Contents
Japanese spirea Albiflora (also Bumald’s spirea “White-flowered”) is a popular dwarf ornamental shrub in Our Country, unpretentious in care and resistant to low temperatures. This variety is distinguished by high decorative qualities – it retains an attractive appearance even after flowering, until late autumn, when the light green color of the leaves is replaced by rich orange.
Description of Japanese spirea Albiflora
It is a small deciduous shrub, about 80 cm tall. The diameter of the bush is an average of 1,5 m, the crown is sprawling, dense. Young shoots of this variety are slightly pubescent.
Spirea Japanese Albiflora grows slowly. The annual growth is only 10 cm.
The shape of the leaves is elongated, ovoid. The edges are slightly serrated. The length of the leaf plate reaches 7 cm. The foliage is painted in delicate green tones, however, in September the leaves turn yellow and gradually acquire a bright orange color.
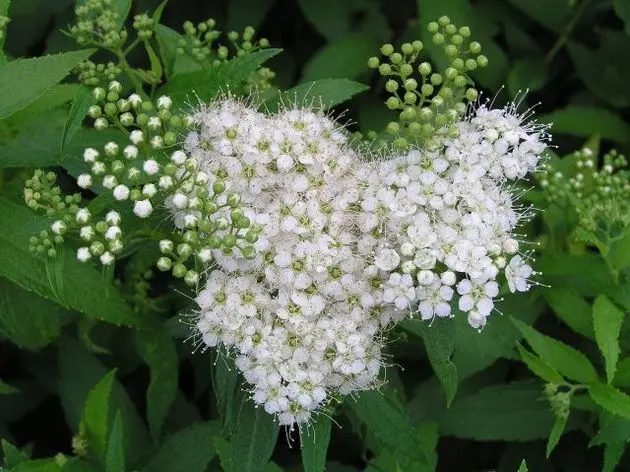
The description indicates that the flowers of the Japanese spirea variety Albiflora are small, as can be seen in the photo below, and they are collected in dense corymbose inflorescences, the diameter of which does not exceed 6-7 cm. The color of the petals is white.
One of the leading characteristics of the variety is abundant flowering, which lasts from July to August.

Spirea Albiflora in landscape design
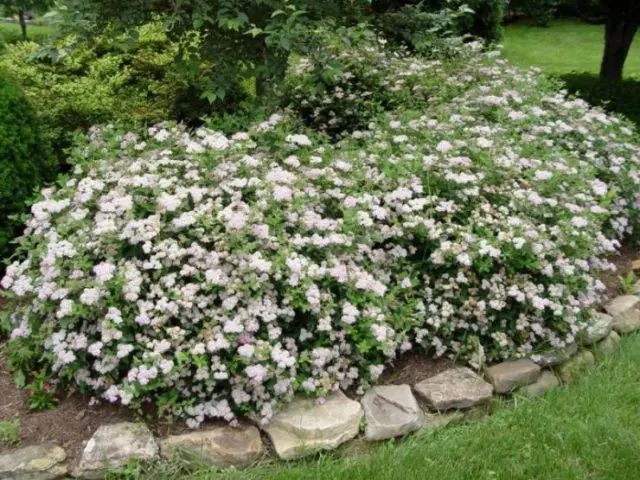
Japanese Spirea Albiflora is highly valued in landscape design for its resistance to air pollution, which allows the shrub to be used as a decoration for city parks, medical facilities and playgrounds. Plants are planted both singly and as part of group flower arrangements: rock gardens, borders, flower beds.
This variety can also be used as a ground cover for slopes. In addition, the Japanese spirea Albiflora is often included in multilayer compositions, where the shrub is combined with trees and shrubs weaving along the supports.
The photo below shows a homogeneous composition of the bushes of the Japanese spirea variety Albiflora.

Planting and caring for Japanese spirea Albiflora
This variety is not capricious and grows well both in open sunny areas and in partial shade. The shrub does not impose special requirements on the composition of the soil, however, when planted in loose fertile soils, the flowering of spirea will be more abundant.
Plant care includes the most basic procedures: sanitary and formative pruning, watering and fertilizing. The shrub is one of the most frost-resistant varieties, so adult plants do not need shelter for the winter. Albiflora spirea does not tolerate drought well, so it is important to ensure that the soil in the near-stem circle of the plant does not dry out.
Preparation of planting material and site
Before planting a plant in a permanent place, it is necessary to carefully examine the planting material for mechanical damage. There should be no breaks or cuts on the seedlings – through these injuries, the spirea can be infected with a fungus.
In addition, it is recommended to slightly trim the roots of the plant if some of them are strongly knocked out of the total mass. Only a sharp tool can be used for this. When cutting with blunt scissors or a knife, there is a high risk that creases will remain at the cut site. This greatly affects the survival of the plant in open ground.
If desired, you can also shorten the shoots of the seedling in order to adjust its shape, but pruning should be moderate. Branches are cut only by 20-25%, no more.

The garden plot before planting spirea should be carefully dug up 10-15 days before. At the same time, organic fertilizers are applied to the soil in moderation.
Planting Japanese Spirea Albiflora
The Albiflora variety is planted in the fall, before the leaf fall ends. The landing algorithm is as follows:
- Planting material before planting in open ground is watered abundantly if it was previously in containers.
- The recommended dimensions of the landing pit are 40-50 cm deep and 50 cm in diameter. In many ways, one should be guided by the size of the root system of the seedling – the roots should be freely located in the hole.
- If the soil in the area is heavy and clayey, a drainage layer of brick fragments, small stones or fragments of clay shards is placed at the bottom of the pit.
- After that, the pit is filled with soil mixture, which is usually made independently. To do this, it is necessary to mix peat, fine-grained sand and topsoil from the site in equal proportions.
- For better growth of spirea, complex fertilizer can be added to the pit (about 5 g per 1 kg of the mixture).
- The seedling is carefully lowered into the hole and the roots of the plant are straightened.
- The pit is covered with earth and the trunk circle is lightly tamped.
- Planting is completed with abundant watering, loosening the soil near the plant and mulching. This is done so that the soil better retains moisture after rains and watering. Sawdust, dry grass, tree bark or wood chips can be used as mulch.

You can learn more about the features of planting Japanese spirea variety Albiflora from the video below:
Watering and top dressing
Spirea Japanese Albiflora responds well to regular watering. This is especially true for young plants, since their roots have not yet had time to develop sufficiently and are not able to provide the shrub with the necessary amount of moisture from the lower layers of the soil. Adult spirea is watered about 1 time per week.
In the spring, plantings are fed with nitrogen fertilizers for a better set of green mass or complex mineral fertilizers for horticultural crops. In autumn, potassium and phosphorus are added to the soil.

Trimming
Abundant flowering of spirea provides annual pruning. The procedure involves moderately shortening healthy shoots and removing dried branches. Pruning old shoots stimulates the formation of young shoots. It is recommended to remove about ¼ of old branches annually.
You can trim the shrub both in spring and autumn. After pruning, planting is abundantly fertilized with manure solution in a ratio of 1:6. Pour the mixture directly under the roots. After that, you can fertilize them with a solution of superphosphate. The optimal dosage is approximately 8 g per 10 liters of water.
Preparation for winter
Despite the fact that the Japanese spirea Albiflora is a cold-resistant variety, it is better to cover young seedlings for the winter, especially in regions with a cold climate. Prepare them like this:
- Before the onset of the first frosts, the trunk circle is loosened and spud, forming a hill about 15-20 cm high in the center.
- Bushes are mulched with peat or compost.
- The branches are tied and bent to the ground, laying them on leaves or burlap.
- After that, the shoots are fixed on the ground with metal staples and covered with insulating material.

Reproduction
It is possible to propagate Japanese spirea Albiflora varieties both vegetatively and by seeds, but the first method is still preferable. Seed propagation requires a lot of time.
Vegetative methods include cuttings and the formation of layering.
The harvesting of cuttings is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Semi-woody branches of the current year are selected on the bush and cut closer to the ground.
- The resulting cut is further divided, resulting in cuttings about 10 cm long each. For propagation, you can use both extreme cuttings and the inner part of the shoot.
- The bottom of the cuttings is cleaned of leaves.
- The lower cut is treated with a root growth stimulator, after which the cuttings are planted in containers.
After a year, spirea can be transplanted to a permanent place.

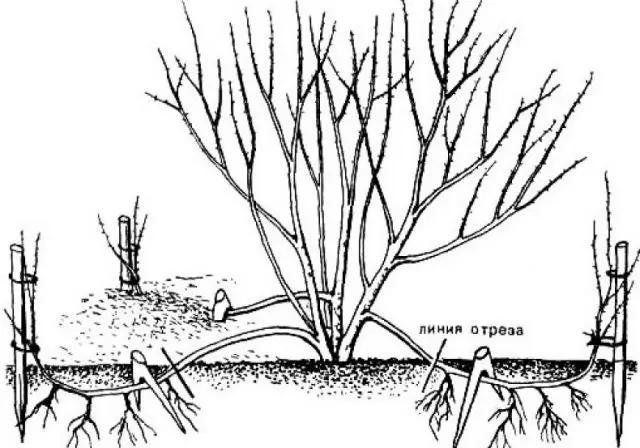
Reproduction by layering is considered one of the easiest ways to breed Albiflora spirea:
- Before the leaves bloom, the side branch of the bush is bent and fixed in the ground.
- During the season, layering is regularly watered.
- In autumn, the branch is finally separated from the mother bush and transplanted.
Diseases and pests
Spiraea Japanese Albiflora practically does not get sick, but occasionally pests can infect plantings. These include:
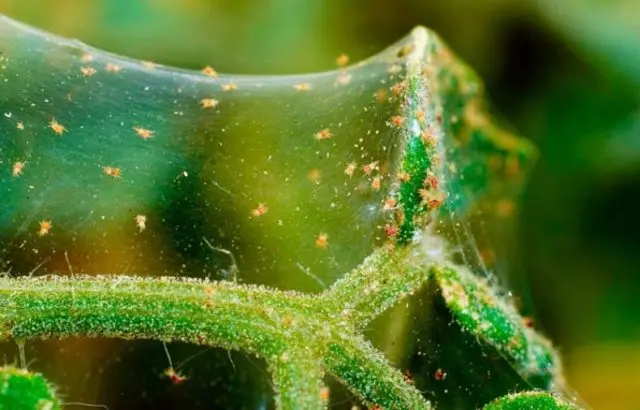
- spider mite;
- rose leaf;
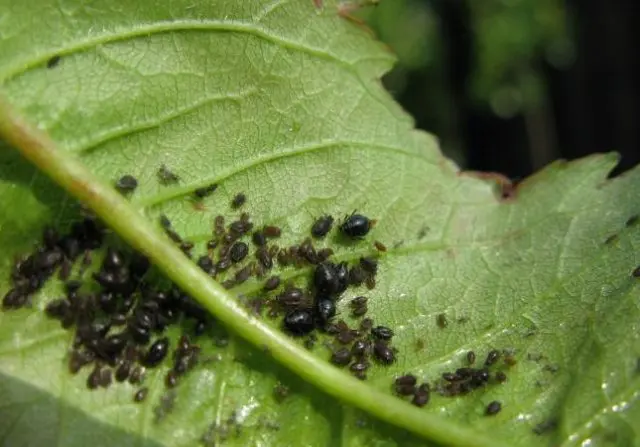
- aphids.
Among these insects, the tick is the most dangerous. The appearance of the pest is given out by whitish spots on the leaves and a thin cobweb. If nothing is done, the spirea leaves will begin to turn yellow and crumble, and small holes will appear in the inflorescences.

In order to get rid of the tick, it is necessary to treat the bushes with insecticides. Such drugs as “Phosfamide” and “Karbofos” effectively cope with the pest.
In the middle of summer, the bushes can attract aphids, which gnaw at the inflorescences and suck the juice out of them. Against this pest, the drug “Pyrimor” is used, which also copes well with the leaflet.
Folk insect control methods include treating spirea with a solution of ash or laundry soap.

Conclusion
Spiraea Japanese Albiflora is a shrub with abundant flowering, care for which is very simple. The main advantage of the variety is the fact that it rarely gets sick and does not need shelter for the winter. In addition, it is characterized by abundant flowering and retains its decorative effect until late autumn.









