Contents
Sarcoma is a malignant tumor arising from the embryonic mesoderm. Pathology is localized most often in the lower and upper extremities, less often in the mammary gland, heart, lungs, digestive organs or large vessels.
Soft tissue sarcoma is a fairly rare disease, occurring in approximately 1-2% of the total incidence of malignant neoplasms. Most often, men aged 35 to 65 are ill, however, there are cases of the development of pathology in people under 30 years of age.
Types of sarcoma
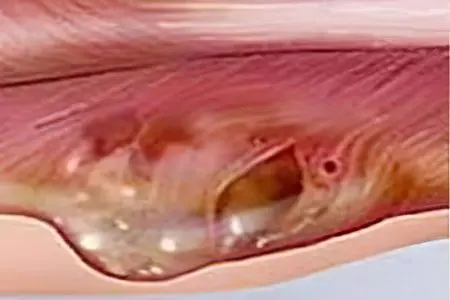
A large number of types of soft tissue sarcoma have been identified, each of which develops in different ways.
The most common types:
fibrosarcoma (cells – fibrocytes are affected);
myxofibrosarcoma (a type of connective tissue sarcoma);
desmoid tumor (also develops from the connective tissue, but more slowly and without spreading to other parts of the body);
liposarcoma (fat cells of the body are affected);
synovial sarcoma (affects the area around the joints);
rhabdomyosarcoma (usually develop on actively working muscles – skeletal and liver-striated muscles), in turn, this type is divided into three subspecies:
embryonic (children are most often affected);
alveolar (tumor of “young”);
pleomorphic (mostly older people get sick).
– leimosarcoma (tumor of smooth muscles (wall of the uterus, stomach or intestines) and peripheral nervous system);
angiosarcomas (affect the cells of the organs of the circulatory system);
sarcoma of the gastrointestinal tract (affects the walls of the digestive organs);
Kaposi’s sarcoma (the disease has a specific course, it begins with damage to skin cells, then pathological spots can develop on any of the organs).
Stages of development of soft tissue sarcoma
I stage – low-grade tumors, without metastases;
II stage – malignant neoplasms up to 5 cm in diameter;
III stage – deep-seated malignant neoplasms with a diameter of more than 5 cm.
IV stage – the presence of metastases in distant organs and tissues.
Causes of the disease
Reliable reasons for the development of this pathology have not been identified, but there are a number of factors contributing to its development:
exposure to chemical carcinogens;
genetic predisposition;
immunological factors (congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies);
viruses (HIV, herpes);
environmental factors;
radiation radiation;
frequent injuries.
Symptoms of soft tissue sarcoma
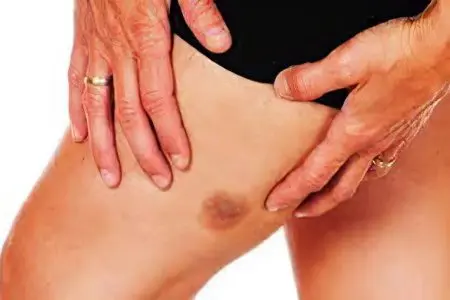
The term “soft tissue sarcoma” combines a large number of varieties of malignant neoplasms, however, there are a number of common symptoms for all:
the appearance of swelling or swelling;
visually noticeable neoplasm;
manifestation of pain syndrome (occurs when the tumor touches the nerve fibers);
constant feeling of malaise, fatigue, lethargy and insomnia;
a sharp decrease in body weight;
change in the skin in the area of development of the neoplasm (change of color, ulceration).
Diagnostics
Sarcoma is an inconspicuous and insidious disease, it can only be detected by symptoms in the later stages. For early diagnosis, you should consult a doctor with the first manifestations of unknown neoplasms, especially if there is a predisposition to the development of tumors.
Methods for diagnosing soft tissue sarcoma:
radiography – detection of neoplasm and its localization;
computed tomography (CT) – the study of the tumor in cross section, giving information about the presence of metastases and the size of the neoplasm;
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – establishing the nature of the neoplasm, after removal – confirmation of the absence of any signs of pathology;
biopsy – the collection of cells directly from the tumor neoplasm, for their further diagnosis and diagnosis;
testing of cellular composition for chromosomal changes.
Treatment of soft tissue sarcoma

If soft tissue sarcoma of any kind is detected, treatment should be started immediately. As a rule, this is a complex therapy, which includes:
surgical intervention;
radiation therapy;
chemotherapy treatments.
Surgical treatment is the main and much decisive method for the treatment of severe pathological conditions, including cancerous neoplasms. The amount of surgical intervention depends primarily on the size of the tumor and its location. Excision is made within a certain anatomical region. If the form of the disease is advanced and complicated by metastases, amputation of the limbs or organ is performed.
As an additional method of treatment, radiation therapy is used. Preoperative irradiation greatly facilitates the procedure for removing the tumor, and also reduces the risk of recurrence. Brachytherapy is one of the methods of radiation therapy, which allows you to irradiate directly to the tumor, while not affecting the adjacent tissues.
Chemotherapeutic procedures aimed at treating malignant neoplasms became so popular only a few years ago. Anticancer drugs are prescribed both before and after surgery, with or without radiation therapy. Due to this effect on the body, the development of metastases and relapses has significantly decreased.
Prevention
There are no specific methods for the prevention of soft tissue sarcoma. However, it is worth taking seriously the fact that people with the greatest likelihood of developing malignant tumors should undergo a follow-up examination at least once a year. Particular attention is paid to people who have received immunosuppressive therapy.
Separately, preventive measures are allocated for people who have already been operated on, as a rule, they are under dispensary observation in order to prevent the development of relapses.
When a sarcoma is detected in the early stages of development, the prognosis is usually favorable, the survival rate is up to 80%. In cases where the tumor has spread widely throughout the body, the survival rate is significantly reduced to 35%.









