Contents

Itching of the skin of the body is a sign of any disease: systemic or dermatological.
In addition, itching on the skin can occur due to excessive dryness, poor hygiene, etc.
Diseases that cause itchy skin
Among the causes of itching are:
Diseases of the liver and biliary tract. Pathologies that lead to pruritus – cirrhosis, hepatitis, cancer of the head of the pancreas, primary sclerosing cholangitis, obstruction of the major bile duct and major duodenal papilla by tumors or stones, Giardia infection, cholestasis
Kidney disease, in particular kidney failure. Patients with uremia, especially at the terminal stage of the disease, suffer from severe itching. The more impaired the functionality of the kidneys, the stronger the itching of the skin. Dialysis contributes to its weakening, however, such a procedure is not able to completely eliminate renal itching;
Diseases of the thyroid gland. Up to 10% of patients with thyrotoxicosis indicate a pronounced persistent generalized itching. Most often, itching affects people with diffuse goiter, which is not treated for a long time. Scientists believe that itching occurs in this case due to increased blood flow to the skin, which entails a local increase in temperature;
Another cause of skin itching in hyperthyroidism is the development of chronic urticaria. If the patient is diagnosed with urticaria, it makes sense to suspect the autoimmune nature of the pathology of the thyroid gland. In addition, patients with myxedema (an extreme form of hypothyroidism) also complain of pruritus. It is caused by excessive drying of the skin and gives the patient serious anxiety;
carcinoid syndrome. Itching occurs due to frequent hot flashes in the head and neck, especially against the background of previous stress, overeating or drinking alcohol;
Diabetes. Patients with elevated blood glucose levels most often suffer from genital itching. It is caused by developed candidiasis lesions of the mucous membranes. In the area of the scalp, itching appears with diabetic neuropathy. As for generalized itching, in diabetes, it, as a symptom, is quite rare. If patients complain of generalized itching, then most often it is associated with metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus against the background of kidney damage;
Hematological diseases. Among these pathologies: lymphogranulomatosis, various lymphomas, polycythemia vera, leukemia, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, myelomas, mastocytosis, paraproteinemia, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia.
With true polycythemia, almost 50% of patients complain of generalized pruritus. Most often it occurs after contact with a liquid. That is why such itching is often called aquagenic. Sometimes itching appears much earlier than the disease itself and may precede it for several years in advance. Aspirin helps reduce itching, antihistamines are ineffective, although the level of histamine in the blood of such patients is elevated;
Also, itching can accompany iron deficiency anemia. Its severity is not related to the degree of anemia, however, after the start of treatment for the underlying disease, this symptom quickly disappears;
With lymphogranulomatosis, up to 30% of patients complain of itching. It haunts a person both during an exacerbation of the disease and during remission. Most often, it is localized in the region of the lower extremities, gradually moving to the lower part of the body, and later spreading to the entire body. Itching is accompanied by a burning sensation, the patient is most disturbed at night;
With lymphomas, itching is not so common, although in patients with Cesari’s syndrome, it is always recorded as a complaint. Moreover, patients talk about excruciating itching that arose many years before the onset of the disease;
Sometimes itching is accompanied by paraproteinemia, mastocytosis, lymphocytic leukemia. In some cases, scientists associate its occurrence with an increase in the concentration of serotonin, in others – with an increase in the level of histamine and other amines.
If the course of the disease can be brought under control, then itching, as a rule, becomes easily eliminated.
Senile or senile itching. By age 70, more than 50% of people experience itchy skin. Most often, it is associated with excessive dryness of the skin, when they are no longer able to retain fluid, and the performance of sweat and sebaceous glands is impaired. Additional risk factors for itching are overheating of the skin (in old age, people begin to dress warmer), dry air, frequent trips to the shower. In addition, older people become more susceptible to histamine, their skin regenerative function decreases, nutrition is insufficient, they are more likely to experience depression. These or other factors lead to the appearance of pruritus after the age of 70 years;
Itching with human immunodeficiency virus. Often, HIV-infected people complain about itchy skin that bothers them. In 92% of cases, it is associated with concomitant infections that develop as a result of a fall in immune forces. With the progression of the underlying disease, itching can cause excessive dryness of the skin. Particularly severe itching worries patients in the cold season;
Mental disorders: psychogenic itching. Skin itching may well be triggered by conditions such as stress, overwork, increased levels of anxiety, and depression. It is the latter factor that most often affects the occurrence of itching. With the development of depression in the blood, the level of dopamine, serotonin and other internal opioids increases, which leads to the development of itching. In addition, people with mental illness are able to experience generalized itching, which they attribute to parasitism, which is actually an illusion. Parasitophobia can be quite obsessive, and patients even provide the doctor with a wide variety of evidence of their own infection.
Nodular periarteritis and other systemic diseases;
Diseases of the nervous system: brain tumors, multiple sclerosis. In multiple sclerosis, itching starts suddenly and stops after a few seconds. With a severe attack of itching, a person can wake up in the middle of the night.
Itching may appear some time after a cerebral hemorrhage. It manifests itself on the opposite side from the site of brain damage, in addition, motor and sensory disturbances are observed;
Postherpetic neuralgia is another cause of itching, which is accompanied by painful sensations.
Allergic reactions. Contact dermatitis can occur due to the application of various medications to the skin, due to the use of inappropriate cosmetics or detergents. It can be provoked by contact with clothing, chemicals at work, wearing jewelry and jewelry.
Allergic urticaria occurs after ingestion of allergenic products inside, during the course of therapy with drugs that are inappropriate for a person, from exposure to dust, due to insect bites, as a result of temperature changes, under the influence of cold and light;
Eczema often occurs in people prone to allergic reactions. It can also develop against the background of chronic diseases, after vaccination or taking medications, it can become the body’s response to stress or the use of allergenic foods.
Parasite infestation. In this case, we are talking about helminthic invasion, in which itching occurs in the anus, but can also spread throughout the body.
Head lice leads to skin itching, when the scalp, temples and the back of the head are predominantly itchy. Sometimes eyebrows and eyelashes are affected by lice. The longer the hair, the more itching will be;
Clothes itch is another cause of itchy skin. At the same time, parasites live in the folds of clothing and affect the places where the skin and things come into contact most often;
Phthiriasis or pubic pediculosis is the next cause of itchy skin. In this case, it itches mainly the inguinal region. However, lice can also affect the ear area, mustaches, beards, eyebrows and eyelashes;
With demodicosis, itching is caused by mites – iron glands. They affect the hair follicles of a person, his sebaceous glands;
Scabies can cause itching when the skin is affected by a microscopic mite. The tick damages the skin of the hands, elbows, the skin of the abdomen, buttocks, thighs, and mammary glands.
Fungal lesions of the skin. Keratomycosis, in which the stratum corneum is affected. Itching can cause diseases such as erythrasma, actinomycosis and pityriasis versicolor.
Also, itching can be triggered by dermatophytosis, which affects the epidermis. Among such diseases are epidermophytosis, favus, trichophytosis;
Skin candidiasis most often develops in people who are overweight, as well as in children with poor hygiene;
Severe itching of the skin of the body can also be triggered by a fungal disease such as ringworm.
Avitaminosis. Most often, itching is associated with drying of the skin. It can be provoked by a lack of vitamin A, B vitamins, vitamin C. In addition, zinc deficiency negatively affects the skin condition. With its lack, a person begins skin problems – acne, boils appear, which causes skin itching;
Hygiene violations. Non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene is the most obvious reason that can lead to itching of the skin;
Menopause. Itching during menopause most often affects the genitals and is associated with hormonal changes in the body;
Folliculitis. One of the symptoms of the disease can be severe itching in the area of folliculitis. Itching is especially difficult to tolerate in the presence of many inflamed follicles;
Neurodermatitis. With neurodermatitis, itching, rashes and redness of the skin, its peeling are observed;
Insect bites, including flea bites at night;
Psoriasis. Itching in psoriasis most often worries a person with a progressive course of the disease. In addition to itching, the patient suffers from severe peeling in the affected area.
Spots on the skin and itching – what does it mean?
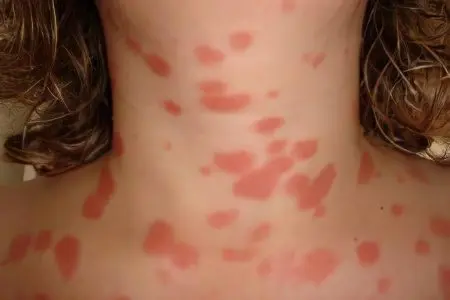
If the occurrence of itching is accompanied by the appearance of spots, then most often this indicates a skin disease, and not a systemic pathology. Perhaps the person suffers from allergies or inflammation, including contact and atopic dermatitis. See also: Atopic dermatitis in adults and children.
With contact dermatitis, itching and spots are localized in the place where the allergen came into contact with the skin. Redness has well-defined borders. To determine the allergen yourself, you should remember about new hygiene products, buying a new washing powder or thing, etc. Contact dermatitis is different in that after the allergen is removed, the inflammatory reaction on the skin and itching are eliminated on their own.
As for atopic dermatitis, it is most often diagnosed in childhood, although it sometimes affects adults. The reason also lies in an allergic reaction, but it occurs in response to an allergen that has entered the body. If in children the cheeks turn red in the first place, then in adults – the elbows, knees (at the bends), as well as the wrists.
If a red spot appears on the skin, it itches and is located at the site of a previous injury, then this symptom often indicates diabetes mellitus. Mostly such spots are formed on the lower extremities.
Sometimes red patches are signs of psoriasis and may be itchy but may not cause any discomfort.
Itchy red spots on the lower extremities, which subsequently become darker, may indicate trophic disorders.
Photodermatosis is another reason for the appearance of various types of itchy spots. They can rise above the surface of the skin, they can look like bubbles, they can be located on the same level with the rest of the skin.
Lichen planus also manifests itself in the form of itchy spots that rise above the skin. Often such spots form on the feet and in the lower leg area, may have a purple hue, and also merge, forming larger spots.
Ringworm also manifests itself in the form of spots that have clear boundaries and a rounded shape. Along the periphery of such an itchy spot is a pink roller, represented by bubbles and nodules.
As for eczema, it is also characterized by red spots, which, as the disease progresses, transform into vesicles, and then open. Itching may be present, but sometimes eczema does not make you want to scratch the inflamed area.
Urticaria is characterized by the appearance of itching and blisters protruding above the surface of the skin.
Bullous pemphigoid occurs most often in places of maximum friction with clothing and accessories.
Also, the cause of the appearance of itchy spots may be limited or diffuse neurodermatitis.
Skin rashes with itching in adults
Itchy rashes on the skin of an adult may indicate the following diseases:
Eczema manifests itself as a spot, on which bubbles subsequently form, and after their opening – crusts;
T-cell lymphoma is accompanied by a rash and appears in places that are most often in contact with ultraviolet rays;
Folliculitis is characterized by the formation of small vesicles, which are subsequently filled with purulent contents;
Scabies manifests itself in the form of vesicular rashes that are red and transparent. Tick passages are visible under the skin;
Allergic dermatitis can also appear as a small or large rash. Its appearance is accompanied by skin itching;
Diseases of the internal organs (liver, kidneys), blood diseases can manifest themselves as a small itchy rash on the skin.
When rashes appear, which are accompanied by itching, it is necessary to consult a doctor and clarify the cause of their occurrence.
Types of itching on the skin
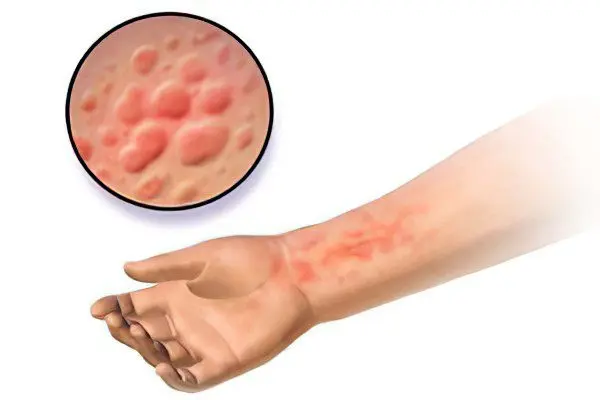
Depending on the cause and origin of pruritus, the following types are distinguished:
Proprioceptive (arising in response to stimulation of C-fibers with a pruritogen), an example is itching with scabies, insect bites;
Neuropathic (occurring when the nervous system is damaged), an example is itching with neuralgia and vascular thrombosis;
Neurogenic (has a central origin, does not depend on nervous pathologies), an example is cholestasis;
Psychogenic (accompanied by mental disorders), an example is parasitophobia;
Mixed, an example is itching with uremia.
Depending on the prevalence of the symptom, itching can be localized, when it is possible to clearly define the itching place, and generalized, when the whole body itches. An example of localized itching is scabies, pediculosis, ringworm, atopic dermatitis, etc. Generalized itching occurs with kidney failure, with helminthic invasion, with diabetes, with gout, etc.
Ways to treat itching
In order to get rid of itching, it is necessary first of all to decide on the tactics of treating the disease that provoked this symptom. It is important that the vicious circle, in which patients with itching often find themselves (itching – scratching – more pronounced itching), be interrupted.
Drug treatment is selected on an individual basis, however, with excessive dryness of the skin, the following rules must be followed:
The room where a sick person spends most of the time must be thoroughly ventilated. It is important that the air stays cool;
Overly warm blankets should not be used during the night’s rest, and it is also important to wear light clothing made from natural fabrics. This will avoid overheating;
While taking baths, it is necessary that the water is not too hot;
It is often undesirable to take a shower, especially with the use of soaps or gels.
[Video] Euromed Clinic – Symptoms, causes and treatment of severe itchy skin:









