Contents
Spirea Shirobana is an ornamental shrub of the Rosaceae family, which is very popular in Our Country. This is due to the endurance of the variety, the low price of planting material and the beauty of the plant. In addition, Shiroban’s spirea is highly valued for its resistance to low temperatures and unpretentiousness.
Description of Shiroban’s spirea
Japanese spirea Genpei Shirobana is a small plant, about 70-80 cm high. The bush is strongly branched and quickly grows in width – the diameter of the shrub can reach 120 cm. The young branches of the spirea are pubescent. The color of the shoots is reddish-brown.
The shape of the leaves is ovoid, slightly elongated. They are small in size. The outer part of the leaf plate is painted dark green, but the leaves are gray below. In autumn, green tones turn into orange or even reddish hues, thanks to which the spirea bush looks beautiful even after flowering has ended.
The color of Shiroban’s spirea flowers varies from white to pale pink. This variety blooms throughout the summer.

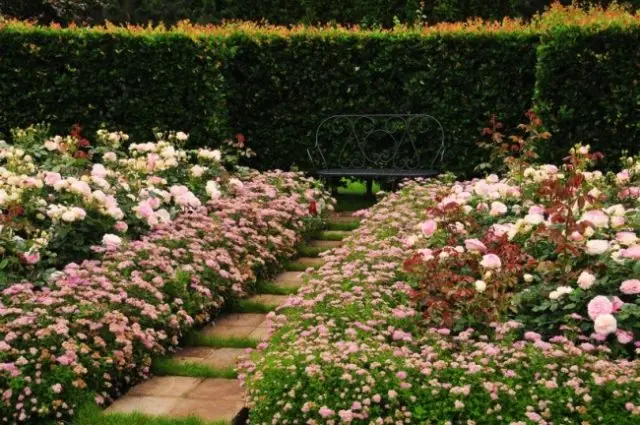
Spirea Shirobana in landscape design
The Japanese spirea variety Jenpei Shirobana in landscape design is used to form a homogeneous hedge, borders and decorate slopes. The shrub is also planted along with other varieties to create spectacular group compositions. Due to the fact that different varieties bloom at different times, the decorative effect of such flower beds stretches for the whole season.

Planting and care of Japanese Shirobana spirea
Planting Shiroban’s spirea, as well as the subsequent care of the plant, as a rule, does not cause much difficulty. What you should pay attention to before planting a shrub:
- Spirea Shirobana prefers open sunny areas, but grows well in partial shade.
- There are no special requirements for the composition of the soil, but it is better to plant spirea on loose, light soils.
- The recommended planting time for the Shirobana variety is early September.
- It will be easier for seedlings to adapt to a new place if the landing is carried out in rainy, cloudy weather.
This horticultural culture is unpretentious and non-compliance with these recommendations will do little harm to it, however, the listed conditions are necessary for the most abundant flowering of the bush.

Preparation of planting material and site
Preparing the site for planting Shiroban’s spirea comes down to digging the site and applying organic fertilizers to the soil. As for planting material, it does not need any special preparatory procedures. It is enough to inspect the seedlings and reject specimens with significant damage: cuts, fractures of shoots and root breaks.

Planting spirea Shirobana
The algorithm for planting the Shirobana variety is as follows:
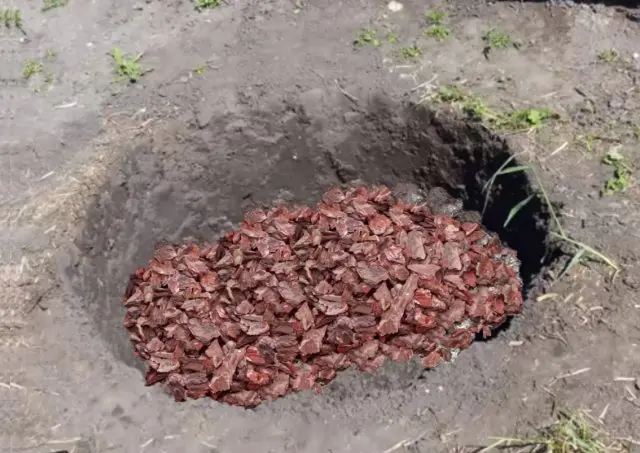
- Holes are dug on the site, the diameter of which should be slightly larger than the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe roots of the seedlings. The depth of the pits should not exceed half a meter.
- I put drainage at the bottom of the pits: pebbles, gravel, broken bricks or clay shards.
- The drainage layer is sprinkled with a mixture of peat, sand and garden soil, taken in equal proportions. A thin layer of soil must be poured over this soil mixture so that the roots of the spirea do not directly touch the peat.
- The seedlings are lowered into the holes, the roots are evenly distributed along the bottom and covered with earth. The root neck should be level with the ground or slightly higher; it cannot be deepened.
- Landings are watered and mulched. Mulch contributes to a better preservation of moisture in the near-stem circle. The best mulch is peat or walnut shells.

Watering and top dressing
Spirea Shirobana needs more care in the first year of life, which includes frequent watering. The soil near the bush should not dry out. Mature plants are watered at least 2 times a month. At the same time, about 10-15 liters of water are consumed for each bush.
Bushes are usually fed in the spring. Complex fertilizers are applied to the soil according to the instructions. Young seedlings can be fed in summer with a solution of mullein with the addition of 
Trimming
Sanitary pruning of last year’s shoots is carried out in early spring. In this case, it is important to have time before the buds open. Weak shoots can be removed completely. The procedure promotes more active growth of young shoots.
In the 4th year of life, an intensive anti-aging pruning of the Shiroban spirea can be carried out. To do this, the branches are cut so that only stumps about 30 cm long remain. Starting from the age of 4, such pruning can be done annually.

After each pruning, planting is abundantly watered and fertilized. To do this, you can use a solution of manure or superphosphate. Recommended proportions: 10 g per 10 liters of water. Fertilizer is applied under the very root of the spirea.
Preparation for winter
Shiroban’s spirea is able to overwinter without harm to development without covering material, but this only applies to adult plants. Young seedlings are too weak to survive the winter under natural cover – snow. They are recommended to be sprinkled with a thick layer of dry leaves.

Reproduction
Shiroban’s spirea can be propagated in the following ways:
- cuttings;
- layering;
- division of the bush;
- seeds.
The latter method is used very rarely, since seed propagation often results in the loss of varietal qualities of a horticultural crop.
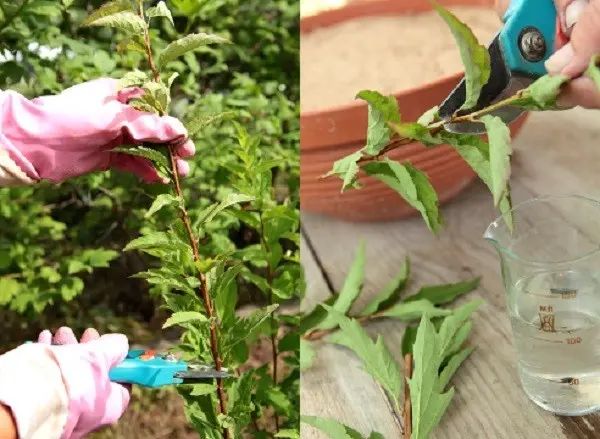
Spirea cuttings are the most popular. The advantage of the method is the high survival rate of planting material even without the treatment of cuttings with growth stimulants.
Shiroban’s spirea is bred by cuttings as follows:
- The shrub is inspected and an annual shoot is selected on it.
- It is cut almost to the root and the resulting cut is divided again into several parts. The length of the cutting should be an average of 15 cm. Each part should have no more than 6 leaves.
- The bottom of the cuttings must be cleared of foliage.
- The remaining leaves are cut in half.
- The cuttings are dipped for 5 hours in a solution of the drug “Epin” (1 ml per 2 liters of water).
- After this time, the lower cut of the cuttings is sprinkled with a growth stimulator (Kornevin can be used), after which the planting material is planted in containers filled with sand.
- Cuttings are deepened at an angle of 45 °.
- Then the cuttings are covered with jars or film, after which the containers are removed in the shade.
- With the onset of the first cold weather, the boxes are dug into the ground and covered with dry leaves.
- In the spring, the boxes are opened and the spirea is transplanted to a permanent place.

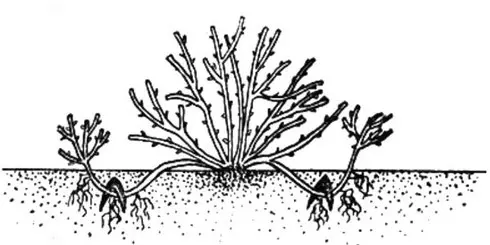
No less popular is the cultivation of Shiroban’s spirea by layering. Layers are formed according to the following scheme:
- One of the branches of the spirea is gently bent to the ground, trying not to break it.
- The end of the shoot is buried in the ground and fixed with a metal bracket or a heavy object.
- When the layering forms a full-fledged root system, it can be separated from the mother bush and planted in another place.
Another vegetative method of propagation of Shiroban’s spirea, in which all varietal qualities are preserved, is the division of the bush. The procedure is carried out like this:
- In the spring, before the buds open, the bush is dug up together with an earthen clod.
- The roots of spirea are lowered into a basin of water. This is necessary in order for the earth to soften. So, it will be easier to clean the root system of the plant.
- The rhizome is divided into 3-4 equal parts, after which each part can be seated.

Diseases and pests
Shiroban’s spirea is rarely sick, but plantings can be affected by pests. The most dangerous for this variety include the following insects:
- aphid;
- spider mite;
- rose leaf.
The fact that the spirea was struck by a tick is indicated by the formation of a thin cobweb on the leaves. In addition, the shrub begins to turn yellow ahead of time. It sheds its leaves soon after.
The danger of the spider mite lies in the fact that it depletes the bush very quickly. It is impossible to delay the fight with him. Any insecticide effectively copes with the pest, but the preparations “Phosfamide” and “Karbofos” have proven themselves especially well. The dosage is indicated in the instructions.
Aphids annoy gardeners in the second half of summer. The presence of the pest is determined by the inflorescences eaten, from which the insect sucks the juice. It also goes to the leaves, on which small holes appear. You can get rid of aphids using the Pirimor insecticide, a solution of grated laundry soap or ash.

Reviews of Shiroban’s spirea
Conclusion
Spirea Shirobana is ideal for those who do not have the opportunity or desire to spend a lot of time caring for a garden plot. This variety does not require special attention, so even a beginner can handle the cultivation of shrubs. The frost resistance of Shiroban’s spirea allows it to be grown in almost all regions of Our Country.









