Contents
- What does the tick tick look like?
- First aid for a tick bite
- Where to go for a tick bite?
- Bite prevention and other recommendations

Blood-sucking mites – potential carriers of pathogens of some infections dangerous to humans. The most famous infection of this group in Russia is tick-borne encephalitis. Also dangerous are borreliosis (Lyme disease), ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis and a number of other diseases transmitted by ticks.
! Every year, up to 400 thousand Russians turn to medical institutions for tick bites, a quarter of the victims are children under 14 years old. It is not known how many tick bites citizens of our country receive during foreign trips.
The maximum number of suctions is registered in the Siberian, Volga and Ural federal districts, the minimum – in the South and North Caucasus.
The attack of ticks is characterized by seasonality. The first cases of bites – early spring with an average daily soil temperature above 0,30C, the last – deep autumn. The maximum number of tick bites falls on the period from mid-spring to the first half of summer.
Ticks are potential carriers of one, and sometimes several types of microbes and viruses at once. Accordingly, the carriage of one pathogen is a mono-carrier, and two or more pathogens is a mixed carrier. In regions with high population density, ticks are carriers of:
mono-infections – in 10-20% of cases;
mixed infections – in 7-15% of cases.
What does the tick tick look like?
The tick is attached to the human body with the help of a hypostome. This unpaired outgrowth performs the functions of a sensory organ, attachment and bloodsucking. The most likely place for a tick to stick to a person from the bottom up:
groin area;
abdomen and lower back;
chest, armpits, neck;
ear area.
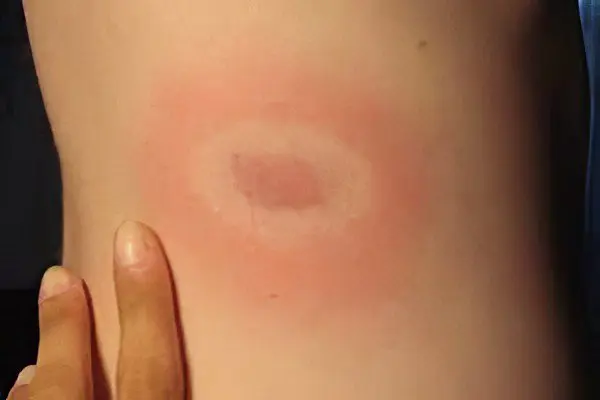
During a bite, under the action of tick saliva and microtrauma, inflammation and a local allergic reaction develop on the skin. The suction site is painless, manifested by reddening of a rounded shape.
The site of a tick bite in Lyme disease (borreliosis) looks characteristic – in the form of a specific patchy erythema, which increases to 10-20 cm in diameter (sometimes up to 60 cm). The shape of the spot is round, oval, sometimes irregular. After some time, an elevated outer border of intense red color forms along the contour. The center of erythema becomes cyanotic or white. The next day, the spot looks like a donut, a crust and a scar are formed. After two weeks, the scar disappears without a trace.
Video: bitten by a tick, what to do? Urgent care:
First aid for a tick bite
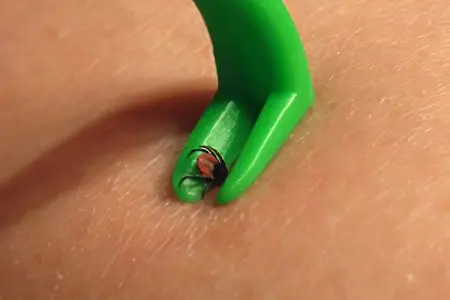
The victim must be helped to remove the tick, place it in a sealed container and sign the label accompanying the biomaterial sample.
The suction of a tick provokes an allergic response of the body, sometimes in the form of Quincke’s edema.
Signs of Quincke’s edema develop within a few minutes or hours in the form of:
swelling of the eyelids, lips and other parts of the face;
muscle pain;
difficult breathing.
This is a very dangerous manifestation of an allergic reaction, you should immediately call an ambulance and try to help the victim before the doctors arrive.
At home, you can do the following:
give one of the antihistamines;
provide access to fresh air;
Diagnostic and therapeutic measures for possible infections are carried out in medical institutions.
Where to go for a tick bite?
It is necessary to perform the following algorithm of actions:
remove the stuck tick;
take it to an accredited laboratory for the detection of infectious agents by PCR (see below for the address);
donate blood (if necessary) to detect antibodies to ELISA in human serum (details below).
undergo a course of treatment according to the results of laboratory tests and clinical indications.
1. Remove the stuck tick
The suction of the tick occurs after fixing it on the human body. This process takes from several minutes to several hours. Absorption of blood lasts from two hours to several days. Suction is imperceptible to humans, and a tick already drunk with blood is round and gray in color.
A sucked tick must be removed urgently, but very carefully! It is necessary to protect his abdomen from damage and leakage of hemolymph and human blood. Hands and the wound at the site of the bite should be treated with an alcohol-containing solution (vodka, alcohol solution of iodine or brilliant green).
Removing a tick with improvised means:
Throw a thread in the form of a loop around the proboscis (close to the skin), tighten and slowly pull it out with swinging movements. Instead of threads, you can use nails, two matches and other suitable items.
Place the tick inside a plastic bag, tie the neck.
Sign the label for the package (indicate the date, time, place of detection, full name of the person from whom the tick was removed, contacts for obtaining information about tick infestation).
Removing a tick with a special tool:
Use medical (manicure) tweezers or devices (Tick Twister, Tick Nipper, Pro tick remedy, Trix, Tricked off, others);
Place the tick in an airtight container (medicine bottle, for example);
Sign the label on the container (see above).
2. Take the tick to an accredited laboratory
Analyzes are carried out free of charge, but it is imperative to clarify this information. PCR study based on ready-made diagnostic kits AmpliSens TBEV (encephalitis, borreliosis, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis), distributor InterLabService LLC. We need to know when the results will be ready. Usually the same day or next morning.
3. Donate blood to detect antibodies
Within 10 days after the bite of a tick, on the recommendation of a doctor, it is sometimes necessary to donate blood to detect antibodies in humans to infections transmitted by ticks. For diagnostics, the test system “VektoVKE -IgG-strip” JSC “Vector-Best” is used. Analysis time: 2 hours 30 minutes.
4. Conduct immunotherapy as recommended by a doctor
According to the results of research on the tick by PCR and / or blood serum for ELISA, based on the doctor’s recommendations, specific immunotherapy is carried out.
The introduction of human immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis is paid!
Gamma globulin is administered free of charge to certain categories of citizens and on the basis of a VHI policy under the tick-borne encephalitis treatment program (be sure to contact the medical institution specified in the contract within 4 days after the bite).
The time during which specific treatment is possible, the period, the frequency of administration of globulin should be found out from the attending physician. The address of the point of medical care for encephalitis is indicated:
in DMS policies;
on the stand in the laboratory.
Bite prevention and other recommendations

The likelihood of a tick attack on a person depends on:
epidemiological well-being of the territory of residence;
profession associated with frequent stay in the forest, field;
the likelihood of visiting places that are unfavorable in terms of tick-borne infections.
Prevention of the consequences associated with a tick bite is based on:
vaccination, but this is a preventive measure; when a person is infected, it cannot be used;
specific immunotherapy is a therapeutic measure (administration of immunoglobulin only in case of infection or suspected infection after a bite);
health insurance to pay for possible treatment;
the use of special clothing and devices to prevent ticks from getting on the body;
the use of repellents, the destruction of ticks;
limiting the number of ticks in biotopes, places where people are likely to be.
Recommendations for choosing a vaccine
Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of disease, it is shown to all people living in disadvantaged regions, and to persons professionally associated with the forest (drillers, geologists, surveyors, foresters). If desired, the vaccination can be given to anyone who is interested in it, in the absence of contraindications.
Primary vaccination is possible from the first year of a child’s life, and then at any age. Adults can be vaccinated with domestic and imported drugs, children are better with imported ones. In Russia, six variants of vaccines are available from four manufacturers from Russia, Germany and Switzerland.
Tick-borne encephalitis vaccines produced in Russia:
The concentrated inactivated vaccine is indicated for use from three years and older;
Encevir (EnceVir), Russia, shown from the age of eighteen and older.
Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis produced in Switzerland:
FSME-Immun Junior (FSME-Immun Junior), shown from one year to sixteen years;
FSM-Immun Inject (FSME-Immun Inject), indications are similar.
Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis produced in Germany:
Encepur Children, shown from twelve months to eleven years;
Encepur adult (Encepur adult), shown from twelve years and older.
Two vaccination schemes: prophylactic and emergency:
Preventive vaccination provides protection against ticks during the first year, and after revaccination – within three years. Re-vaccinations are carried out every three years.
Emergency vaccination provides a short protective effect. Indication – urgent trips to regions unfavorable for encephalitis.
Vaccination is carried out after a preliminary survey of the patient for allergic reactions, clinical examination, thermometry. Persons with health problems are not allowed to be vaccinated. There are contraindications and restrictions.
In Russia, “Human Immunoglobulin Against Tick-Borne Encephalitis”, produced by FSUE NPO “Microgen”, is produced. The drug contains ready-made antibodies to viral encephalitis. It is administered intramuscularly for the purpose of treatment, usually after infection or at the risk of infection. Doses and frequency of administration can be obtained from your doctor.
Recommendations for insurance of costs associated with the treatment of tick-borne encephalitis
It is advisable to recommend insurance as an addition to vaccination or as the only measure in case of impossibility of vaccination. Insurance against tick-borne encephalitis is carried out as part of VHI – voluntary medical insurance. The payments are intended to compensate for the costly treatment of tick-borne encephalitis and other similar infections. When choosing an insurance program and an insurance company, you need to pay attention to:
availability of permits for the execution of VHI by the insured;
the cost of VHI services and the reputation of the insured;
availability of documents for the right to provide medical and preventive care or an agreement with a person authorized to provide such assistance on behalf of the insured;
Availability of a XNUMX-hour free telephone line for emergency advice.
Tips for preventing tick attacks
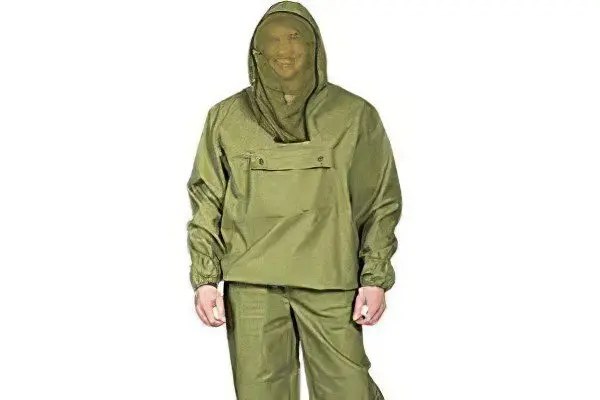

Going to the forest or out of town, choose the right clothes in light colors:
anti-encephalitis suit;
a jacket (shirt) with long sleeves and cuffs and trousers tucked into socks;
a hood that fits snugly to the head and protects the neck.
Every hour you need to inspect clothes from the bottom up for ticks. It is recommended to inspect the body every two hours, primarily the armpits, neck, groin, chest and head. It is worth avoiding or minimizing being in tall grass at the edge of the forest, along the paths.
Various devices are commercially available to prevent ticks from getting on the body in the form of insecticide-impregnated mosquito nets, special shoes, clothing, and so on.
Acaricides (destroy ticks) – have only a contact effect. They should be used exclusively for processing the fabric of outerwear and anti-mite treatment of territories and premises!
On sale you can find acaricides recommended for application to the skin. But they should be used carefully – allergies, poisoning are possible.
Recommendations for the destruction of ticks in biotopes and places where people are likely to be
To prevent the spread of ticks, you should regularly:
mow the grass on the site (ticks guard the victim in the grass, usually at a height of 0,6 m, the maximum height is 1,5 meters; in a hungry state, ticks live from two to four years, according to some sources up to seven years; development from egg to adult individuals – imago takes two to three years or more);
clean shrubs, remove fallen leaves (mites lose their own moisture in the sun, and restore balance in wet shelters);
destroy small rodents – tick hosts (circulation of the pathogen in the wild fauna – a natural focus of infection);
to treat places of probable concentration of ticks (ticks of the middle zone move within 5-10 meters, southern ones – up to 100 meters, orienting themselves with the help of receptors, concentrate along paths, forest edges – in places of probable contact with the victim).
Anti-mite treatments based on knowledge of mite biology are effective when performed annually. In many regions there are organizations that carry out desacarization, deratization, pest control, implement equipment for mowing grass, chemicals for anti-tick treatments.









