In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
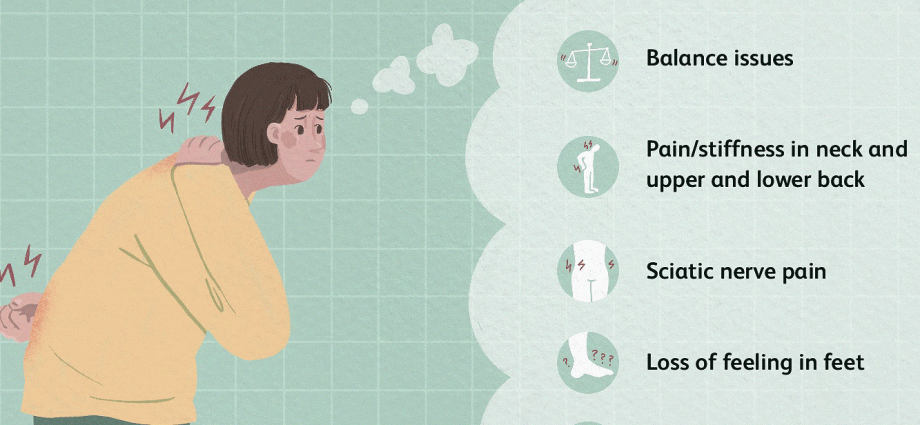
Spine diseases are manifested by pains that often disturb our efficiency and cause problems in everyday functioning. It is with them that we come to the GP, and due to the lifestyle and lack of physical activity – it happens more and more often.
Spine diseases – causes
Structural or traumatic changes in the spine can also place pressure on delicate parts of the nervous system: the spinal cord and nerve roots, causing pain and sensory and motor disturbances in places not directly affected by the disease. An example may be pain radiating along the entire lower limb (so-called sciatica) appearing in the course of discopathy of the lumbar spine or paralysis of two or four limbs as a result of spine fractures and spinal cord tears, eg as a result of an unfortunate jump “on the head”.
Spine diseases include:
- degenerative disease resulting from and the sum of many years of excessive loads, posture defects, injuries and progressive age;
- herniated intervertebral discs commonly referred to as “disc prolapse”;
- osteoporosis;
- primary and, first of all, metastatic neoplastic tumors;
- fractures arising either in healthy bones or in bones weakened by a disease process (e.g., the two above-mentioned) called pathological fractures;
- dislocations and subluxations in the intervertebral joints (a condition where two adjacent vertebrae slide in relation to each other, e.g. in a spondylolisthesis);
- spondyloarthropathies – diseases in the course of which arthritis of the spine occurs, including ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, inflammations associated with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis and many others;
- posture defects: scoliosis, humps starting most often in childhood
Spine diseases – diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of spine diseases usually require a multidisciplinary approach. Family doctors, orthopedists-traumatologists, neurologists, neurosurgeons, specialists in rehabilitation and treatment of chronic pain are involved in the therapeutic process.