Contents

Most adults consider scarlet fever to be exclusively a childhood disease. Actually it is not. The likelihood of infection remains high even in those who have long ceased to be children. Adults with weakened immune systems are more likely to become infected. In this case, the disease will have an erased character in them, it is manifested by inflammation in the throat, intoxication of the body, and a skin rash, which passes very quickly.
Sometimes scarlet fever is severe. Most often this occurs when treatment is not started on time. Therapy is delayed due to the fact that a person does not go to the doctor and does not find out about his diagnosis in time.
The causative agent of scarlet fever is S. Pyogenes, a toxigenic hemolytic group A streptococcus. This microbe is dangerous for toxic damage to the heart, kidneys, joints and other internal organs. The rash that always occurs with scarlet fever is an allergic reaction of the body to the penetration of an infection into it.
What is scarlet fever?
Scarlet fever – This is an infectious disease that is manifested by a state of general intoxication, inflammation of the tonsils and is accompanied by a rash and fever.
How is scarlet fever transmitted?

The transmission of scarlet fever is carried out by airborne droplets, or through household items. You can get infected even by touching the skin of the patient, if there are injured areas on the body of a healthy person, for example, cuts and abrasions. There are several serovars of group A streptococcus, so if an adult has not encountered them before and has not developed immunity, he will definitely get sick.
Scarlet fever most often develops in people who live in temperate climates. The peak incidence occurs in spring and autumn. The microbe enters the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, through microdamages on the skin. The main route of transmission of the disease is airborne. However, the contact-household variant of the spread of infection should not be excluded.
Scarlet fever is spread by talking, coughing and sneezing.
The disease can be transmitted through dirty hands, household items, dishes, toys.
Sometimes infection occurs through close contact with the skin of an infected person.
Not only patients are contagious, but also carriers of the infection. Moreover, about 20% of people are carriers of scarlet fever. They can release a microbe into the external environment for a year.
If a person falls ill with scarlet fever, then his body first met with streptococcus. Infection can happen again, then a rash on the body will not appear. The main symptom of scarlet fever is angina. Antitoxic immunity is developed to any type of streptococcus, and microbial immunity only to a certain serovar of the bacterium. Therefore, it is possible to re-infect with a sore throat, but the rash will not appear.
Symptom scarlet fever
Children aged 4-8 years suffer from scarlet fever very often. The peak incidence occurs in winter. Since the immunity of most of the adult population of the country is weakened by one or another factor, the likelihood of catching an infection from a child remains at a high level.
The incubation period for scarlet fever is 3 to 7 days. The disease manifests suddenly, the symptoms gain full strength within a few hours. In the next 4-5 days, they will intensify. Recovery occurs only after 2-3 weeks. A person will be contagious already in the first hours after the onset of the main symptoms of the disease. Sometimes it also happens that a person recovers and ceases to pose a danger to others, and sometimes, on the contrary, is a spreader of the disease for a long time.
The main symptoms of scarlet fever:
High body temperature.
Headache.
Loss of appetite.
Increased drowsiness, increased fatigue.
Increased heart rate.
Nausea and vomiting. These symptoms occur when scarlet fever is severe.
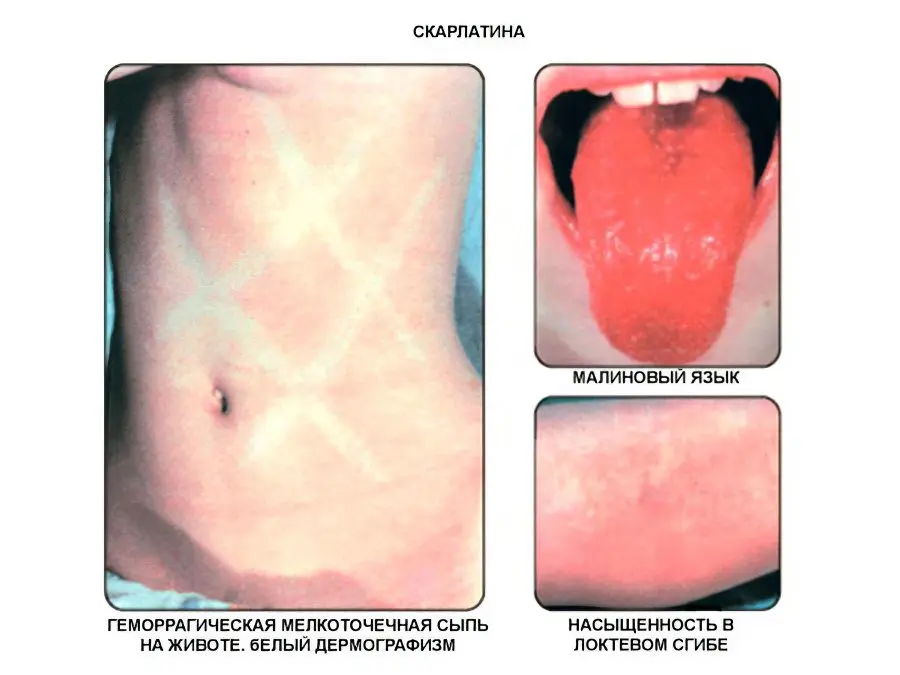
After the temperature rises, a rash appears on the skin on the second day of illness. It is small, red, located on the face, on the neck, on the folds of the arms and legs, on the abdomen, on the chest and on the hips. The rash itches, so many people perceive it as a manifestation of an allergy or toxodermatosis.
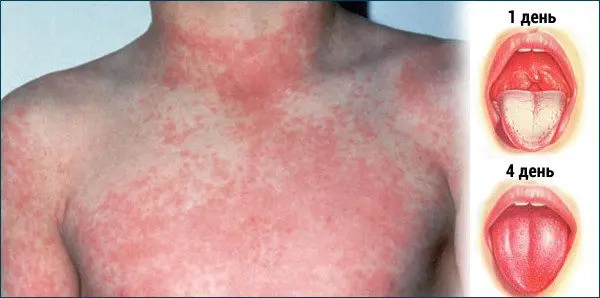
The patient’s cheeks are covered with red spots, the tongue becomes crimson, and the nasolabial triangle turns pale.
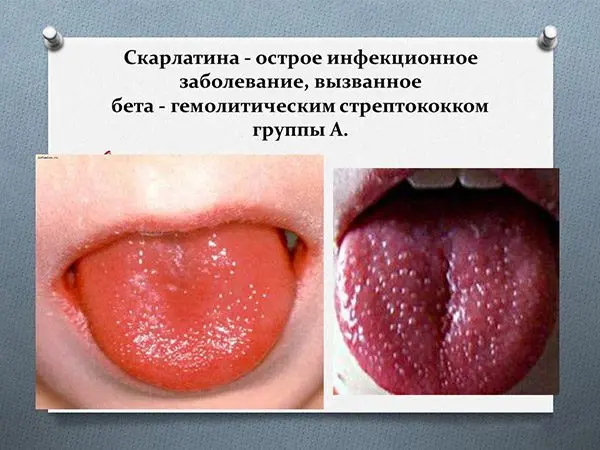
You can distinguish the rash characteristic of scarlet fever in a simple way. It is enough to press on it with the palm of your hand. This will cause it to disappear for a while and then reappear.
The rash passes quickly. Within a week, even traces of it will not remain on the skin. However, after 7-14 days, the skin on the palms and feet will begin to peel off, moving away in layers. On the body, the dermis leaves with small scales.
Sore throat, sore throat symptoms.
When performing a blood test, an increase in the level of eosinophils, neutrophilic leukocytes, ESR will be detected. Hemoglobin during this period may fall. The disease responds well to treatment with antibiotics from the penicillin group. In combination, all these signs allow you to accurately diagnose.
Adults with mild illness can be treated at home. The doctor will prescribe an antibacterial drug for a period of 10 days. Bed rest will be required for a week.
Hospitalization is required for patients with severe disease. In 52% of cases with complications, people aged 16-20 years are brought to the hospital. In 47% – these are persons aged 21-30 years. Only 1% of hospitalized patients are aged 31-40 years.
It is known that 28% of adults with scarlet fever are misdiagnosed.
The disease can be confused with pathologies such as:
Rubella – in 20% of cases.
Measles – in 19% of cases.
Infectious mononucleosis – in 14% of cases.
Pseudotuberculosis – in 13% of cases.
Angina – in 12% of cases.
Allergy to drugs or toxicoderma – in 9% of cases.
SARS – in 5% of cases.
Food poisoning – in 5% of cases.
Adenovirus infection – in 2% of cases.
Meningitis – in 1% of cases.
Despite the development of medicine, in some institutions to date, there are no express tests to determine scarlet fever. Therefore, doctors focus solely on the symptoms of the disease. This explains the misdiagnosis. Accordingly, the treatment will also be chosen erroneously.
Complications of scarlet fever in adults

If the infection had a mild course, then it will not be able to provoke any complications. Patients with severe scarlet fever are at risk of developing serious health consequences. They happen in 5,4% of cases.
These complications include:
Myocarditis and endocarditis
Kidney inflammation
Pneumonia
joint inflammation
Otitis and sinusitis
Children often tolerate scarlet fever easily, while in adult patients the risk of developing severe complications is high.
Sometimes toxic-septic shock can develop:
Intoxication of the body is growing rapidly, body temperature rises to high levels.
After 2 days, the patient manifests heart failure.
The skin is abundantly covered with hemorrhages (bruising), which will be concentrated in places where the rash accumulates.
Lymph nodes become inflamed.
The person’s hands and feet become cold.
Body temperature drops, blood pressure drops.
The pulse slows down. Sometimes you can’t feel it.
There is no urination.
The end of toxic-septic shock is the death of the patient.
Scarlet fever treatment

If an adult feels satisfactory, then he can receive treatment at home. The doctor prescribes penicillin antibiotics for up to 10 days. If the patient does not tolerate them, then it is possible to use cephalosporin drugs or macrolides.
Bed rest will be required for a week. The throat must be treated with antiseptic compounds, including decoctions of herbs (chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus).
To relieve intoxication from the body and reduce the rash, anti-allergic drugs are used, for example, Zirtek or Cetrin.
After completing the course of taking antibiotics, you will need to take drugs to restore the intestinal microflora, for example, Acipol, Hilak Forte or Rioflora immuno.
Is quarantine required for scarlet fever? Prevention

Quarantine is the main preventive measure that will prevent the spread of the disease. The person is isolated from healthy people for up to 10 days. In preschool, quarantine is 2-3 weeks.
People with a severe form of the disease are placed in the hospital. Those children who have been in contact with a sick child should be under medical supervision for 17 days. They do not attend preschool institutions and primary classes. If they have already had scarlet fever before, then they can go to classes, but they must be under the supervision of a medical worker for 17 days. The apartment where the patient lives must be disinfected.
Steps to take in the family:
The patient should be placed in a separate room.
The patient should eat from a separate dish, which is thoroughly disinfected.
The patient’s belongings should be washed separately from the belongings of healthy family members.
Toys must be disinfected.
An infected person should be cared for by one family member.
The patient should not come into contact with other people.









