Contents
- When can spinal traction be used?
- Spinal traction with inversion machines
- Underwater traction traction of the spine
- The essence of the method of underwater traction of the spine
- Vertical traction of the spine according to the method of K. Moll
- Horizontal traction of the spine according to the method of V.A. Lisunova
- Recommendations for the use of underwater spinal traction
- Indications for the use of underwater spinal traction
- Contraindications for underwater spinal traction
- Spinal traction with Detensor therapeutic mat
- Gravity boots for spinal traction
- Home method of spinal traction
- Contraindications and risks of spinal traction with a hernia
- Is it possible to replace spinal traction with hanging on the horizontal bar?
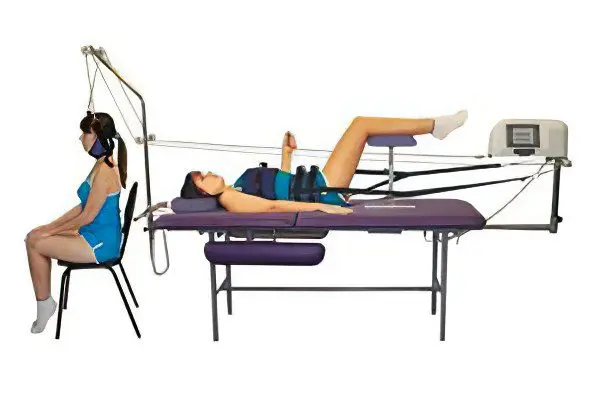
Spinal traction – This is one of the most effective, but also the most controversial methods of treating spinal pathologies. In some diseases, traction brings quick relief and speeds up recovery, while in others it only exacerbates the problem. How justified is the treatment of an intervertebral hernia with the help of spinal traction? There is still no consensus on this issue in the medical community. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the arguments of supporters and opponents of this technique in order to form your own opinion.
Traction of the spine in the direction of exposure is divided into three types:
vertical;
horizontal;
Inversion (upside down).
According to the type of impact, traction is of two types:
Autogravity – under the weight of its own weight;
Hardware – with the help of special devices and loads.
And, finally, according to the conditions of exposure, traction of the spine happens:
“Dry” – the procedure is carried out indoors or outdoors;
“Wet” – the procedure is carried out in water.
We will tell you in detail about all types of spinal traction, as well as the relevance of each specific technique in the treatment of intervertebral hernia.
When can spinal traction be used?
Proponents of this technique argue that traction creates a pressure drop in the intervertebral space and, thereby, contributes to the “absorption” of the hernia. And opponents believe that traction, on the contrary, provokes an increase in hernia and the formation of new protrusions, since this effect, especially with careless use, leads to tissue stretching and damage to fibrous fibers.
Whom to believe, because both opinions are not without foundation? The truth is that each person is unique, and a decision regarding the choice of treatment for a herniated disc can only be made after a thorough examination and identification of all related problems. This disease most often affects people of mature age, with worn bones and cartilage, weakened muscle corset, and even with more serious pathologies: osteoporosis, sciatica, osteochondrosis. That is why only a qualified and experienced specialist can answer the question of whether you can treat a herniated disc with spinal traction.
Spinal traction with inversion machines
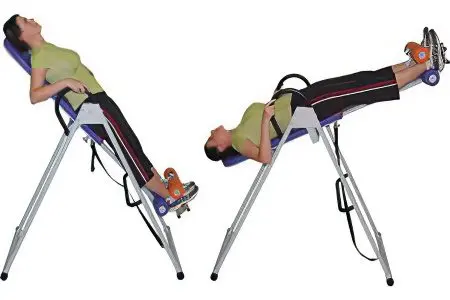
Inversion is turning a person upside down to redistribute pressure on the spine. This simple and effective technique has been known to mankind since the time of the legendary Hippocrates, who documented its essence in his writings: four centuries before our era, healers tied patients with back pain by their knees and ankles to a ladder, and then turned it over 180 ° C. Now there are many convenient devices with which anyone can carry out inversion traction of the spine at home.
Reasonable use of inversion traction of the spine allows you to achieve several positive effects at once:
Relieve back pain;
Slow down the aging of the intervertebral discs;
Align posture;
Stimulate blood circulation and nerve interaction;
Avoid height loss with age due to decompression;
Eliminate congestion in internal organs;
Train the vestibular apparatus;
Relieve muscle pain and fatigue after sports training;
Prevent and reduce the effects of varicose veins and cellulite;
Ensure the best supply of oxygen to the brain.
What is the working principle? The inversion machine is a sturdy, flat table top with hand rails, leg mounts, and a tall base that rotates the machine. Doctors recommend exercising on the inversion table for 10 minutes a day, starting with an inclination of 25 ° C and gradually increasing it to 180 ° C, that is, upside down.
In addition to simply hanging upside down, you can perform the following simple exercises on the inversion simulator:
Being in an inverted position, stretch your hips up or slightly bend your knees;
Having fixed the legs, put your hands behind your head or on your chest and raise the body by 30 ° C relative to the table surface, moreover, the more the simulator is turned over, the stronger the load on the muscles will be;
In the upside down position, keep your arms pressed along the body and try to “squat in reverse”, that is, pull your hips to your feet;
The most effective exercise for an intervertebral hernia on an inversion simulator is rotation, you just need to fix your legs, turn upside down, and then use the handrail to rotate 90 ° C in one direction or the other.

What is the effectiveness of such spinal traction? Strictly speaking, classes on the inversion table are not an independent method of treating a herniated disc. Such training contributes to a speedy recovery, prevents an increase in protrusions and their transition to a herniated disc. Inversion therapy works well in combination with other conservative hernia treatments. And for those patients who have an acute inflammatory process, or have concomitant pathologies of the spine, or the weight exceeds the allowable norm, it is impossible to engage in an inversion table. In any case, you should not start training without consulting your doctor.
Underwater traction traction of the spine
From “dry” methods of traction of the spine, we move on to “wet”. The term “traction” literally means “stretching”, respectively, underwater traction therapy is a set of measures to stretch the spine while diving. How was this technique born, and why is it better than “dry” autogravity methods?
Underwater traction of the spine has several advantages:
Water naturally supports a person, neutralizing the pressure of most of his mass on the spine, and also relaxes the muscles and provides a more even distribution of the load during the procedure;
Increasing the temperature of the water and adding substances with a therapeutic effect to it allows for even greater relaxation and a beneficial effect on the patient’s health.
The essence of the method of underwater traction of the spine

Simultaneous exposure to traction and warm water gives a good effect in the treatment of intervertebral hernia, spondylosis, discogenic sciatica, the initial stage of Bechterew’s disease and many other pathologies of the spine. The procedure is carried out either in fresh water, or in natural mineral waters, or in artificially created therapeutic baths with the addition of hydrogen sulfide, radon, sea salt and turpentine.
Each type of underwater traction therapy using medicinal waters has its own advantages:
Turpentine and hydrogen sulfide baths effectively dilate blood vessels, stimulate blood circulation and lymph flow, improve skin condition, promote weight loss and eliminate cellulite, neutralize congestion in the body and most intensively relax muscles;
Baths with sea salt are indicated for patients with thrombophlebitis, atherosclerosis, varicose veins and other vascular pathologies, since sodium chloride salts and iodine have a beneficial effect on the condition of veins and capillaries, strengthen their walls, increase elasticity and eliminate blood stasis;
Radon baths relieve pain well, so traction therapy is performed in patients with diseases of the spine, accompanied by severe pain syndrome (herniated disc, spondylolisthesis, sciatica, osteochondrosis).
Underwater traction of the spine is most relevant for intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region, since the position in the water with legs stretched forward immediately reduces lordosis and relieves radicular pain. Experts also note that this technique does little to help patients with a very large intervertebral hernia (more than 6 cm), and has a more pronounced therapeutic effect on men than on women. Apparently, this is due to the fact that the average man has a better developed muscle corset, which supports the back after the procedure.
There are several types of underwater spinal traction:
Vertical and horizontal;
By simple sagging and with weights.
Vertical traction of the spine according to the method of K. Moll

Underwater traction of the spine according to the Moll-Buschelberger method is exactly the treatment for which patients from all over Europe come to Hungarian resorts. The author himself, Dr. K. Moll (born 1953), calls this traction therapy “stress baths”.
The National Institute of Rheumatology and the State Rheumatology Clinic of St. André (Heviz) confirm the effectiveness of the Moll technique and support their opinion with the results of numerous studies conducted over the years in the resorts of Hungary: most patients manage to eliminate pain in the shortest possible time and ensure stable remission.
Domestic experts are more reserved about vertical underwater traction of the spine. In our country, such traction therapy is not used in any of the sanatoriums and health centers.
According to Russian physiotherapists and rheumatologists, this method is poorly suited for the treatment of a herniated disc for several reasons:
The procedure increases intradiscal pressure too much, which is fraught with microtraumas and ruptures of fibrous fibers;
Load traction is not accurately regulated and dosed, moreover, it affects the entire spine at once, and not just the disk affected by a hernia;
After the procedure, the patient has to get up and use exactly those muscles that should remain relaxed at the moment in order for the therapeutic effect of traction to be fixed.
Horizontal traction of the spine according to the method of V.A. Lisunova

Russian physiotherapist V.A. Lisunov invented a technique for underwater traction of the spine, in which the risk of injury is minimal, and the therapeutic effect is very expressive. Traction therapy according to Lisunov looks like this: the patient is placed on an inclined, almost horizontal plane, the shoulder girdle is fixed, and the load is attached to the hips.
This method of traction is more gentle than vertical traction, and also more modern, since the Lisunov installation allows you to calculate the load for each individual patient with an accuracy of a gram. Horizontal underwater traction according to the Lisunov method has been successfully used in many Russian clinics for twenty years, and clinical practice confirms its effectiveness in the treatment of intervertebral hernia.
Recommendations for the use of underwater spinal traction
Before going to a sanatorium or resort where it is possible to attend underwater traction therapy procedures, be sure to consult with your doctor, undergo X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging of the spine, and take the results with you to show to the local specialist.
During the entire period of treatment of an intervertebral hernia by the method of underwater traction of the spine, you need to take care of yourself, avoid sudden movements and loads, dress warmly, avoid drafts and wear a special supportive corset, which you will surely be provided in a sanatorium. Up to five procedures are performed per week, and in total the standard course of underwater traction therapy includes up to fifteen procedures. After treatment, it is necessary to continue wearing a corset and sleeping on an orthopedic mattress for one and a half to two months.
Indications for the use of underwater spinal traction

Underwater traction therapy is used as an adjunct to the treatment of the following conditions:
Herniated disc;
Lumbalgia with neurological symptoms;
Violations of flexibility and restrictions on the motor freedom of the spine;
Scoliosis, kyphoscoliosis and lumboschialgia;
Root compression;
Flattening of the lumbar lordosis;
The initial stage of Bechterew’s disease;
Compression radiculopathy;
discogenic sciatica;
Progressive spondylosis and spondylosthesis.
Contraindications for underwater spinal traction
Underwater traction of the spine is contraindicated in the following cases:
At the acute stage of the inflammatory process with a pronounced pain syndrome;
With a sequestered hernia of the intervertebral disc and compression of the “horse tail”;
At the age of over 60 years and with a body weight of over 100 kg;
At the stage of rehabilitation after laminectomy;
With spinal instability, osteoporosis, fractures;
Against the background of inflammatory diseases of the intervertebral space (arachnoiditis, adhesive epiduritis);
In the presence of tumors of any etiology and tuberculous spondylitis;
In patients with severe heart and / or pulmonary insufficiency, as well as in the presence of skin diseases that preclude contact with water.
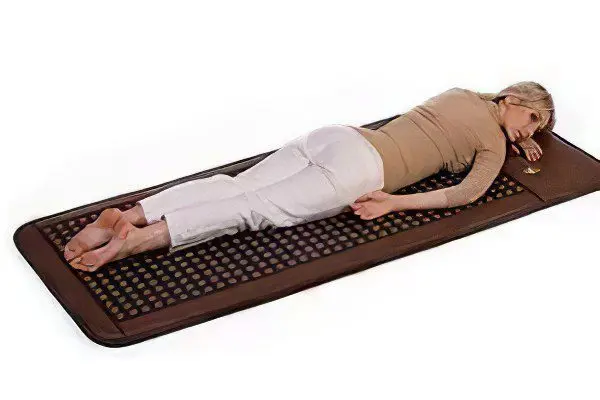
Spinal traction with Detensor therapeutic mat

Turning to autogravity horizontal methods of spinal traction, let us dwell in detail on the most effective equipment for these purposes. We are talking about the German-made Detensor therapeutic mat, which has allowed thousands of people around the world to get rid of excruciating back pain in a natural and safe way.
If you have a herniated disc, your doctor probably recommended that you sleep on a special orthopedic mattress. But the Detensor mat is more than just a mattress, as its design is much more complex and sophisticated. The Detensor Therapy Mat was invented in 1980 by the German physiotherapist Kurt Kienlein and has since undergone several modifications to make it perfect.
Lying and sleeping on this mat bring three benefits to a patient with a sick spine:
The distance between the vertebrae increases, and at the same time, the pressure on the pinched nerves weakens, but the traction of the spine occurs much more smoothly and gently than when using vertical techniques;
Paravertebral muscles are massaged, blood supply and lymph flow increase, filling and restoration of intervertebral discs is accelerated;
Comfortable conditions are created for rest and sleep in any position, limbs do not become numb, a person wakes up rested and full of strength.
What is the principle of the therapeutic effect of the therapeutic mat? The Detensor therapeutic mat is a plane on which ribs made of elastic and resilient material are located at specially calculated angles. When a person lies down on the mat, the ribs bend and move apart at the same time, which provides the effect of gentle stretching of the spine. No matter how you toss and turn during sleep, the ribs of the therapy mat will form a comfortable point of support for your body and keep it in a physiologically correct position.
A person spends a significant part of his life in a dream, and all this time a force equal to about a quarter of the total body weight acts on his spine. And rest on a therapeutic mat allows you to reduce this load to 5-7%. It is also noteworthy that the Detensor mat is available with three stiffness options: for people with a large weight, for patients of normal build and for small children.
Sleeping on a therapeutic mat is indicated for the following pathologies:

Compression fractures;
Scoliosis, osteoporosis, osteochondrosis;
Protrusions and hernias of intervertebral discs;
Posture disorders;
Fatigue from intense physical exertion;
Chronic headaches and migraines.
There are no contraindications for the Detensor therapy mat.
Gravity boots for spinal traction

There is a more mobile, simple and affordable equipment for spinal traction – these are gravity boots. They are wide and soft removable cuffs, fixed around the legs with adjustable straps. On the sole of gravity boots there is a special mount with which you can securely fasten your legs to the crossbar of a regular horizontal bar and hang upside down without fear of falling.
Such equipment can be found in the arsenal of many professional athletes, as well as among the medical equipment of sanatoriums and health centers. It is very easy to use boots, besides they quickly and effectively relieve fatigue. Regular hanging on the horizontal bar upside down forms a beautiful posture, relieves headaches and muscle spasms, prolongs the youthfulness of the back and the whole body. But how useful are such shoes for people with a sore spine?
How do gravity boots help with back pain? Boot hanging is an autogravity vertical spinal extension method, just like the inversion machine, but it works in a very different way. Although the body is affected exclusively by the force of gravity and its own weight, there is no support under the back in the form of a hard table. Therefore, the stretching effect is stronger. The distance between the vertebrae increases, the intervertebral discs fill with fluid and straighten out, the pressure on the nerve roots weakens, and back pain recedes. But only those people whose spine is practically healthy can count on a positive effect.
Contraindications: hanging on gravity boots is strictly contraindicated in patients with acute herniated discs, osteoporosis, scoliosis, spondylolisthesis and other serious pathologies of the spine. Using this device without first consulting a doctor and a thorough examination is not recommended for anyone, since hanging upside down can damage the ligaments and intervertebral discs and aggravate existing problems. Remember also that gravity shoes are exactly health-improving sports equipment, the purpose of which is not to treat a herniated disc, but to relieve fatigue and maintain good physical shape.
Home method of spinal traction

A horizontal spine traction machine can be made at home from an ordinary bed. But we will immediately warn you that for all its simplicity and harmlessness, this type of traction therapy may not be safe for some types of intervertebral hernia, so before turning on Kulibin, consult your doctor.
To make a home trainer you will need:
Single bed with headboard;
Two bricks or wooden blocks of the same height;
Straps from an old backpack or just loops from belts or ropes;
Large towel or blanket
Place the bricks under the legs at the head of the bed, fix the loops on the sides, lie down on the bed, put your hands through the loops up to your shoulders, put a rolled up towel under your lower back and try to lie in this position for several hours. It is very important that in the process you do not experience discomfort, that is, the straps should be long enough not to cut into the armpits, and the back pain should subside, and not vice versa, intensify. If a positive effect cannot be achieved in 3-4 procedures, you need to stop the treatment, it does not suit you.
Contraindications and risks of spinal traction with a hernia
The human skeleton is designed in such a way that during traction, the facet joints of the spine are first of all stretched, and especially strongly in the lumbar and cervical sections of it. Let’s see what happens at this moment inside the intervertebral discs?
The fibrous rings are deformed unevenly: the posterior sections are stretched, and the anterior ones, on the contrary, are narrowed, because the traction causes the vertebrae to approach the front edges. If you imagine a horizontal section of the spine in this situation, it will be in the form of a wedge with the top sticking out of the back. The jelly-like contents of the intervertebral discs flow from the compressed anterior sections to the released posterior ones. And if the back walls of the fibrous rings are not elastic enough (as happens in people with a sick spine), they are overloaded and ruptured, followed by protrusion of the intervertebral nucleus. But that’s what a hernia is!
Supporters of traction therapy willingly list its advantages:
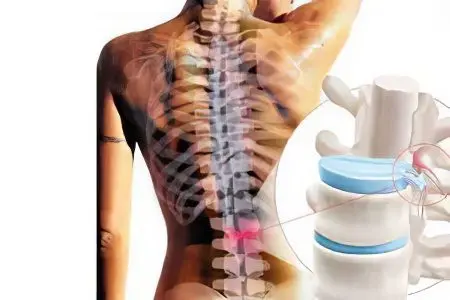
Increasing the height of the disks;
Expansion of the foramen;
Elimination of pressure on the nerve roots;
Neutralization of venous stasis;
Acceleration of microcirculation of blood and lymph.
But for some reason they forget to mention that all these effects last only while the facet joints are in a stretched state. As soon as the traction procedure is completed, the patient will stand up and his spine will return to its previous shape. True, the fibrous rings by this time will already be overstretched, or even damaged. The elementary laws of physics say that traction of the spine with a herniated disc has only a temporary analgesic effect, which is inevitably followed by a deterioration in well-being.
Is it possible to replace spinal traction with hanging on the horizontal bar?

In conclusion of the conversation about spinal traction, let’s discuss the simplest vertical autogravity method – hanging on the horizontal bar with your feet down. To perform this exercise, you do not need any special devices or skills, so some domestic doctors directly recommend that their patients with a herniated disc go to the playground or stadium and hang on the horizontal bar, they say, they will relieve pain like a hand. Is this good advice?
Regardless of which part of the spine you have a hernia – in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar, hanging on the horizontal bar is harmful, and here’s why:
For safe extension of the spine, a force equal to no more than 10% of the total weight of a person should act on each specific point of it. If you have a hernia of the lumbar spine, then when hanging on the horizontal bar, the weight of the entire lower part of your body will exert pressure on the diseased intervertebral disc, and this is at least 30% of the total body weight. Overstretching and microdamages under such a load are almost inevitable;
When you hang on your hands, the trapezius muscle works, which is attached to the bones at two points, and the spine acts as a kind of diagonal of this trapezoid. Sagging under your own weight causes the trapezius muscle to contract and the diagonal to shorten, that is, you “compress” the upper part of your spine. With a hernia of the cervical and thoracic regions, hanging on the bar instead of relief causes only increased pain.









