Contents
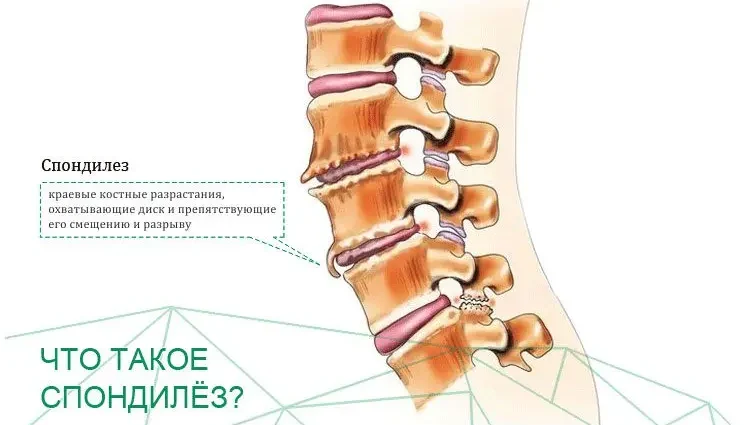
Spondylosis is quite common. The disease is accompanied by degenerative and dystrophic changes in the spine. One or several of its departments can suffer. With the disease, the vertebral discs, which are represented by elastic tissues, are destroyed. This leads to a narrowing of the gaps between the vertebrae, as a result of which the joints begin to rub against each other. This pathology causes severe pain.
The body starts a compensatory mechanism in an attempt to reduce friction. Therefore, spikes form on the surface of the vertebrae. They are called osteophytes. These growths put pressure on the nerve fibers, which contributes to increased pain.
Spondylosis is a chronic disease that often affects the elderly.
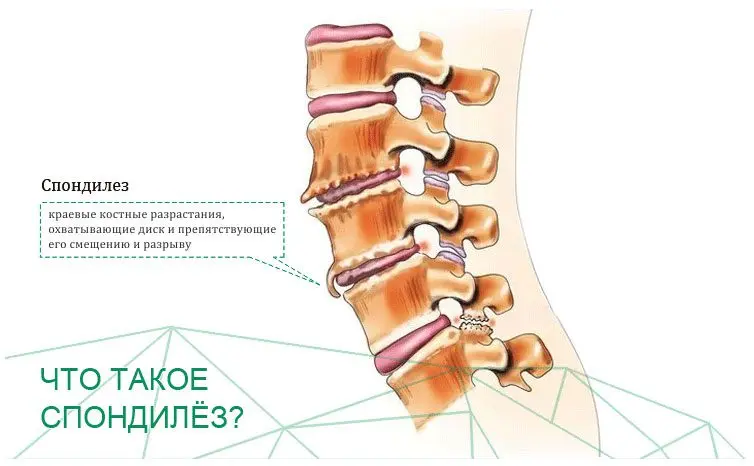
Spondylosis – what is it?
Spondylosis is a chronic disease of the musculoskeletal system, characterized by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spinal column. Any of its departments can be involved in the pathological process, but most often the lumbosacral zone suffers. In the initial stages of the development of the disease, the symptoms resemble osteochondrosis, so the person is in no hurry for medical help. As the pathology progresses, it makes itself felt more and more. Neurological disorders will be especially pronounced in the case when spondylosis affects the cervical spine.
Causes of spondylosis
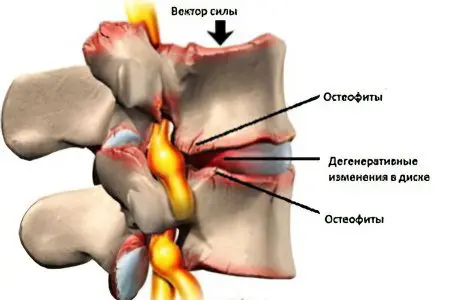
In the early stages of the development of the disease, its symptoms are absent. Characteristic neurological symptoms appear much later, when nerve fibers are involved in the pathological process.
Reasons that can lead to the development of spondylosis:
Disturbances in metabolic processes.
Age-related changes in the body.
Excessive load on the spine, which leads to persistent spasms.
Long-term static load on the spine.
Hypodynamia.
Infections.
Hereditary predisposition.
Tumor neoplasms.
Classification
Depending on the location of the pathological process, the following types of spondylosis are distinguished:
cervical spondylosis.
Thoracic spondylosis.
Spondylosis of the lumbar spine.
Symptoms of the disease will vary, depending on which department has been affected.
Stages of spondylosis
Spondylosis is progressing all the time.
Over time, it will go through 3 stages of its development:
First stage. In the vertebral body, small processes are formed that do not extend beyond its limits. Therefore, the symptoms of a person’s illness do not bother.
Second stage. Osteophytes continue to grow, which causes limited mobility of the spine. The person begins to experience aching pain. They gain strength during physical exertion, when the body is exposed to cold or draft.
Third stage. The vertebrae fuse with each other, which causes complete immobility of the spine. A person suffers from severe pain, his muscle tone increases. The level of uric acid in the muscles reaches critical levels. As the disease progresses, the person’s health deteriorates.
Most often, the disease affects from 1-2-3 vertebrae in the cervical or lumbar region. The thoracic region is less commonly affected.
Symptoms of spondylosis of various departments
Symptoms of spondylosis can be both subtle and very intense. The disease has a chronic course and, if left untreated, leads to the fact that a person becomes disabled.
cervical spine
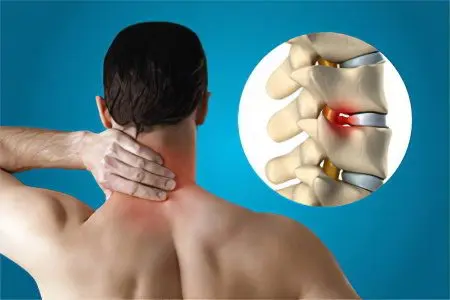
Spondylosis of the cervical spine is often diagnosed, due to the demands of modern life. Many people work in the intellectual field, which forces them to be in a static position for a long time.
The main symptoms of cervical spondylosis include:
Periodic pain. They give to the hands, to the fingers, to the arm, to the shoulder.
Stiffness in the cervical and shoulder spine. It appears in the morning hours.
Numbness in the affected area.
Weakness in arms, fingers and hands.
Headaches radiating to the back of the head.
Imbalance.
Difficulty swallowing food.
Thoracic spine
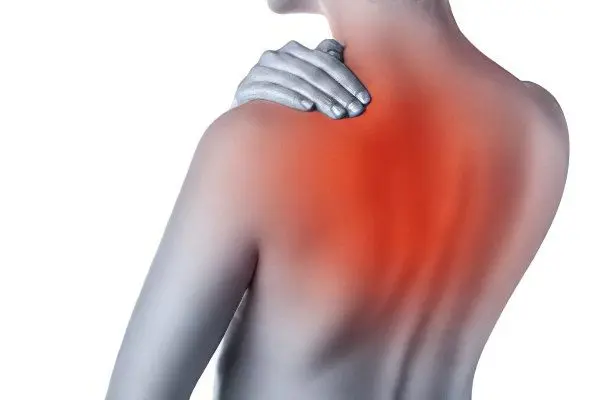
The thoracic spine spondylosis affects less often, but in this case, the disease will lead to severe symptoms, including:
Pain in the back, in its upper and lower parts.
Pain when bending and straightening the body.
Stiffness in the back in the morning.
A feature of painful sensations is that they occur on one side of the body, on the left or right. During palpation of the affected areas, the pain will be concentrated along the spine, as well as from the front of the chest.
Lumbar spine
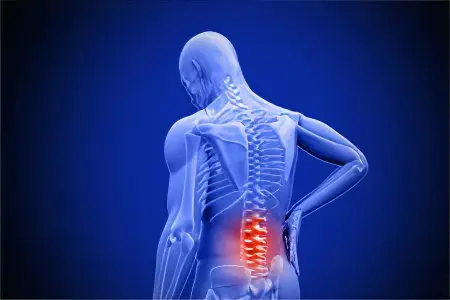
With the defeat of the lumbar spine, the 4th and 5th vertebrae are most often affected. Pain can be concentrated on one or both sides.
The main symptoms of pathology include:
Pain that comes and goes from time to time.
Stiffness in the lumbar region in the morning.
Pain that gets better after exercise.
Numbness in the lumbar region.
Ischialgia.
Gait disturbance.
Tingling sensation in the lower back, legs and feet.
Disorders in the work of the intestines and bladder. The functions of these organs rarely suffer, most often this occurs when the cauda equina is compressed.
When you lean forward, the pain goes away. A person may develop intermittent claudication, but it will be false, since the pain with it disappears when he bends his back in a ball.
Pinching of nerve endings and radiculitis develops when spondylosis of the lumbar spine is combined with osteochondrosis.
What is dangerous disease?
At an early stage of development of spondylosis, there are no pathological symptoms. However, without treatment, the disease will progress. Cervical spondylosis leads to the fact that the blood flow in the vertebral arteries is disturbed, due to which the patient may lose consciousness, or he will be haunted by panic attacks.
In the future, spondylosis can lead to a loss of motor skills, to a deterioration in mobility. A person can become disabled, as a certain part of the spine will simply be immobilized.
Diagnosis of spondylosis

Diagnosis of spondylosis in the early stages of its development presents certain difficulties. The disease develops gradually, and the pain that it causes can be confused with pain in osteochondrosis.
Therefore, the doctor should clarify the following questions with the patient:
How long has the person experienced pain?
What precedes the onset of pain.
Where does the pain radiate?
What factors contribute to increased pain.
After the survey, the doctor evaluates the range of motion that is available to the patient. He asks him to turn his head in different directions, raise it up, lower it down. The next step is to assess sensitivity, identify pathological reflexes, determine muscle strength and ability to maintain balance.
You can identify signs of developing spondylosis using x-rays. The picture will show osteophytes.
If myelopathy is suspected, the passage of such instrumental examination methods as:
MRI. The technique provides information about damage to the nerve trunks.
CT This method is more informative than radiography.
Electromyography and study of nerve conduction. To assess the conductivity of the nerves, electrodes are attached to the patient’s skin, through which electrical impulses of various frequencies are applied. This allows you to evaluate the conductivity of nerve fibers, namely, the speed and strength of the transmitted signals. EMG requires local anesthesia, as a needle electrode is inserted into the muscle to conduct the study. After that, the electrical potential of the muscle is estimated. Most often, EIG and nerve conduction studies are carried out in combination.
Treatment
Degenerative processes that are triggered in a patient with spondylosis are irreversible.
Treatment of the disease, regardless of its variety, has the following goals:
Elimination of the inflammatory reaction, relief of pain.
Relieve muscle spasms.
Improving the nutrition of the disk due to the normalization of blood circulation.
Regulation of metabolic processes.
Slowing down the rate of destruction of the elements of the spine.
NSAIDs may not be suitable for all patients with spondylosis. They are not prescribed to patients with severe heart disease, with pathology of the liver and kidneys, with bronchial asthma, hypertension, stomach and duodenal ulcers.
Muscle relaxants. These drugs allow you to relieve spasms from the muscles, eliminate cramps and painful contractions from them. They have a relaxing effect on muscle fibers.
Multivitamins. They are complexes of useful substances that allow you to strengthen tissues, improve joint mobility and increase immunity in general.
Antiplatelet agents. These drugs are prescribed in order to prevent the formation of blood clots, as they contribute to the normalization of blood circulation due to the expansion of blood vessels.
Chondroprotectors. Chondroprotectors are most often prescribed when a patient is diagnosed with cervical spondylosis. These drugs allow you to restore cartilage tissue, improve metabolic processes and eliminate pain. Improvement in well-being can be achieved within 14-21 days after the start of therapy.
Surgery
Indications for surgical intervention in patients with spondylosis:
The patient has a pinched nerve.
There is compression of the spinal cord.
There is a real risk of damage to the nervous system.
Pain cannot be eliminated in other ways.
You need to understand that the operation will not allow you to achieve recovery. It is aimed at stopping the pathological process of destruction of spinal tissues and eliminating pain.
Surgical intervention can be of the following types:
Anterior discectomy. It is indicated when the deformed disc puts pressure on the nerve fibers.
Cervical laminectomy. During the procedure, the surgeon removes bone growths that put pressure on the spinal cord.
Intervertebral disc prosthetics. During the procedure, the patient’s own disc is replaced with an artificial one. This technique is innovative, so there is no data on its effectiveness in the long term.
Honored doctor of Ukraine, neuropathologist of the “Bersenev Medical Center” Bersenev Vladimir Andreevich talks about such diseases of the spine as spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis: