Contents
Seborrhea is not life-threatening, but can significantly affect its quality. This common skin disease has long ceased to be just a cosmetic defect. In modern medicine, it is considered a serious pathology, the appearance and development of which is associated with a violation of the functions of the sebaceous glands. Why does seborrhea appear, how does the disease behave, and how effective are the known methods of treating this disease? We’ll figure out.
What is seborrhea?
Seborrhea (seborrheic dermatitis) is a chronic dermatosis, which is manifested by redness of the scalp, the appearance of rashes of white scales on it, accompanied by itching. The disease can occur due to the banal neglect of the rules of personal hygiene and the advice of a nutritionist. Many mistakenly believe that seborrhea is just dandruff. This is not so, being one of the forms of dermatitis, seborrhea in most cases proceeds in a chronic form. To get rid of discomfort and unpleasant symptoms, many patients have to be treated for years, but even in such cases, relapses are likely. Exacerbations of the disease are observed in the autumn season, in the summer there is a remission.
Men get sick more often than women. Very active seborrheic dermatitis develops in adolescence with hormonal imbalances characteristic of puberty. Elderly people rarely get sick, due to the extinction of sexual function, cases of seborrhea almost never occur.
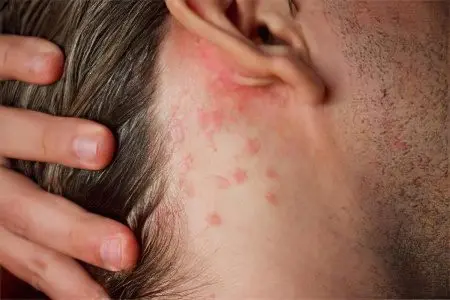
Seborrhea begins with a violation of the sebaceous glands. They are located all over the skin, except for the soles and palms. The secret of the sebaceous glands is a very important component for the body, it contains fatty acids, carbohydrate compounds, cholesterol, vitamins, salts, bactericidal substances and hormones. Together with sebum, toxins leave the body, and a thin water-fat layer protects the skin and hair from drying out. A healthy person produces no more than 200 grams of sebum per week. In case of malfunction of the sebaceous glands, these norms are violated, in people diagnosed with seborrhea, the indicators are 1,5 times higher.
With seborrheic dermatitis, not only the amount of sebum secreted changes, but also its quality. The content of linolic acid decreases, this causes changes in the microflora of the skin. The skin begins to lose its antimicrobial properties very intensively, the protective functions weaken, which creates favorable conditions for inflammatory processes and the development of various infections.
The disease spreads to almost all areas of the skin that have sebaceous glands. The higher their density, the more lesions are observed. There are so-called seborrheic zones, they are mainly concentrated on the scalp, chest, back, face, shoulders and the area between the shoulder blades.
The appearance of signs of seborrhea should not be ignored. This is always an alarming sign, signaling health problems. There can be many reasons for the appearance and development of the disease, as well as consequences. Every tenth case of untreated seborrhea ends with baldness. This is the worst complication that can be avoided.
Symptoms of seborrhea
Common symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include:

Oily sheen on the skin;
Itching and peeling;
Dandruff;
Hair loss;
increased sweating;
Acne rash.
Depending on the type of disease, all these signs can manifest themselves in different ways. Sometimes they complement each other, combine, disappear and again remind of themselves. Such unpredictability in the behavior of the disease is quite understandable, too many factors and irritants are involved in its development.
Causes of seborrhea
There are many reasons for the appearance of seborrheic dermatitis, and all of them are associated with an imbalance in fat metabolism. The main culprit of the disease is a yeast-like fungus Pityrosporum ovale. Its presence in the body is considered normal. This is the most common inhabitant of the microflora, which does not prevent a person from living as long as he is in the so-called spore state. If a person is healthy and his immunity is in perfect order, the fungus is not afraid of him, but at any moment it can become active and harm. This is facilitated by hormonal, immune, endocrine disorders and stressful conditions. All these unwanted processes cause seborrhea.
The disease can be caused by serious physical exertion and malnutrition, there are risks of getting sick with climate change and inheriting pathology.
Other reasons are known, among them:
Mental disorders and neuralgic diseases;
Problems with the stomach and intestines;
Hormonal disbalance;
Urological problems (in men) and gynecological (in women);
Dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
vitamin deficiency;
Vegetovascular dystonia;
Bad ecology.
Types of seborrhea
Dry seborrhea
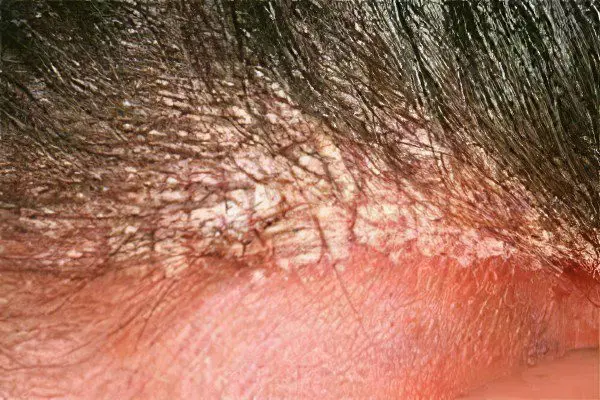
At the initial stage of the disease, the first signs of dry seborrhea appear, these are dandruff and pruritus. This type of seborrheic dermatitis responds well to treatment, but in its absence, the sebaceous glands are activated. Seborrhea progresses and affects new areas. Dry seborrhea is characterized by reduced secretion of sebum. The entire head is covered with small, dry scales. Hair becomes thin, loses its healthy appearance, breaks and falls out.
Dandruff is dry, crumbles easily, sometimes it stratifies and forms yellowish-gray crusts. All this is accompanied by itching. The skin only at first glance seems dry. The process of sebum production continues, it is released slowly and has a viscous consistency. From this, the superficial skin layer looks overdried, but the skin remains very sensitive.
Oily seborrhea
With a protracted course of the disease, in addition to severe peeling and severe itching, red plaques and spots on the skin can be observed. These symptoms are characteristic of oily seborrhea. This is the most common type of disease. With excessive secretion of sebum, a characteristic shine appears. The skin loses its elasticity, becomes shiny, easily inflamed and may be covered with red spots.
The very next day after shampooing, the hair becomes untidy, greasy, they stick together in strands, and oily scaly dandruff forms on the head. Trying to get rid of unpleasant external manifestations, patients often try to wash their hair, but they usually do not achieve the desired effect. Hair remains greasy, moreover, frequent shampooing activates the functions of the sebaceous glands, which makes the hair dirty even faster. All this is accompanied by a strong, sometimes incessant itching. The foci of inflammation cover a thick layer of scales and crusts. When combing, spotting is sometimes noticeable. The cells of the epidermis do not have time to mature, their protective functions are lost, as a result, the skin becomes thin and vulnerable, easily infected and injured.
Any load enhances the clinical manifestations of seborrhea. Serious changes in the structure of the hair lead to their active loss. If you do not contact a dermatologist in time, the disease will progress. After a disease, restoring hair growth is extremely difficult.
There are known cases of mixed seborrhea. This species is characterized by a combination of signs of dry and oily seborrhea.
Complications and consequences of seborrhea
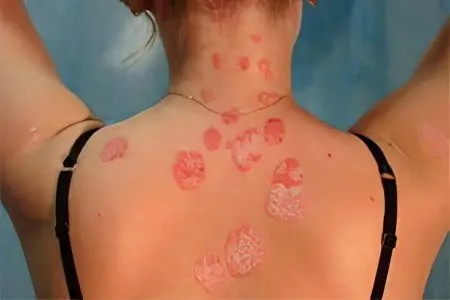
Incorrect and untimely treatment of the disease can seriously affect the condition of the skin. Complications can manifest themselves in different ways, the nature of the symptoms depends on the age of the patient. So, the consequences of seborrhea, transferred at a transitional age, can haunt a person throughout life. Any hormonal imbalance leads to an exacerbation of the disease, which is accompanied by pore enlargement, the appearance of black spots and youthful acne.
During the period of maturity, the patient continues to develop acne, there is a high probability of developing such complications as seborrheic eczema. Secondary bacterial infections of the skin can join seborrhea: folliculitis, boils, pyoderma. Metabolism at this age slows down, the ability of tissues to recover decreases, all this can result in scarring of inflamed pores. “Craters” appear on the skin, they look like depressions, have a reddish tint and turn pale with time. The surface of the skin is leveled very slowly, it remains bumpy and greasy for a long time. If left untreated, seborrhea can spread to smooth skin.
For the elderly, the consequences of seborrheic dermatitis are manifested in the formation of a large number of papillomas.
Answers to popular questions
Seborrhea is one of the most common diseases. It always brings discomfort and a lot of inconvenience. The desire to get rid of the disease as quickly as possible often leads to mistakes and uncontrolled use of drugs and drugs that can only harm. It is advisable to avoid such phenomena and contact specialists who know how to properly treat the disease. With seborrhea, individual therapy is prescribed.
Let’s highlight the most pressing issues that are most often of concern to those who have already encountered a problem or want to protect themselves:
What causes seborrhea in adults? This is the most important and urgent question, the answer to which doctors find during the examination of the patient. A treatment plan is drawn up only after the cause has been identified. There can be many provoking factors, all of them are not fully understood, but thanks to scientific research in the field of seborrhea, it was possible to identify the main causes and their role in the development of the disease.
Is seborrhea associated with excessive or, on the contrary, insufficient production of sebum? Many dermatologists who specialize in the treatment of this disease are sure that seborrhea develops for several reasons at once. Everything is important: hereditary predisposition, the state of the nervous and endocrine systems, the level of hormones and the patient’s lifestyle. This statement is supported by clinical studies. It turned out that even with a normal amount of sebum secreted, a person may experience symptoms that characterize seborrheic dermatitis. Intense excretion can be provoked by yeast fungi that inhabit the scalp and produce chemicals that cause irritation.
What do these types of seborrhea “dry”, “liquid”, “mixed”, “thick” mean? Seborrhea manifests itself in different ways, the symptoms may vary. Previously, the terms “fat”, “dry”, “mixed”, “thick” seborrhea were very often used in diagnosing the disease. Nowadays, the situation and approaches have changed, the division of seborrheic dermatitis into types is losing its significance. At least in foreign medical sources, all these concepts and designations have not been used for a long time. Seborrhea is not divided into types, types and stages, since this is not considered important when choosing treatment tactics.
Seborrhea is a fungus, so is it contagious? Is it transmitted from person to person? Seborrhea is indeed a fungal disease, but it is not contagious and is not transmitted from person to person. A microscopic fungus can influence the development of the disease, but it is present on the scalp and in healthy people. This is part of the human microflora, the fungus promotes the breakdown of fat and saturates the scalp with fatty acids. Hypersensitivity to these fungi can lead to inflammation, it can be caused by various reasons.
Is seborrhea related to hormonal imbalance? There is a connection, according to recent clinical studies, the development of seborrhea can be caused by hormonal disorders. However, for many who have experienced seborrhea, problems with hormones and the endocrine system may not be observed. If, in addition to signs of seborrheic dermatitis, other problems caused by hormonal failure are found, be sure to consult a doctor. This may be a violation of the menstrual cycle, the appearance of acne, difficulty conceiving. All these deviations in combination with seborrhea require careful examination and control. If the connection between seborrheic dermatitis and hormonal disorders is confirmed, the doctor may prescribe contraceptives that block the action of androgens.
Seborrhea can be a sign of poor immunity or serious diseases of the internal organs? There is a possibility. Very often, it is serious chronic diseases, neuralgic disorders and weakened immunity that cause the development of seborrhea, but their presence should not always be accompanied by this skin disease. There are cases when the disease occurs in people who are physically and psychologically healthy.
Can the development of seborrhea be associated with stress? This is possible, since psychological health always affects the state of a person. Some experts are sure that any deviations provoked by overwork, irritability and negative emotions can call for certain exacerbations characteristic of seborrhea.
Could there be some connection between seborrhea and the medications I’m taking? According to clinical observations, some drugs can actually provoke the onset or exacerbation of the disease. Before you start taking medication for seborrhea, tell your doctor what you are taking. This information will help in choosing a course of treatment. Particular care must be taken if the list of drugs taken includes buspirone, ethionamide, chlorpromazine, fluorouracil, cimetidine, haloperidol, griseofulvin, lithium preparations, interferon alfa, psoralen.
Is seborrhea hereditary? There is a predisposition, in some families seborrheic dermatitis can actually develop in parents and be transmitted to children.
How is seborrhea treated?
A complete cure for seborrhea is possible, but this process can take a long time. Relapses are very common, even after stopping treatment and eliminating symptoms, itching, flaking and dandruff may recur after some time. The patient will need patience and self-control.
Treatment should be comprehensive, it always begins with a medical examination by a dermatologist or trichologist. For an accurate diagnosis, it is enough for the patient to take tests (biochemical and blood for hormones). Based on the research data and examination of hair and skin, the doctor makes a conclusion. If deviations are identified and the doctor knows the cause of the disease, the necessary appointments are made. But not everything is so simple in the case of seborrheic dermatitis, since there can be several provoking factors at once. Treatment involves not only the elimination of external defects, it is very important to normalize the work of all systems and organs that can cause pathology. This may require additional tests and participation in the treatment of several specialists at once.
Local treatment
The success of the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis depends on skin care, it must be correct and regular. A doctor can help with advice.
With dry seborrhea, the use of salicylic acid, compositions with sulfur, cinchona bark emulsion is effective. Creams containing vitamin F help well. By reducing skin dryness, they improve blood circulation and increase skin elasticity. The patient may be prescribed drugs such as caratolin, aevit, propolis, biotin. In nutrition with dry seborrhea, preference is given to foods with a high content of fatty acids. These are soy, vegetable and corn oils.
Treatment of oily seborrhea involves the use of alcohol solutions containing sulfur, resorcinol, salicylic acid. In cases where the scales tightly cover the scalp, they are softened with oils, sulfuric ointment or petroleum jelly. After that, the skin is treated with antifungal drugs.
Particular attention should be paid to seborrhea hygiene products, in particular shampoos. Some of them can provoke inflammation and irritation, which can negatively affect the course of the disease. It is recommended to use products that have a therapeutic effect. They do not cause allergies, do not contain dyes, fragrances and preservatives, have soothing properties and perfectly restore the structure of damaged hair. In order to avoid relapses, treatment with shampoos may continue for several months.
Depending on the type of seborrhea, the patient may be offered:
Antifungal containing nizoral.
Antibacterial, which include zinc pyrithione and octopirox.
Exfoliating, acting like a treasure. They contain sulfur and salicylic acid and have an excellent anti-aging effect.
Shampoos rich in herbal extracts. Such products remove excess fat from the scalp and have an anti-seborrheic effect.
Physiotherapy for seborrhea
In complex therapy, physiotherapy procedures are used as additional measures. The procedures improve microstimulation, relieve itching and promote more active detachment of the epidermis.
The most effective for seborrhea are:
Cryomassage;
Darsonvalization;
Massage with liquid nitrogen;
Mesotherapy;
Ultraviolet irradiation;
Phytotherapy.
The problem of treating seborrhea is that fungi on greasy skin multiply very quickly and easily adapt to medicinal preparations of both traditional and traditional medicine. To achieve results, it is desirable to change and combine means and recipes. Any corrections in treatment are made under the supervision of a physician.
Author of the article: Herman Olga Leonidovna, trichologist, specially for the site ayzdorov.ru









