Contents
What is a skin nevus?
Naevus – This is a benign formation that develops from pigment cells on the skin or mucous membrane, called a birthmark or mole. As a rule, it does not bring any physical discomfort, remaining invisible under clothing. Many signs are associated with the appearance of moles on one or another part of the body: some promise happiness in life, others promise health and longevity. Is it really?
Pigment or nevus cells are laid in the prenatal period of development. They are the precursors of normal melanocytes, but remain in the deeper layers of the dermis, forming special clusters. Under the influence of a number of factors, nevus cells actively produce pigments that are visible on the skin as moles.
Modern medicine claims that ultraviolet rays that fall on the skin during a person’s life are of great importance in the appearance of birthmarks. They are stimulators of modified melanocytes of the dermis, the accumulations of which are dormant in its different layers. Having received the necessary dose of UV rays, these pigment cells begin to intensively produce melanin, which manifests itself in the form of various brightly colored spots – moles.
In addition, it should be noted the influence of the hormonal background on the development of nevi. So, during pregnancy, during adolescence and with hormone therapy, the number of moles increases. In addition, already existing moles may slightly increase in size and change shape under these conditions.
In young children, birthmarks can hardly be found on the body, but in the dermis they already have accumulations of altered melanocytes, waiting for stimulation. The older the person, and the more time he spent in the sun, the more moles can be found on his body. In an average person, you can find about 20 different types of nevi, it happens that their number exceeds a hundred, or moles merge into one huge spot. Interestingly, moles are much more common in representatives of the Caucasian race; in a person with dark skin, the number of nevi is many times less.
Types and types of nevi
There are 3 types of moles:
Intraepidermal nevus occurs most frequently. This is a flat formation of a rounded shape with clear boundaries, having a uniform color from light to dark brown. As a rule, such a nevus occurs in the first two decades, and in adulthood it gradually depigments. The size of an intraepidermal mole during life is directly proportional to the increase in height and body weight, the color of its surface may change.
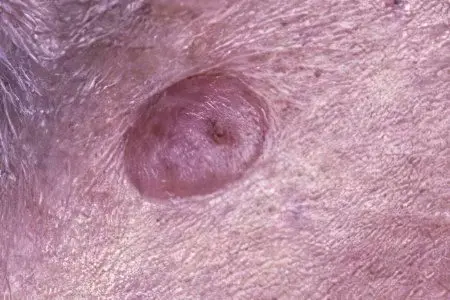
Intradermal nevus differs in its dome-shaped form, it is a formation of a different color, uniform color, rising above the surface of the skin. The appearance of moles of this type is typical after 30 years, their size can vary from a few mm to 5-10 cm.
Complex (mixed) nevus is a transitional form of intradermal and intraepidermal formations. It almost always has a rounded, spherical shape, dense texture, clear boundaries.
Several types of nevi should be distinguished, all of them are united by a benign course:
vascular (strawberry, strawberry),
dysplastic,
papillomatous,
Nevus Becker
nevus of Setton
blue.
A vascular nevus appears as a result of abnormal growth of the walls of blood vessels. At the same time, a spot of a reddish hue appears on the skin, dense to the touch, without hairline. Due to the coloring, such a mole was called strawberry.
A dysplastic nevus can appear on the skin throughout a person’s life. This is the result of the chaotic life of nevocytes under the influence of stimulating factors: UV rays, hormones, radiation, etc. Such a mole is small in size, as a rule, its color varies from red to dark brown. Their group arrangement on the body is characteristic.
A papillomatous nevus has the appearance of a papule, with uneven outlines and a rough surface, often with hair growing on it. It is located mainly in the neck.
Becker’s nevus occurs mainly in young men in the pubertal period due to the intensive production and entry into the blood of large amounts of male sex hormones. Its appearance is preceded by the formation of several brown spots on the skin, which then merge. Thus, Becker’s nevus has uneven contours and a large size. Over time, its surface becomes uneven, hair appears.
Setton’s nevus is a brown nodule, up to 10 mm in diameter. Its distinguishing feature is the presence of a depigmentation rim (white circle) surrounding the mole along the periphery and 2-3 times larger in diameter.
The blue nevus is so called because of its color. This is a small nodule with clear boundaries, always smooth.
Also, all nevi should be divided by size into:
small (5-15 mm),
medium (up to 10 cm),
large (10-20 cm),
giant, occupying the entire anatomical region.
Nevi in newborns
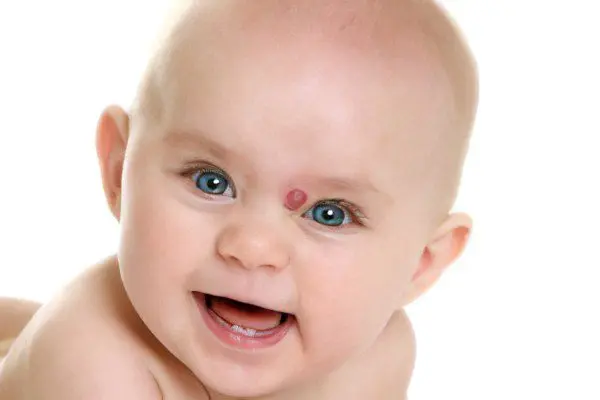
Congenital nevi are, in fact, benign tumors. They are quite rare: in only 1-5% of cases, a nevus can be found on the body of a newborn child or a baby up to a year old. At birth, there are already accumulations of altered melanocytes in the skin, waiting for some kind of stimulation for their further development. Most often they appear during the period of hormonal changes in the body and under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
Congenital nevus, as a rule, has a rounded shape with clear boundaries. Its color is always uniform and can be both light and dark brown, black. The size of such a mole is from 5 mm to 2 cm. The surface is smooth or slightly bumpy, with a slight hairline. Also, a birthmark can reach a gigantic size, occupying the entire anatomical region of the body, while its surface will be soft, velvety to the touch.
If a newborn child has many moles on the body, or birthmarks occupy most of the body, this is a reason to carefully monitor them, since there is a high risk of malignancy and degeneration into melanoma or another tumor. Consult with a specialist.
Malignancy of nevi is possible with the constant influence of a number of irritating factors on it.
They are most often:
chronic traumatization of the mole,
frequent exposure to aggressive chemicals,
hormonal imbalances, often sexual,
adverse physical effects, UV rays, etc.
With malignancy (transition to a malignant tumor), the nevus causes concern. This may be due to a burning sensation, tingling or itching in the area of the mole, the rapid growth of its volume.
If the process of malignancy has already begun, then the nevus acquires characteristic features:
bleeding and wetting of the surface,
rapid increase in size
ulcerated contours, indistinct borders,
uneven pigmentation,
bumpy surface, domed growth.
If you experience disturbing symptoms, you should consult a specialist. With the help of a medical examination, the doctor can reliably determine the nature of the birthmark and select the necessary treatment.
Nevus removal
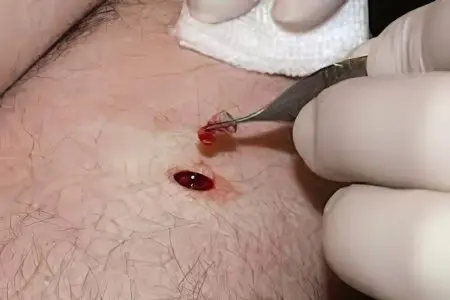
Moles that cause various kinds of discomfort must be removed. There are several methods for getting rid of moles – these are traditional medicine recipes, cryodestruction, and excision with a scalpel or laser. Surgical removal and the laser method have proven themselves the most, since they give almost 100% getting rid of nevi. You should definitely consult a specialist, it is the doctor who will be able to choose the best treatment option for you.
There are a number of indications, in the presence of which an experienced dermatologist will advise you to get rid of the nevus. First of all, this is due to oncological alertness, since nevi quite often become malignant.
It is recommended to remove moles when:
their frequent trauma, which is typical for nevi located in the inguinal and axillary regions, on the head, in places where belts and a bra are worn.
a sharp increase in the size, boundaries, color of the birthmark.
increasing discomfort, itching, burning, tingling, soaking, bleeding.
high risk of malignancy, for example, if it is a giant congenital nevus.
with a preventive purpose.
In addition, the removal of a mole is possible at the request of the patient, which is especially common when the nevus is located in an open area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe body or when it is large. Then getting rid of this formation will be a cosmetic operation with an aesthetic purpose.
Removal of a nevus with a laser
Laser excision of moles is now very common. This is a fairly reliable, proven method. Laser can be used to remove small moles located on any part of the body.
The essence of the technique is as follows: laser radiation penetrates exactly to a given depth in the right place. The procedure is painless, and there are no such frequent complications as scars, burns and scars.
But there is also a significant drawback of this technique – when a large amount of nevus is removed, a whitish (depigmented) spot remains on the skin.
Surgical removal of a nevus
Surgical excision of nevi is still most commonly used. This method is reliable and convenient because it does not require special expensive equipment. Basically, large nevi are excised in this way.
The main disadvantages of the procedure are:
cosmetic defect on the skin. Since the dermatologist surgeon must remove at least 3-5 cm of healthy dermal tissue around the nevus, scarring is almost inevitable.
excision of a nevus with its small size is performed under local anesthesia, in other cases, as well as in childhood, it is possible to remove a mole surgically only under general anesthesia.
The consequences of removing the nevus
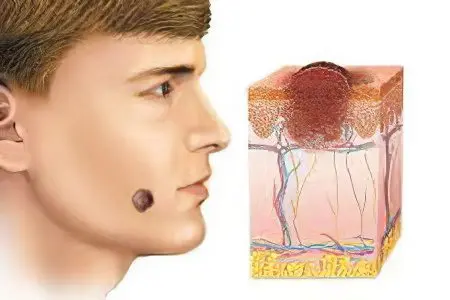
The consequences of a birthmark removal procedure depend on a number of factors. It is necessary to take into account the quality of the treatment, and the individual reaction of the body, and the thoroughness of postoperative care.
After removal of the nevus, in any case, discomfort occurs, lasting no more than a month, more often several days. In the first days after excision of the mole, a dark crust forms in its place, which in no case should be disturbed. You should strictly follow the recommendations given by the doctor, most often this is the daily treatment of the wound surface with a solution of brilliant green and slightly pink manganese. It is important not to take a bath during the first 2 weeks, not to visit saunas and pools, to use creams and other cosmetics with caution. Subsequently, the dark crust falls off, leaving a patch of pink, youthful skin. At this time, it is necessary to protect the body from the sun as much as possible. You should definitely not visit the solarium at this time. Complete healing of the damaged tissue occurs 5-6 months after the procedure.
Complications after removal of the nevus occur more often when an infection enters the wound surface, then inflammation, burning, and possibly suppuration appear. In this case, it is necessary to seek medical help, the specialist will select sufficient antibiotic therapy and monitor the dynamics of recovery.
Possible complications of nevus removal also include its recurrence, which is associated with incomplete excision of the formation tissue. More often this happens with a surgical method of treatment.









