Contents
- What varieties of plums can be planted in the Leningrad region
- When the plum ripens in the Leningrad region
- The best plum varieties for the Leningrad region with a description
- Plum varieties for the Leningrad region
- Planting and caring for plums in the Leningrad region
- Plum varieties for the Northwest
- Plum varieties for Karelia
- Conclusion
- Reviews
Plum in the Leningrad region, from year to year pleasing with a plentiful harvest of delicious fruits, is a gardener’s dream, quite capable of becoming a reality. To do this, it is necessary to choose the right variety, taking into account the specifics of the climate and soil conditions of the North-West of Our Country, as well as adhere to the rules for planting and caring for crops developed for this region.

What varieties of plums can be planted in the Leningrad region
Plum is considered to be one of the most capricious and whimsical fruit trees, because it is very sensitive to environmental conditions. The temperate continental climate of the Leningrad Region and the North-West of the country is a serious test for this culture. High humidity, harsh cold winters, late spring frosts and cloudy rainy summers, diluted with a small number of sunny days – all this significantly limits the choice of gardeners regarding which plum to plant on the site. Nevertheless, thanks to the painstaking work of breeders, today there are many recommended and promising varieties that feel quite comfortable in the difficult conditions of the North-West.

Varieties that have proven themselves under the indicated conditions, but which are still being tested, are considered promising.
Ideally, a plum suitable for growing in the North-West of the country (including the Leningrad region) should have the following qualities:
- small tree growth;
- strong winter hardiness and resistance to temperature extremes;
- high rates of disease resistance;
- self-fertility (very desirable for the gardens of the North-West);
- early fruit ripening is preferred.

When the plum ripens in the Leningrad region
According to the ripening period of fruits, plum varieties cultivated in the Leningrad region and in the North-West can be divided into:
- early (first decade of August);
- average (approximately from 10 to 25 August);
- later (end of August – September).

The best plum varieties for the Leningrad region with a description
According to the reviews of the farmers of the Leningrad region and the North-West of Our Country, you can get an idea about the best plum varieties for this region, which are invariably popular in local gardens:

| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
| Red-breasted Red | Early | 25 – 40 Feet | Medium (up to 3,5 m) | Oval-spherical, wide | Up to 15 g, raspberry-violet, without pubescence, with yellow, dryish flesh, sour-sweet | Yes (according to other sources – partially) | Renklod collective farm, Hungarian Pulkovskaya | |
| Early ripening round | Average | 10–15 (sometimes up to 25) | Medium (2,5–3 m) | Thick, spreading, “weeping” | 8–12 g, red-purple with a bluish bloom, yellow flesh, juicy, sweet with “sourness” | No | Early maturing Red | |
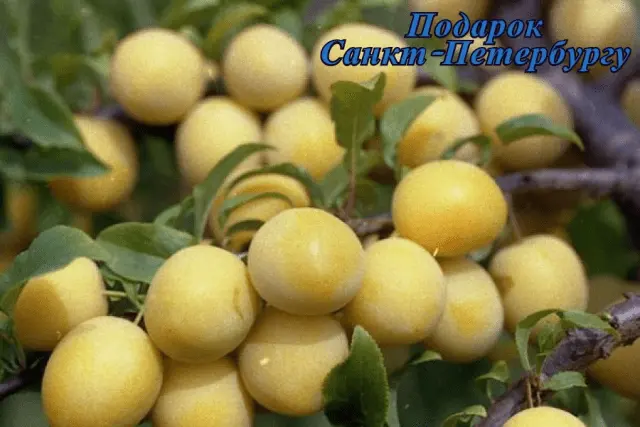
| Gift to St. Petersburg | A hybrid involving cherry plum and Chinese plum | Early | Up to 27 (max 60) | Average | Spreading, medium density | Up to 10 g, yellow-orange, yellow flesh, juicy, sweet and sour | No | Pavlovskaya yellow (cherry plum), Pchelnikovskaya (cherry plum) |
| Ochakiv yellow | Late | 40 – 80 Feet | Average | narrow pyramidal | Up to 30 g, color from pale green to bright yellow, sweet, “honey”, juicy | No | Renklod green | |
| Renkloed collective farm | Hybrid of thorn and renclod green | Mid-late | About 40 | Average | Round-spreading, medium density | 10–12 g (occasionally up to 25), greenish-yellow, juicy, sour-sweet | No | Volga beauty, Eurasia 21, Moscow Hungarian, Red early ripening |
| Etude | Average | Before 20 kg | Above average | Raised, rounded | About 30 g, deep blue with a burgundy tint, juicy, sweet with “sourness” | Partially | Volga beauty, Renklod Tambov, Zarechnaya early | |
| Alenushka | Chinese plum | Early | 19 – 30 Feet | Undersized (2–2,5 m) | Elevated, pyramidal | 30-50 g (there are up to 70), dark red with bloom, juicy, sweet with “sourness” | No | Early |
| The Volga beauty | Early | 10 – 25 Feet | vigorous | Oval-rounded, raised | Up to 35 g, red-violet, juicy, dessert flavor | No | Red-breasted Red | |
| Anna Shpet | Variety of German selection | Very late (late September) | 25 – 60 Feet | vigorous | Dense, broad pyramidal | About 45 g, dark blue with a brick tint, juicy, dessert flavor | Partially | Renklod green, Victoria, Hungarian home |
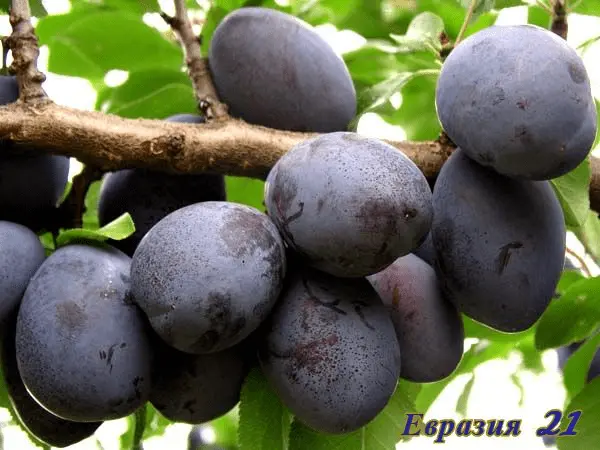
| Eurasia 21 | A complex hybrid of several types of plum (diploid, Chinese, cherry plum, domestic and some others) | Early | 50–80 (up to 100) | vigorous | Раскидистая | 25–30 g, burgundy, fragrant, juicy, sweet and sour | No | Renkloed collective farm |
| Edinburgh | Variety of English selection | Average | vigorous | Rounded, medium density | About 33 g, purple-red, with a blue coating, juicy, sweet and sour | Yes |


Plum varieties for the Leningrad region
The assortment of plums for the Leningrad region and the North-West, of course, is not limited to the above items. It is necessary to characterize other varieties suitable for cultivation in this part of the country, grouping them according to certain characteristics.
Yellow plum for the Leningrad region
Plums with amber, yellow fruits are deservedly popular among gardeners – not only because of their exotic appearance, but also due to the sweetness and aroma inherent in these varieties, good winter hardiness and productivity.

In the Leningrad region, as well as in the North-West of the country, you can successfully grow such of them:
| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
| Lodva | Diploid plum of Belarusian selection | Early | 25 kg / ha | Average | Round-pyramidal | About 35 g, round, tender, very juicy, sweet and sour taste with a “caramel” aroma | No | Dream, Bliss |
| Mara | Diploid plum of Belarusian selection | Late | 35 kg / ha | vigorous | Spreading, rounded | Average 25 g, bright yellow, very juicy, sour-sweet taste | No | Asoloda, Vitba |
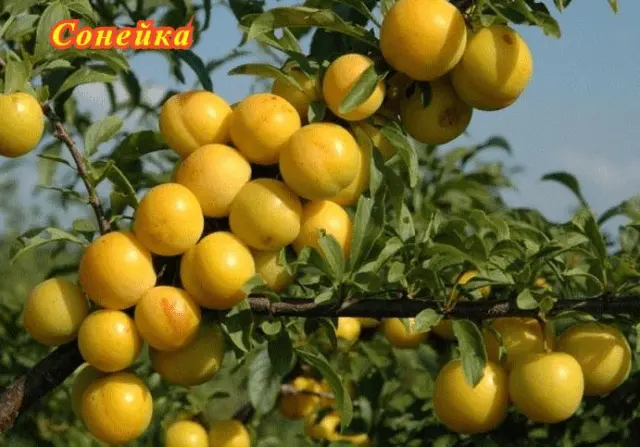
| Soneyka | Diploid plum of Belarusian selection | Late | Until 40 | undersized | drooping, flattened | About 35–40 g, rich yellow, juicy, aromatic | No | Eastern European varieties of plums |
| Firefly | Hybrid of Eurasia 21 and Volga beauty | Average | Until 20 | Vigorous (up to 5 m) | Raised, oval | 30–40 g, yellow-green, juicy, slightly sour in taste | No | Collective farm renklod, Productive renklod |
| Yakhontovaya | Hybrid of Eurasia 21 and Smolinka | Early | 50 – 70 Feet | Vigorous (up to 5,5 m) | Globular compact | 30 g, yellow, juicy, dessert taste, sweet and sour | Partially | Early ripening red, Hungarian Moscow |
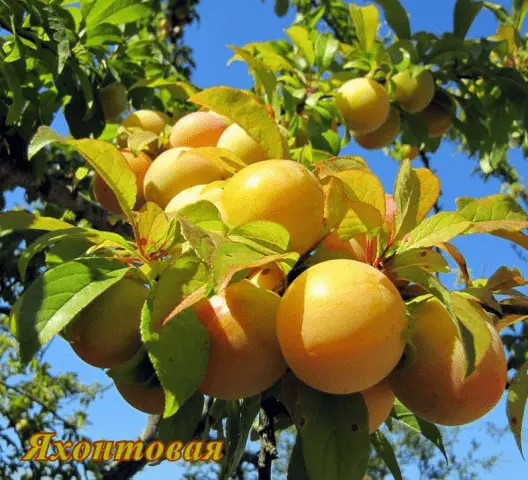

Self-fertile domestic plum for the Leningrad region
For plums growing in the gardens of the Leningrad region and the North-West of Our Country, a very significant positive property is self-fertility, at least partial.

A variety with this quality will become a real treasure for the farmer in the event that it is not possible to plant several trees on the site. If the garden is large enough, then the yield of self-fertile plum varieties with the right pollinators will be beyond praise.
| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
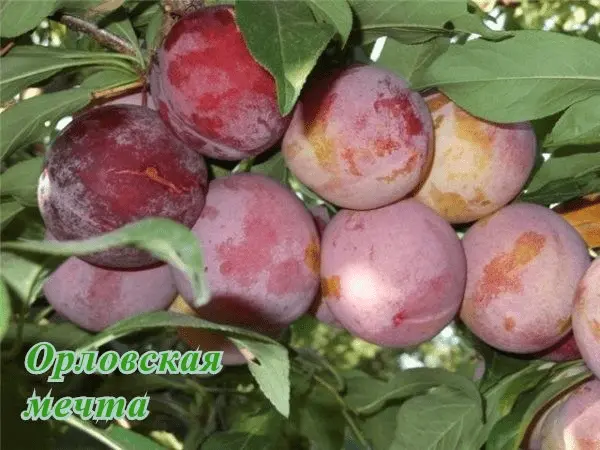
| Oryol dream | Chinese plum | Early | 35:50-XNUMX:XNUMX | Average | Pyramidal, raised, spreading | About 40 g, red, with a slight bloom, juicy, sweet and sour | Partially | Skoroplodnaya, varieties of cherry plum hybrid |
| Venus | Variety of Belarusian selection | Average | 25 t / ha | Average | Раскидистая | From 30 g, red-blue with a strong coating, round, sweet and sour | Yes | |
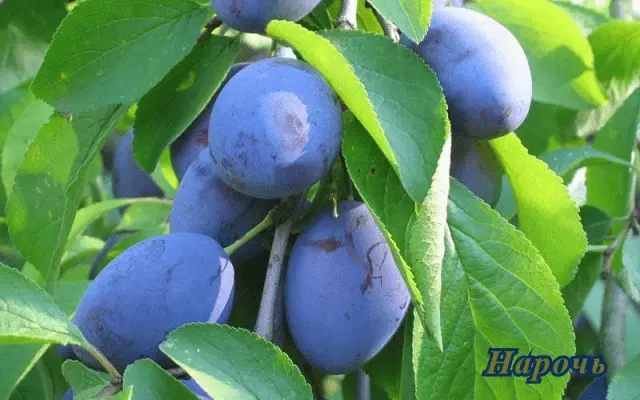
| Naroch | Late | Average | Globular, thick | Average 35 g, dark red with a thick coating, sweet and sour taste | Yes | |||
| Nezhenka | Chinese plum | Early | Until 40 | Undersized (up to 2,5 m) | Globular, thick | Average 24–29 g, scarlet, round, juicy, melting flesh | Partially | Varieties of Chinese plum |
| Stanley (Stanley) | American selection variety | Late | About 60 | Medium height (up to 3 m) | Spreading, rounded oval | About 50 g, dark purple with a thick bluish bloom and yellow flesh, sweet | Partially | Chachak best |
| Orlovsky souvenir | Chinese plum | Average | 20:50-XNUMX:XNUMX | Secondary | Wide, spreading | 31–35 g, purple with spots, dryish flesh, sweet and sour | Partially | Any variety of fruitful plums |

Varieties of low-growing plum for the Leningrad region
Another advantage of the plum in the eyes of the gardener will be a small, compact tree. It is easier to take care of this one, it is easier to collect fruits from it.

| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
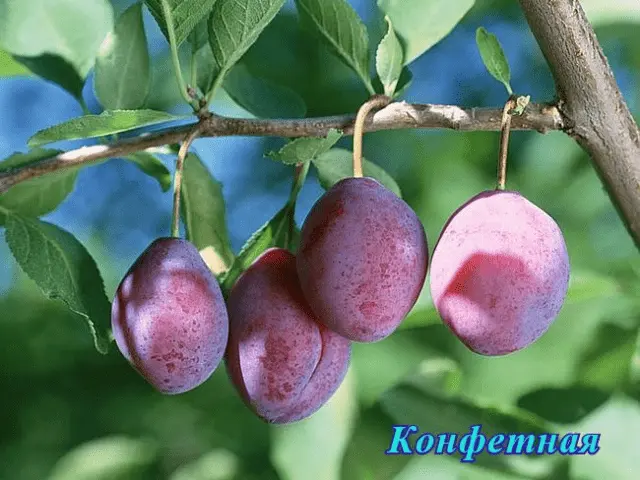
| Candy | Very early | About 25 | Undersized (up to 2,5 m) | Round, neat | 30–35 g, purple-red, honey flavor | No | Renklod collective farm, Zarechnaya early | |
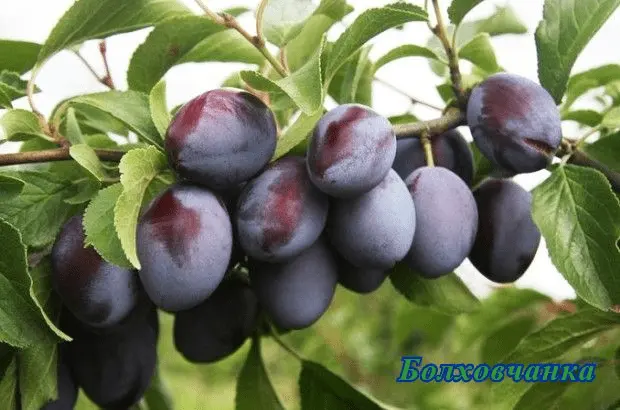
| Bolkhovchanka | Late | Average 10–13 | Undersized (up to 2,5 m) | Rounded, raised, thick | 32–34 g, burgundy-brown, juicy, sweet and sour taste | No | Renkloed collective farm | |
| Renklod Tenkovsky (Tatar) | Average | 11,5 – 25 Feet | Undersized (up to 2,5 m) | Scattered, “broom-like” | 18–26 g, yellow with a red “blush”, strong patina, medium juiciness, sweet and sour | Partially | Early ripening red, Early ripening new, Eurasia 21, thorn | |
| Pyramidal | Hybrid of Chinese and Ussuri plums | Early | 10 – 28 Feet | Undersized (up to 2,5 m) | Pyramidal (in adult trees – rounded), thickened medium | About 15 g, dark red with a strong bloom, juicy, sweet and sour with bitterness near the skin | Partially | Pavlovskaya, Yellow |
| Red ball | Chinese plum | Medium | Until 18 | Undersized (up to 2,5 m) | Drooping, round-spreading | About 30 g, red with a bluish bloom, | No | Chinese early-fruited, cherry plum |
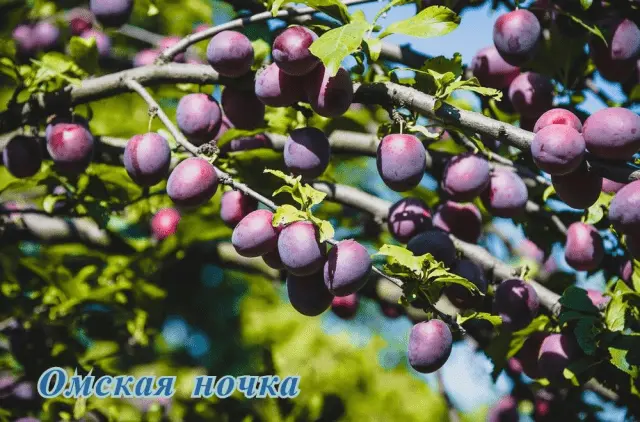
| Omsk night | hybrid of plum and cherry | Late | Before 4 kg | Undersized (1,10–1,40 m) | compact bush | Up to 15 g, black, very sweet | No | Bessea (American creeping cherry) |


Early plum varieties for the Leningrad region
Early varieties of plums in the conditions of the Leningrad region and the North-West of Our Country, as a rule, ripen in early August.

This allows you to taste fragrant fruits earlier and, of course, harvest before the onset of autumn frosts. The tree will have enough time to recover and then successfully overwinter.
| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
| Nika | Early | Until 35 | Medium or vigorous (sometimes up to 4 m) | Wide oval, spreading | 30-40 g, dark purple with a thick blue bloom, sweet with “sourness” and slight astringency | No | Renklod soviet | |
| Zarechnaya early | Early | From 15 from a young tree (further increases) | Secondary | Compact, oval or spherical | 35-40 g, dark purple with bloom, juicy, sour-sweet | No | Volga beauty, Etude, Renklod Tambov | |
| Starting | Very early | 61 kg / ha | Secondary | Spherical-oval, dense | About 50 g, dark red with a strong coating, very juicy, sweet and sour | No | Eurasia 21, Volzhskaya beauty | |
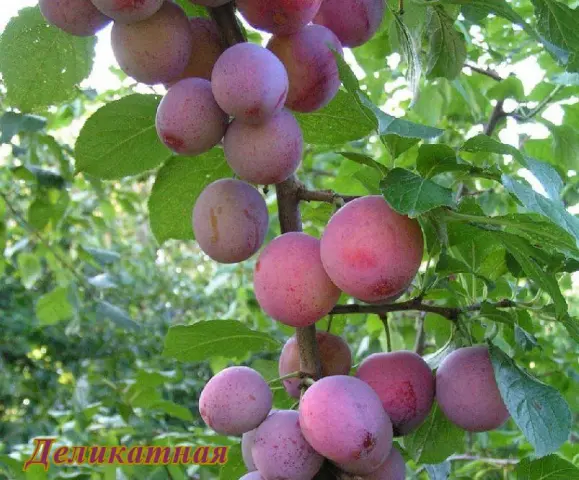
| Delicate | Medium | 35 – 40 Feet | tall | Spreading, rounded | Up to 40 g, bright red, juicy, sweet and sour | Partially | Victoria, Edinburgh | |
| Renklod early | Variety of Ukrainian selection | Very early | Until 60 | Vigorous (up to 5 m) | Rounded | 40–50 g, yellow-orange with a pink “blush”, sweet with “sourness” and honey aftertaste | No | Renklod Karbysheva, Renklod Ullensa |

Planting and caring for plums in the Leningrad region
The specifics of plum cultivation in the Leningrad region and the nuances of caring for it in this region are directly related to the fact that geographically this is the northernmost part of the country where stone fruit trees can be successfully grown. The most important success factor is a correctly selected variety, which, according to its characteristics, is suitable for the North-West. However, competent tree planting on the site and proper care for it, taking into account the characteristics of local soils and climate, play an equally important role in obtaining a crop.
When to plant plums in the Leningrad region
Plum is usually recommended to be planted in autumn or spring. The last option for the Leningrad region and the North-West is more preferable. This is due to the fact that plum is a thermophilic culture. Landing in the ground is advised to be carried out 3–5 days after the soil has completely thawed, without waiting for the buds to bloom on the tree.
If the gardener nevertheless decided to plant a plum in the fall, he should do it 1,5–2 months before the time when frosts usually occur in the Northwest. Otherwise, the seedling may die without having time to take root before the winter cold.

Planting plums in the spring in the Leningrad region
The choice of a site for planting plums in the Leningrad region and in the North-West of the country is determined by the following features:
- it is preferable that the soil is fertile, loose and well-drained;
- it is advisable to choose a place on a hill (upper part of the slope): in winter there will not be too much snow, and in spring melt water will not accumulate;
- the level of groundwater in the area where the plum will grow must be deep (at least 2 m).
Where exactly the plum will grow should be planned in advance. Within a radius of 2 m from this place, you need to dig the soil well, weed the weeds, and apply fertilizer to the soil.

A couple of weeks before the proposed planting of a tree, it is necessary to prepare a planting hole:
- its width should be approximately 0,5–0,6 m, and its depth – 0,8–0,9 m;
- at the bottom of the pit, it is advised to lay a part of the fertile soil extracted from it, mixed with humus and mineral fertilizer, as well as a small amount of chalk, dolomite flour or slaked lime;
- it is advisable to immediately establish a support for the garter of the future tree (optimally – on the north side), given that there should be at least 15 cm between the peg and the seedling.
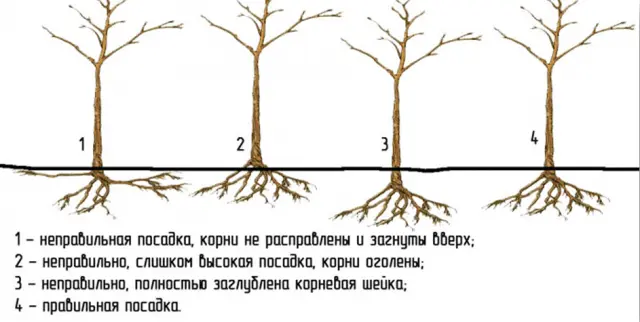
Planting a seedling in the ground in the North-West of the country is carried out according to the general rules:
- fertile soil is poured into the lower part of the pit with a mound;
- a seedling is carefully placed on top of it and its roots are straightened;
- then the soil is carefully covered, making sure that the root neck of the tree is 3–5 cm above ground level;
- it is permissible to lightly tamp the soil, making sure not to damage the trunk and roots of the plant;
- then the trunk is tied to a support using a hemp rope or soft twine (but in no case a metal wire);
- the plant is well watered (20–30 l of water);
- the soil in the trunk circle is mulched (with peat or sawdust).
How to cut a plum in the Leningrad region
Plum crown formation begins from the second year.
You can devote time to this in the fall or spring, however, it is believed that the spring pruning carried out before the start of the sap flow processes is easier for the tree to tolerate:
- cut sites heal faster;
- the possibility of freezing of a recently cut tree in winter is excluded, which is especially important for the North-West of Our Country and can contribute to the development of diseases.
The plum is carefully inspected after the winter, removing damaged and frozen branches. Simultaneously with the growth of the crown, shoots thickening it should be removed, as well as those that grow inward or vertically upwards, giving the tree a beautiful and comfortable shape.
In addition, shoots growing within a radius of about 3 m from the roots should be cut. This procedure should be carried out 4-5 times during the summer.
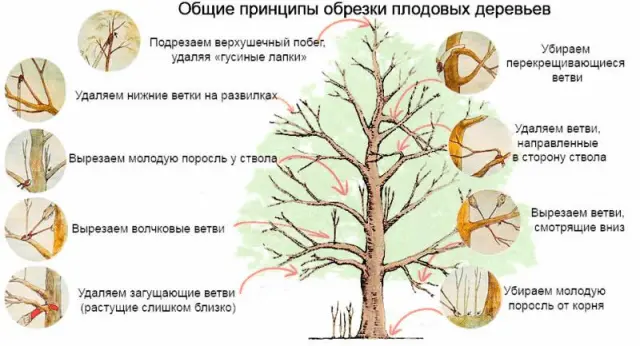
The following are recognized as the optimal schemes for the formation of a plum crown:
- pyramidal;
- improved longline.
Cultivation of plums in the Leningrad region
Plum care in the gardens of the Leningrad Region and the North-West as a whole is subject to the general rules for growing this crop, but it also has some specifics.
When organizing watering, you need to remember that plum is a moisture-loving plant. She does not like waterlogging, but you can not let her dry out. During hot periods in summer, the plum should be watered every 5-7 days at the rate of 3-4 buckets for a young and 5-6 for an adult tree.

It is equally important to properly feed the tree with fertilizers:
- during the first 3 years after planting the plum, spring application of urea to the soil is sufficient (at the rate of 20 g per 1 m3);
- it is advisable for a tree that is starting to bear fruit to receive support annually in the form of a mixture of urea (25 g), superphosphate (30 g), wood ash (200 g) and manure (10 kg per 1 m3 of the trunk circle);
- for a fully fruiting plum, it is recommended to double the amount of organic fertilizers, leaving the previous volumes of mineral fertilizers: in the spring, humus, manure, and urea are added to the soil, while in the fall, potash and phosphorus mixtures are added.
The first couple of years after planting a plum, it is necessary to regularly loosen the soil in the near-stem circle with a fork or shovel to a shallow depth in order to control weeds. In the process, you need to add peat or humus (1 bucket each). For the same purpose, it is possible to mulch the area of the near-stem circle by about 1 m around the tree with a layer of sawdust (10–15 cm).

The area around the tree, which is older than 2 years, can be treated with herbicides. They are brought in in dry calm weather, making sure that the drugs do not get on the leaves and trunk.
Periodically, you need to carefully inspect the tree for pest damage or the presence of symptoms of diseases. Timely measures taken to eliminate the problem will save the gardener from a long and difficult struggle for the health of the plum, which can often end in the death of the plant.
Some simple and useful plum care tips that are also relevant for growing this crop in the Leningrad Region and the North-West can be obtained from the video
Preparing plums for winter
Despite the fact that most varieties of plums suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West have high frost resistance, in winter they still need additional shelter.
The stem of the tree should be whitewashed before the onset of cold weather. Then it is insulated, tied with roofing material, on top of which glass wool and a layer of reflective foil are laid. This will help the plum to safely endure even very severe colds, which are not at all rare for the North-West.
Trunk circles, especially around young plants, are covered with straw on the eve of the winter period. When snow begins to fall, you need to make sure that it does not accumulate much under the tree – no more than 50–60 cm.
Plum varieties for the Northwest
The varieties recommended for the Leningrad region will grow quite successfully in other regions of the North-West of the country.

You can expand this list:
| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
| Red-meat big | Late | Until 20 | Vigorous (up to 4 m) | compact, rare | About 25 g, dark raspberry with bloom, juicy, sweet and sour with “bitterness” near the skin | No | Cherry plum hybrid | |
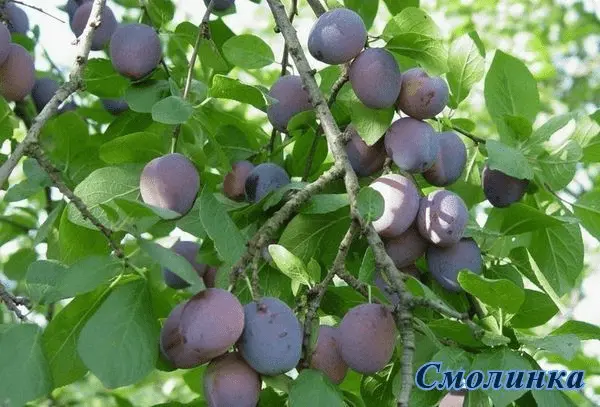
| Smolinka | Average | Until 25 | Vigorous (up to 5–5,5 m) | Oval or round pyramidal | 35–40 g, dark purple with a thick bluish coating, sweet and sour taste, delicate | No | Volga beauty, Morning, Early ripening red, Hungarian Moscow | |
| Tenkovskaya dove | Average | About 13 | Secondary | Broad pyramidal, dense | Up to 13 g, dark blue with a strong coating, sweet and sour | No | Renklod Tenkovsky, Red early ripening | |
| Award (Rossosh) | Late | Until 53 | vigorous | Oval, medium density | 25–28 g, greenish with dark red rich “blush”, juicy | No | ||
| Vigana | Estonian variety | Late | 15 – 24 Feet | undersized | Weeping, medium density | About 24 g, burgundy with a strong touch, sweet with “sourness” | Partially | Sargen, Hungarian Pulkovskaya, Early maturing red, Renklod collective farm |
| Lujsu (Liizu) | Estonian variety | Early | 12 – 25 Feet | Secondary | Well leafy, thick | 30 g, red-violet with golden “dots”, there is a coating, dessert taste | No | Renklod Tenkovsky, Morning, Red early ripening, Pulkovo Hungarian |
| Sargen (Сарген) | Estonian variety | Average | 15 – 25 Feet | undersized | Wide oval, thick | 30 g, burgundy-violet with golden dots, dessert flavor | Partially | Ave, Eurasia 21, Kolkhoz Renklod, Red early ripening, Reward |

Varieties of self-fertile plum for the North-West
Among the self-fertile and partially self-fertile varieties of plums suitable for the North-West (including the Leningrad region), it is certainly worth mentioning the following:

| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
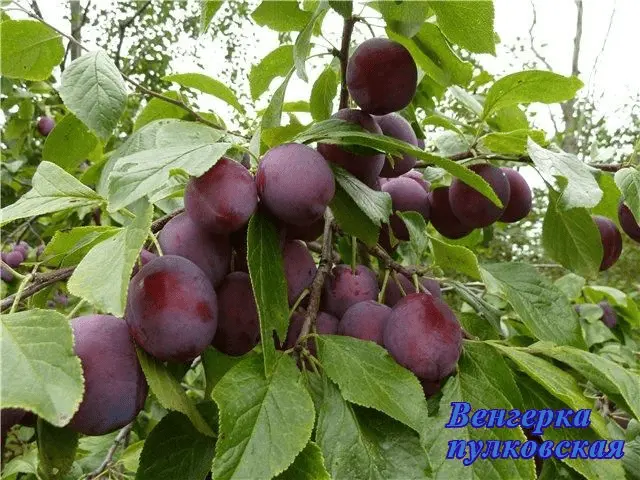
| Hungarian Pulkovo | Late | 15 – 35 Feet | vigorous | Wide, spreading | 20–25 g, dark red with “dots” and a bluish bloom, sweet with “sourness” | Yes | Winter red, Leningrad blue | |
| Hungarian Belarusian | Average | About 35 | Medium (up to 4 m) | Spreading, not very thick | 35-50, blue-violet with a strong bloom, sweet and sour | Partially | Victoria | |
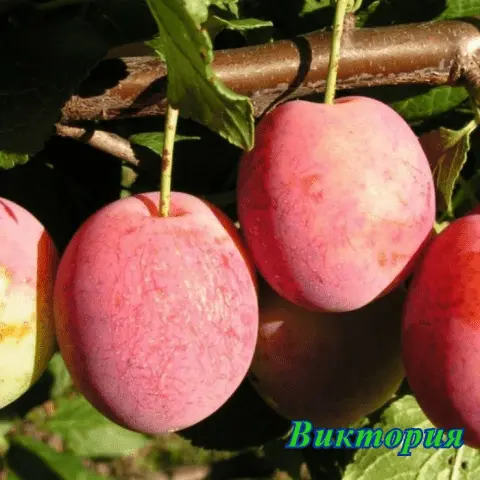
| Victoria | Variety of English selection | Average | 30 – 40 Feet | Medium (about 3 m) | teary-eyed | 40-50 g, red-violet with a strong coating, juicy, very sweet | Yes | |
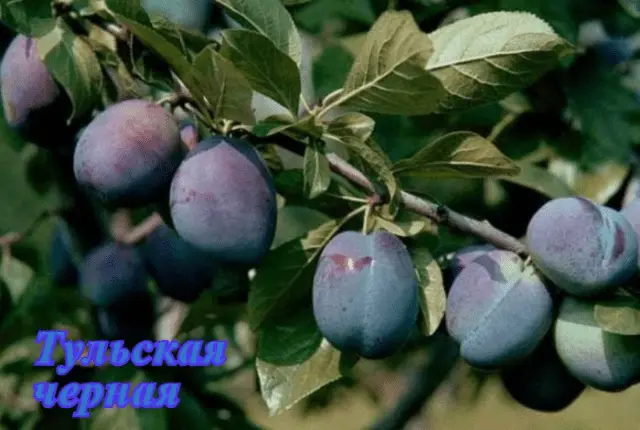
| Tula Black | Mid-late | 12–14 (up to 35) | Medium (from 2,5 to 4,5 m) | Thick, oval | 15–20 g, dark blue with a reddish tinge, with a thick coating, sweet with “sourness” at the skin | Yes | ||
| Beauty CGL | Average | Secondary | Spherical, compact | 40–50 g, blue-violet with bloom, sweet and sour, juicy | Partially | Eurasia 21, Hungarian |

Yellow Plum for the Northwest
To the varieties of plums with a yellow integumentary color of fruits that can grow in the climatic conditions of the Leningrad Region, it is worth adding a few more that can take root in the gardens of the North-West:

| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
| Greengage Kuibyshevsky | Mid-late | Until 20 | undersized | Dense, stony | 25–30 g, greenish-yellow with a bluish bloom, juicy, sour-sweet | No | Renklod collective farm, Volga beauty, Red early ripening | |
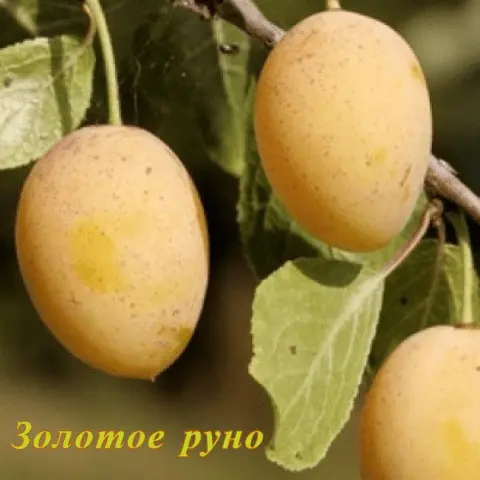
| The Golden Fleece | Mid-late | 14 – 25 Feet | Secondary | Thick, “weeping” | About 30 g, amber-yellow with a milky coating, sweet | Partially | Early ripening red, Eurasia 21, Volga beauty | |
| Emma Lepperman | Variety of German selection | Early | 43–76 c/ha | vigorous | Pyramidal, with age – rounded | 30-40 g, yellow with a “blush” | Yes | |
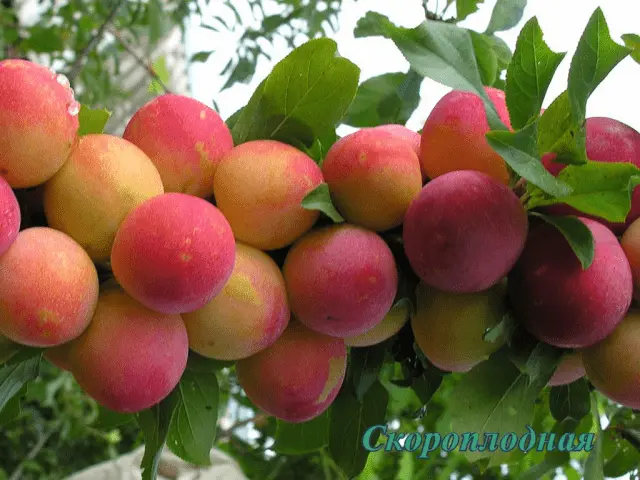
| Early | Chinese plum | Early | About 9 | Average | Fan-shaped | 20-28 g, yellow with a blush, fragrant, juicy, sweet and sour | No | Red ball, any varieties of cherry plum hybrid |

Plum varieties for Karelia
There is an opinion that the northern boundary of the territory where plums can be successfully grown lies along the Karelian Isthmus. For this part of the North-West, gardeners are advised to purchase some varieties of Finnish selection:
| The name of the plum variety suitable for the Leningrad region and the North-West | Feature of origin (if any) | Maturation period | Yield (kg per tree) | Tree height | Crown shape | Fruit | Self-fertility | The best varieties-pollinators (for the Leningrad region and the North-West) |
| Common Blue Crane (Илейнен Синекрикуна) | Late | 20 – 30 Feet | 2 to 4 m | Small, rounded, dark blue with a waxy coating, sweet | Yes | |||
| Common yellow plum (Илейнен keltalumu) | Late | 3 to 5 m | Large or medium, golden, juicy, sweet | No | Kuntalan, red plum, blackthorn | |||
| Blue (Синикка) | Average | Undersized (1,5–2 m) | Small, rich blue with a waxy coating, sweet | Yes |

Conclusion
In order for the plum in the Leningrad region and in the North-West of the country to take root in the garden, not get sick and successfully bear fruit, varieties of this crop capable of growing in this region were bred and selected. They can endure the difficult conditions of the local climate, are less demanding on heat, air humidity and an abundance of sunny days than their southern counterparts, and are highly resistant to common diseases. It is very important to correctly determine the variety, correctly select and prepare the site, provide proper care for the plum, including measures to protect the tree in the winter – and abundant, regular harvests will not keep you waiting.









