, to sanitize the premises in order to avoid such problems in the future.
Bedbugs
Bed bugs are a real scourge, it is very difficult to detect them and eradicate them from the house forever. They attack one by one, at night, choosing places with the thinnest and most delicate skin: on the legs under the knees, in the neck and chest, on the face. During the first 15-20 minutes, the anesthetic contained in saliva acts, so the bug has time to drink blood before it is noticed by the victim. One bloodsucker makes a series of 7-8 bites, moving along the chosen subcutaneous capillary.

In the morning, a person discovers a path of large pink-red swollen spots with blisters in the middle. These blisters itch unbearably, especially if there is a tendency to allergic reactions. It is recommended to apply an antihistamine inside and treat the bitten area with a healing ointment. However, all these efforts will be in vain if the bugs are not removed.
Wasps, bees, hornets and bumblebees
These are rather large and aggressive insects, but since they do not feed on blood, they attack people only when it seems to them that a person is a danger to themselves or their homes. A distinctive feature of this group is the presence of a sting – a sharp harpoon-like outgrowth at the end of the abdomen. During the bite, the bee leaves a stinger inside the victim and dies, pulling out part of the internal organs. This is due to the presence of notches on her sting – it cannot be pulled out. In wasps, hornets and bumblebees, the sting is bare, it is easily removed from the wound, so one insect, if it is angry with a wave of its hands, can bite several times in a row.
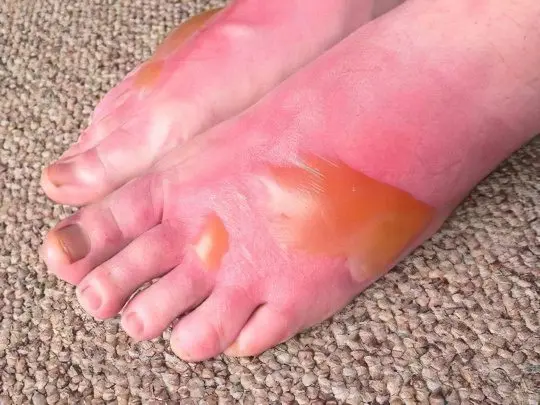
The poison of these insects is potentially very dangerous – 2% of the victims develop anaphylactic shock and Quincke’s edema, which is fraught with death. In all people, without exception, the sting of a bee or wasp causes severe pain and swelling. If the swelling does not subside for a long time even after applying a cool compress, an antiallergic drug should be taken.
Horseflies and Gadflies
These are large flies that parasitize livestock, but sometimes they can also attack humans. The bite of a horsefly and a gadfly is very painful, in addition, the insect injects a toxin and an anticoagulant into the wound, which prevents blood clotting. The wound after the bite is very itchy and does not heal for a long time. It must be treated with an antiseptic and covered with a protective bandage. If the victim shows signs of an allergic reaction, an antihistamine should be taken.
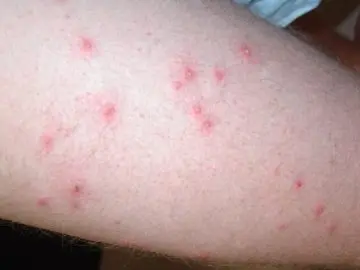
It should also be borne in mind that horseflies act as carriers of many dangerous infections, and gadfly larvae can theoretically develop in the human body, such cases have been recorded. Therefore, if a red spot on a leg or in another part of the body hurts for a long time after an insect attack, while the general well-being is disturbed, it is necessary to visit an infectious disease specialist.
Ants
These highly organized insects for the most part do not show aggression towards humans (we will not talk about exotic species here), but if you accidentally invade their home, for example, during outdoor recreation, the ants may well bite and suffer, before everything, legs. Black forest ants attack in a crowd, covering the skin with small red spots.
During a bite, they inject formic acid into the wound, which is quite harmless, but can cause a violent reaction in allergy sufferers. The bitten area is swollen, sore, blistered and itchy, and fever and nausea may set in. In this case, antiallergic therapy is required. Usually, sanitizing the skin and applying a cool compress is enough.
pliers
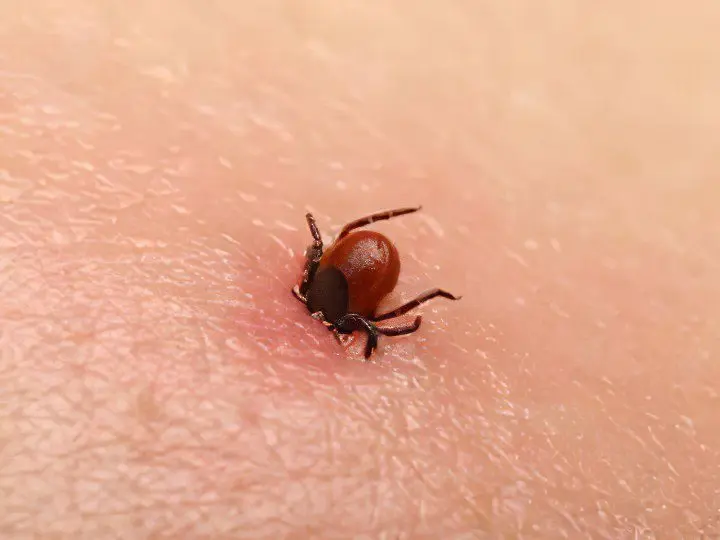
These small blood-sucking insects pose the greatest danger in terms of infection with borreliosis and tick-borne encephalitis. The peak of attacks occurs in spring and autumn, ticks are waiting for their victims in the thickets of shrubs, in the forest park zone, along the banks of reservoirs. Red spots on the legs as a result of a tick bite are not uncommon, usually these insects crawl under the trousers. Hidden in clothes, the tick is introduced under the skin and injects a powerful anesthetic, so it manages to remain unnoticed by the victim all the time while feeding (from one hour to a week). A well-fed bloodsucker falls off the body itself, unless of course it is noticed earlier.
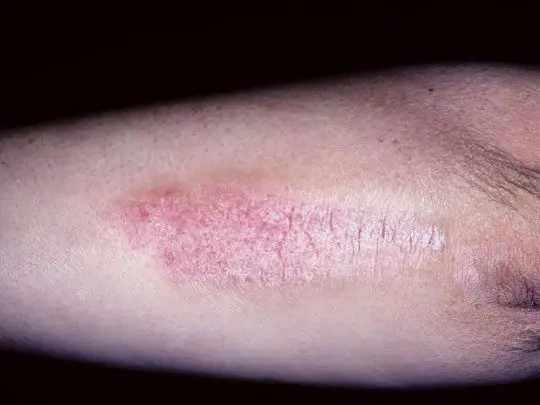
A tick bite looks like a small red spot, in the center of which the culprit’s abdomen sticks out. If the insect has settled for a long time, and an allergic reaction has begun, then an additional red halo forms around this spot. Having found a tick in yourself, you should not try to remove it, you need to go to an ambulance station or an emergency room, where you will be assisted, prescribed preventive therapy, told about the rules for monitoring your health after a bite, and take the tick for analysis.
Video: 10 insect bites you need to be able to recognize:
Blue and purple spots
Defects of similar shades are almost certainly of a vascular or hemorrhagic nature: either the vessels have expanded, or blood stasis is observed, or subcutaneous hemorrhage has occurred. Let’s look at the main causes of purple and blue spots on the legs, starting with the most common and obvious diagnoses.
Hematoma
This term means a banal bruise, which any person has ever received, especially those who are always in a hurry and clumsy. Sometimes the moment of hitting furniture or other piece of furniture is not even remembered, just after a while we notice a blue spot on the leg, which then begins to “bloom”, changing its shade to purple, lilac, and, finally, to greenish yellow.
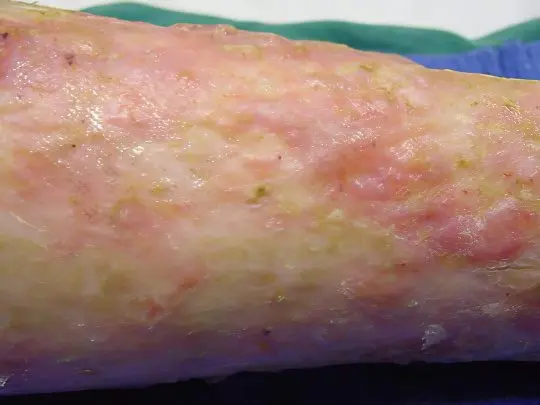
How to distinguish a hematoma from other pathologies? Quite simply – it is painful when pressed, does not itch or peel, around it there is usually swelling of the soft tissues. Large, extensive hematomas can cause serious suffering, they often accumulate a large volume of outflowing blood, and it must be removed by puncture. The introduction of infection into the hematoma cavity is fraught with very dangerous consequences, up to gangrene. And a small bruise on the leg can be easily dealt with at home – if you just hit, apply cold to the bruised area. Local anticoagulants, for example, heparin ointment, contribute to the speedy resorption of the hematoma.
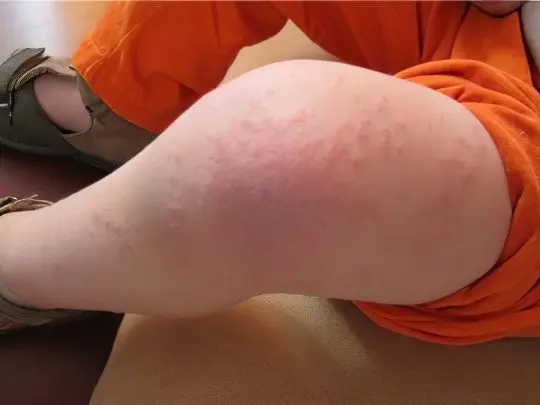
Flaming nevus (port wine stain)
This is a vascular mole formed by a group of dilated subcutaneous capillaries. Port wine stain is so named because of its characteristic color, but its hues can vary from purple to dark purple. Usually the defect is the only one, it has an arbitrary shape, does not rise above the surface of the skin, brightens when pressed, does not disturb the person. A flaming nevus is a congenital feature that can be seen even on the body of an infant. As a rule, port-wine stains look lighter at a young age, and darken with age. They are usually located on the face, but can affect any other area.
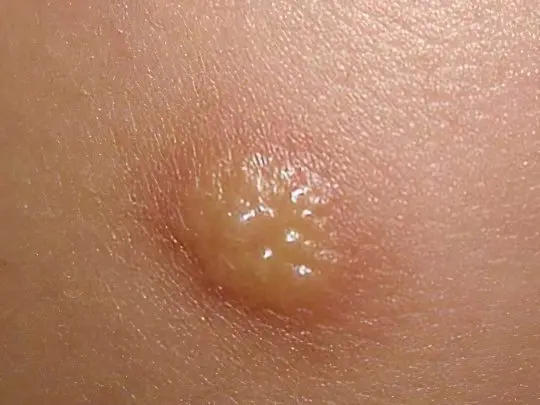
It is impossible to cure a flaming nevus with therapeutic methods. As the wine stain matures, it increases in size along with the person. If the defect is of great concern, you can remove it with a special pulsed laser. The treatment is very effective and allows you to completely get rid of an ugly red-purple spot on the leg or even on the face, moreover, the use of this technology is permissible from early childhood.
Telangiectasia
Doctors use this term to mean what we commonly call vascular networks or asterisks – that is, dilated subcutaneous capillaries with a diameter of 0,5-1 mm, forming a pattern like a “spider” or arranged randomly. Telangiectasias are congenital and acquired, they are among the symptoms of many diseases, but sometimes they appear on their own, creating a cosmetic defect.
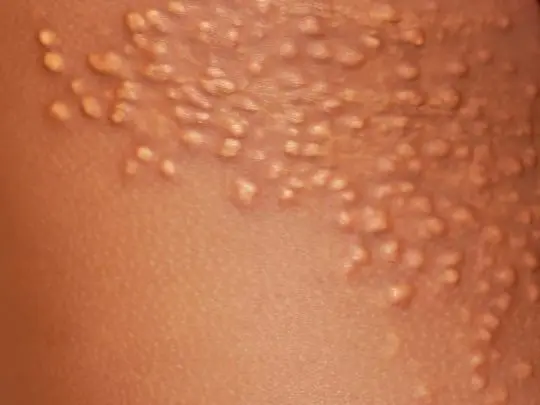
Spider veins appear mainly on the face and wings of the nose, as well as on the legs, especially often on the back of the thighs and lower legs, closer to the knee joints. Women over 40 often suffer from such skin defects, the good news is that the treatment of telangiectasias is not difficult – they are easily removed by sclerotherapy and laser surgery.
Phlebeurysm
The disease is characterized by thinning of the venous walls of the lower extremities, expansion of the lumen of the vessels, the formation of convolutions and knots protruding through the skin, as well as heaviness, burning and pain in the legs, fatigue when walking and night cramps. Evening itching indicates the beginning of trophic changes. Varicose veins are dangerous for their complications – phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis and venostasis. In the first stages, patients are only concerned about a cosmetic defect. But without treatment, the situation will inevitably worsen. It is possible to remove varicose nodes only by surgery, for this you should contact a phlebologist surgeon.
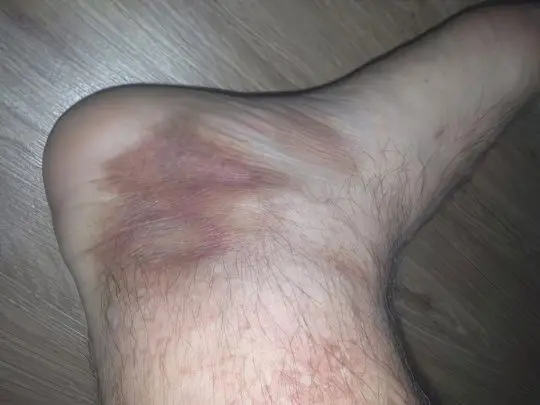
To determine that the cause of purple and blue spots on the legs lies precisely in varicose veins, it is quite simple according to the symptoms described. This disease mainly affects women of mature age, especially those who are overweight. But you need to be careful – sometimes in the absence of varicose veins, deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities develops. This is a very dangerous condition, which is manifested by bursting pain, an extensive red or blue spot on the leg, severe swelling and local fever. If you do not see a doctor in time, you can lose your leg.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis
This disease is otherwise called Shenlein-Genoch syndrome, allergic or rheumatic purpura. Hemorrhagic vasculitis has a mixed, not fully established etiology, mainly autoimmune. It usually occurs after a severe infection. Connective tissues are affected, including the walls of blood vessels and capillaries, which leads to numerous subcutaneous hemorrhages. Pinpoint spots are called petechiae, in the form of stripes – vibexes, small-spotted – ecchymosis, large-spotted – bruises.
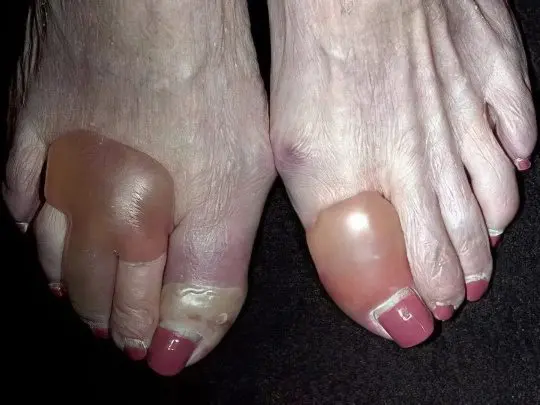
The disease begins with the appearance of red-violet spots on the legs, in the ankle area. These formations slightly protrude above the surface of the skin, do not hurt or itch. Sometimes they merge into a common amorphous mass and spread higher to the thighs and buttocks. After a few days, the spots darken, turn brown and gradually disappear. The course of hemorrhagic vasculitis is usually benign, but there are also severe forms of the disease, accompanied by articular, abdominal and renal syndrome – their outcome is unpredictable. Treatment is reduced to taking antiplatelet agents, heparin and nicotinic acid, sometimes plasmapheresis is prescribed.
Schamberg disease
Hemosiderosis, Schamberg’s disease or chronic pigmentary purpura is a disease of unknown etiology, most likely autoimmune, affecting mainly men of mature age. As a result of the destruction of subcutaneous capillaries, numerous small dark spots appear on the legs – petechiae. They may have a reddish, brown or brown tint. There are other signs of hemosiderosis: telangiectasias (vascular networks and asterisks), plaques, nodules, and sometimes several types of rashes at once.
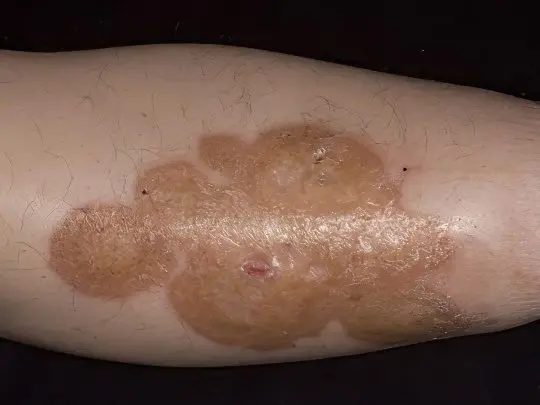
Schamberg’s disease has a benign course, only subcutaneous capillaries are affected, internal bleeding does not develop. Dark spots on the legs with this pathology do not disturb the patient in any way – they do not hurt or itch, but they can occupy large areas and thereby create serious cosmetic inconvenience. In this case, hormonal and anti-inflammatory treatment, a hypoallergenic diet, blood purification procedures – hemosorption, plasmaphoresis are indicated.
Idiopathic (immune) thrombocytopenic purpura
In another way, it is called Werlhof’s syndrome or primary hemorrhagic diathesis. The reasons for the development of the disease are not completely clear, patients have a persistent deficiency of healthy platelets, most often women of middle and mature age suffer. The disease is characterized by the spontaneous occurrence of subcutaneous hemorrhages and cutaneous hemorrhages, as is the case with the vasculitis described above.
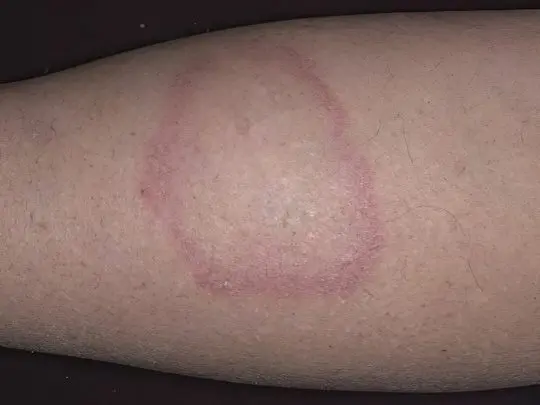
In addition to brown, purple and blue spots on the legs, sometimes similar to ordinary hematomas, patients are concerned about nasal, gingival and uterine bleeding, abdominal pain, hematuria, iron deficiency anemia, fever, enlarged spleen. Hemorrhage may suddenly occur in the retina of the eye or even in the brain. With any, even minor damage to the skin, bruises remain on it, but more often they occur for no reason at all. Treatment of thrombocytopenic purpura is complex, very complex, success and prognosis depend on the severity of the disease.
Video: Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Spots on the legs with diabetes
Almost all diabetics have minor skin defects, about half have severe lesions, and the more severe and longer the disease, the higher the risk of serious complications – trophic ulcers and gangrene. Negative changes in the skin and soft tissues in people with diabetes mellitus are dictated by a chronic excess of glucose in the blood and the accumulation of waste products of pathological metabolism.
Diabetic dermopathy
First, small oval light brown or reddish spots 0,5-1,5 cm in diameter appear on the outer lateral surfaces of the feet or the front of the legs. They are often symmetrical and form on both legs at the same time. Then the spots grow, darken and often merge into a common affected area, which is characterized by dryness, peeling and itching.
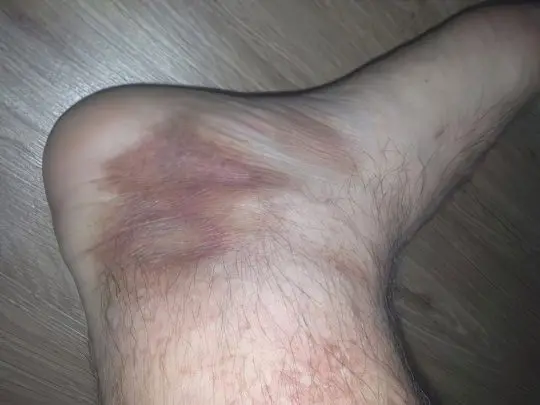
If diabetic dermopathy is accompanied by polyneuropathy, pain and burning may also be observed. Such symptoms most often develop in older and long-term ill men. Diabetic spots on the legs spontaneously disappear after a few years, but may reappear.
Pemphigus
True autoimmune pemphigus accounts for only 1-1,5% of all dermatoses, that is, it is extremely rare, while it is life-threatening and has an extremely unfavorable prognosis. Against the background of type XNUMX diabetes mellitus, the development of diabetic pemphigus is possible, which is manifested by the appearance of bullae of various sizes, mainly on the skin of the lower extremities.
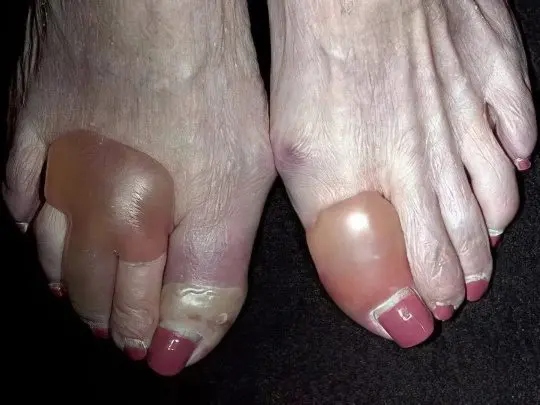
These blisters are filled with cloudy yellowish serous contents, they burst, and in their place painful wound surfaces are formed, constantly weeping and difficult to heal. It is important to prevent infection of wounds, they require careful care.
Lipoid necrobiosis
The disease is a consequence of a violation of carbohydrate-fat metabolism and is associated with diabetes mellitus in about 75% of cases. The pathological process begins with the formation of bright pink or red nodules, surrounded by a cyanotic border and having a yellow-gray notch in the middle. These formations are localized mainly on the skin of the lower extremities, namely, in the region of the legs.
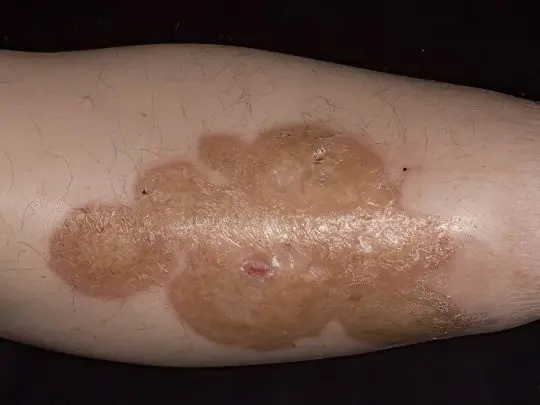
Over time, individual nodules merge into large dense plaques with a characteristic waxy sheen, as if covered with a translucent film. In the center they are atrophic and resemble foci of scleroderma, and along the edges they have a brown or purple roller, slightly rising above the surface of the skin. Diabetic women suffer from necrobiosis lipoidis approximately 3 times more often than men. The disease does not go away spontaneously, it is very difficult to treat and often recurs.
granuloma annulare
Otherwise known as anular granuloma, it has an unknown etiology and is associated with several diseases, including tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, rheumatism, and diabetes mellitus. Pathogenesis begins with the appearance of dense, smooth, shiny spots on the legs, arms, chest, abdomen or back. Formations may have a beige, pink, red or purple hue. They don’t flake or itch.
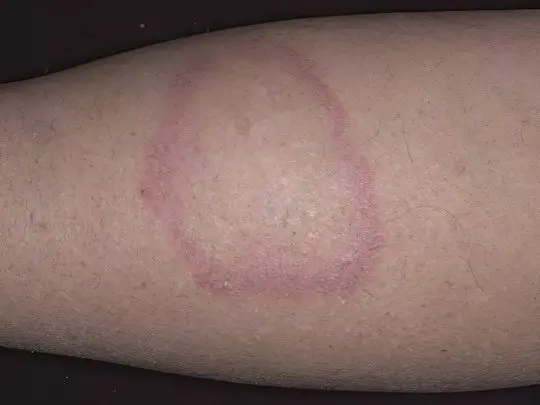
After a few months, rounded papules merge into a common conglomerate like a plaque with jagged edges that have a brighter color than the middle part. Annular granuloma can reach a significant size – up to 10 cm in diameter or more. Treatment of such spots on the legs in diabetes mellitus is reduced to maintaining normal blood sugar levels and topical application of corticosteroids in case of inflammation and tenderness of granulomas.
Trophic ulcer
This is a formidable complication of diabetes mellitus, predominantly of the second type. An ulcer can form in the lower leg (on the front or side surface) or on the foot (in the area of the finger joints, on the sole). For the second option, there is a separate collective term – “diabetic foot”. Why do trophic ulcers occur in diabetes? Firstly, the skin of the legs loses its sensitivity, and the person does not notice small cuts and cracks into which the infection penetrates. Secondly, due to venous stasis, trophic disorders and chronic oxygen starvation of tissues, the purulent inflammation that has begun cannot be stopped by any means.
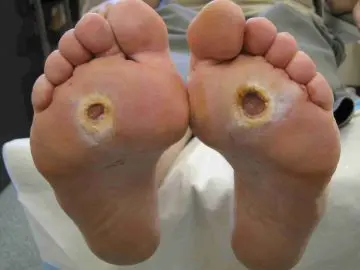
The formation of trophic ulcers begins with the appearance of a dense, light, glossy elevation, from the center of which lymph is released, then the wound opens and rots inward, sometimes to the very bone. Inflammation is bacterial and / or fungal in nature, in every fourth case it ends with gangrene and amputation of the affected limb. The reason is that trophic ulcers do not heal, no matter how thorough the treatment.
Gangrene
The most dangerous complication of diabetes is recorded in approximately 15% of older people with a long and severe course of the disease. There are two types of diabetic gangrene: dry and wet. The first type is more favorable in terms of prognosis, in which part of the lower limb (usually one or more fingers) simply turns black and mummifies, and can even tear itself away from the body.
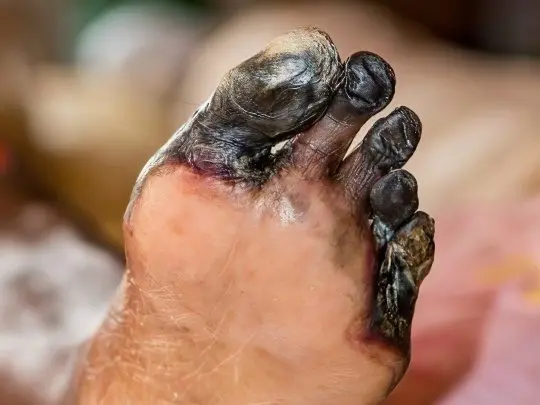
The decay products of tissues still enter the blood, but not in such a huge amount as with wet gangrene, which is much more common, especially if the diabetic is overweight. In this case, black spots on the legs are constantly weeping foci of decay, toxins poison the body, cause sepsis and death if the affected leg is not amputated in time.
Video: type 2 diabetes and leg complications:
What to do if the spots on the legs itch and peel off?
To eliminate itching, it is necessary to take an antihistamine drug inside, but it must be understood that the use of such drugs without a doctor’s prescription is highly undesirable.
It is better to visit a dermatologist and show him your spots on your legs. The doctor will diagnose, determine the exact cause of the problem and prescribe adequate therapy. No need to suffer, sorting through various ointments in a pharmacy and hoping that one of them will finally help you get rid of itching and flaking.
Which doctor should I contact for spots on the legs?
If you come to an appointment with a local therapist or pediatrician, you will certainly not be mistaken, since the general doctor has sufficient experience and knowledge to establish the initial diagnosis. If necessary, he will refer you to a specialized specialist: dermatovenereologist, allergist-immunologist, hematologist, rheumatologist, endocrinologist, hepatologist, gynecologist, infectious disease specialist, phlebologist, oncologist, surgeon, cosmetologist – the choice is very wide and depends on the specific disease. The main thing to do if there are incomprehensible spots on the legs is to really get together and go to the doctor, and not engage in self-diagnosis. Take care of yourself and be healthy!









