Contents
Scabies is one of the most common skin diseases caused by parasites. The first mention of the disease appeared 2500 years ago, in the writings of Aristotle and on the pages of the Old Testament. In ancient Greece, scabies belonged to a group of skin diseases called psora. The Romans called scabies scabies, and this terminology is used today.
The etiology of the disease and the causative agent (scabies mite) became known only during the creation of optical magnification. In 1687, the Italian physician Giovan Cosimo Bonomo first described the symptoms of the disease and its etiology. A detailed description of the etiology and pathogenesis of scabies was compiled by the German physician Ferdinand Gebra in 1844.
Despite the prescription of scabies, the disease still exists today. Moreover, atypical forms with different symptoms and pathogenesis are noted.
Etiology of the disease
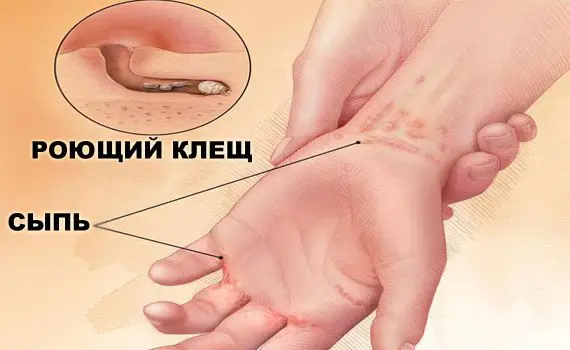
The causative agent of the disease is the scabies mite Sarcoptes Scabiei. Such mites are absolute parasites that live in human skin and spend most of their lives there. The period of the life cycle of the parasite is determined by the level of its nutrition and reproduction. Conventionally, such a cycle is divided into 2 stages – short cutaneous and long intradermal.
Infection is possible in case of close contact with the parasite. The introduction of the parasite into the skin can take from 10 minutes to an hour. Intradermal passages for moving the tick are determined by the individual characteristics of the structure of the skin, the type of hair growth, and the activity of the regenerative abilities of the skin. Typically, such moves are localized in the area of the hands, wrists, feet and elbows with the greatest thickness of the stratum corneum. The mite feeds on the horny scales of the human epidermis.
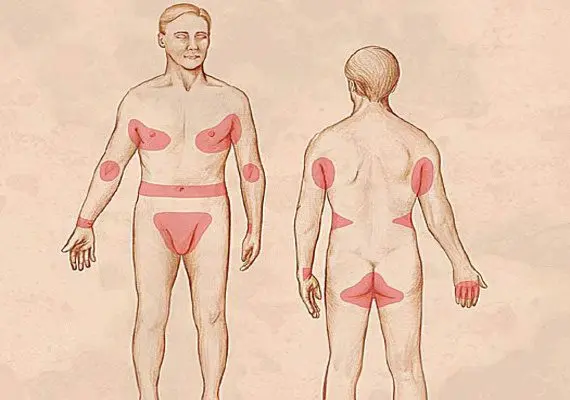
Interestingly, the area of the skin where scabies mites are located is characterized by a lower temperature level of 2-4 ° C. Intradermal passages for moving the tick are located in areas with minimal or no hair growth. The active introduction of optics in medicine made it possible to study in detail the life cycle of parasites. So, the epidermal passages, which are laid by female parasites, are filled with liquid in the form of a postal secret. This is the most favorable environment for a comfortable habitat for ticks and breeding. Moves without the content of a secret attract females who are on the verge of completing their life.
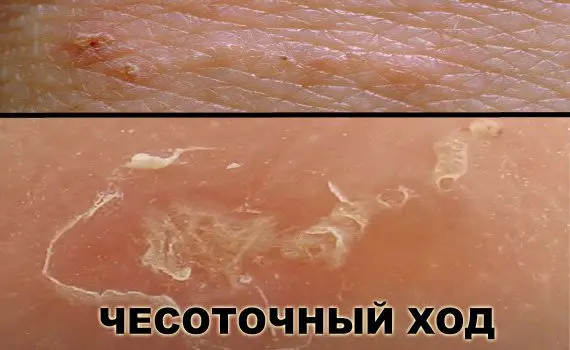
The presence of an incubation period in case of infection by a female is not detected. Immediately upon penetration into the skin, the female begins to pave the way for breeding offspring. If the infection came from the larva, then the duration of the incubation period is usually about two weeks. The most characteristic manifestation of scabies is itching, which is associated with the process of sensitization of the body to the pathogen. Such a symptom usually appears a month after infection, and in the case of reinfection, within a day. Dangerous for humans are the waste products of the tick – feces, glandular secretion.
Where and how can you get scabies?
Scabies can be contracted through close bodily contact. The source of infection in the disease is the carrier of scabies and a group of people who have been in contact with the sick person. The pathogen is most active at night, so the risk of infection during this period is highest. This method of infection is considered a direct route of transmission. Persons living together, especially those with a common bedroom – hostels, barracks, are considered a dangerous focus.
An indirect method of infection through household items is also possible, which is associated with a high level of parasitic index – from 50. Extrafocal infection occurs in hotels, saunas, trains, where there is constant contact of people with common household items.
Symptoms of different types of scabies
The disease is constantly progressing, which is associated with the emergence of new forms and manifestations of infection.
Today there are the following types of scabies:
Typical view;
Scabies cleanliness;
Scabies without the presence of moves;
Type of scabious lymphoplasia of the skin;
Scabious erythroderma;
Scabies associated with complications – secondary pyoderma, dermatitis, urticaria;
Norwegian scabies;
Pseudosarcoptosis.
[Video] What SCABIES looks like (Pic 1-8). Symptoms of scabies:
Complications of scabies
Other diseases, such as pylderma or dermatitis, can join scabies. Less commonly, scabies is accompanied by urticaria with eczema of a microbial nature. According to nosological forms, staphylococcal pyoderma, osteofolliculitis and deep follicles are most common. Impetigo appears in the area of frequent formation of passages, osteofolliculitis – in the place of tick metamorphosis, and microbial eczema – in the area of scabious lymphoplasia of the skin.
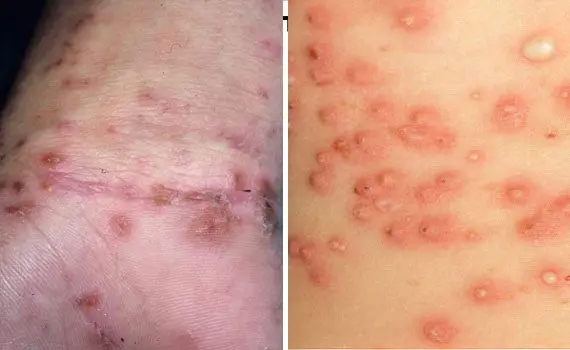
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of the disease is established by an infectious disease specialist or dermatologist based on the symptoms and clinical course, epidemiological data and laboratory tests. Itching that worsens at night, linear scratching, papules, and Ardy’s symptom are reasons to suspect the presence of scabies. A prerequisite for the diagnosis is the detection of the pathogen.
Diagnostic methods:
Staining method for diagnosing scabies. The alleged scabies course is smeared with an alcohol solution of iodine or aniline dye. With a positive diagnosis, the scabies course acquires a color.
Oil vitropressure is carried out by pressing a glass slide in order to bleed the capillary bed. Mineral oil is applied to enhance the effect.
Extraction of ticks with a disposable sterile needle. The needle opens the projection of the passage with the presumed placement of the tick, which is removed from the skin and placed on a glass slide for further microscopic examination.
Scraping to detect scabies. In this case, a drop of 40% lactic acid is applied to the surface of the skin, and then the loosened area of the skin, together with the pathogen, is scraped off for further microscopic examination.
Dermoscopy is an effective research method that allows you to accurately diagnose the disease, especially with a typical form.
Laboratory diagnostic methods confirm the presence of scabies if a tick, larva, eggs, nymph, egg shells are found. If excrement is found, a repeated laboratory study from other areas of the skin is necessary.
Differential diagnostics
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases:
With atopic dermatitis, in which the leading symptom is also itching. When studying the localization of the affected foci, an accurate diagnosis can be made. In scabies, the leading is the definition of the pathogen and the presence of scabies. Atopic dermatitis is localized on the flexor and extensor surfaces, more often in childhood.
Diagnosis with seborrheic dermatitis, which is characterized by the formation of scales and papular rashes. In this case, the lesions are localized in areas with abundant skin secretions – the forehead or scalp. The feeling of itching is weak or absent.
Diagnosis with contact dermatitis, in which vesicles and papules form in areas with hyperemic skin. The chronic form of dermatitis is characterized by peeling, but is not accompanied by pronounced itching, like scabies.
Non-bullous impetigo, characterized by the appearance of honey-colored crusts. Due to the possibility of infection of scabies, these diseases can exist simultaneously.
Diagnosis with acropustulosis in children. In this case, vesicles and papules appear in the area of the hands, feet and wrists with the possibility of recurrence. The main difference is the absence of scabies and pathogen.
Prognosis of the disease
With timely detection, the prognosis is favorable and does not pose a threat to life and health. A timely visit to a doctor allows you to eliminate all the manifestations and consequences of scabies, with a full restoration of working capacity. Most often, complications are observed in childhood in the form of pyoderma or sepsis. Norwegian scabies has a special course, which is difficult to treat and leads to intoxication of the body with damage to the cardiovascular system. Timely access to a doctor is the key to rapid diagnosis of the disease and effective treatment.
Treatment of scabies
The type of treatment depends on the goal chosen by the attending physician. There are the following types of therapy:
specific;
Preventive;
Therapeutic.
Specific therapy is necessary if the diagnosis is confirmed laboratory and clinically when pathogens are detected.
Preventive therapy is carried out for persons who have been in contact with the sick person, even in the absence of clinical symptoms in the close environment. It is for the following groups:
For family members, as well as close associates in the form of a nurse or nanny under conditions of close contact or joint sleep in the same bed. Another condition may be the presence of children with scabies who are in contact with all family members, as well as in the case of detection of radiating foci with two cases.
For members of an invasive-contact group with a shared bedroom or several sick people.
Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy is carried out 3 days after treatment, and then repeated after a week and a half months.
Trial therapy is possible in cases where the doctor suspected the presence of the disease, but the pathogen was not detected during the diagnosis of the infection.
The principles of therapy include the following approach:
Simultaneous treatment of the patient and the entire environment, who have symptoms of infection.
For more effective therapy, anti-scabies preparations are applied in the evening, when tick activity is most noticeable.
Applying anti-scabies in children to all parts of the body.
Mandatory hand washing before and after each application of anti-scabies.
Exposure of the drug for 12 hours, including at night.
Treatment of complications is carried out simultaneously with the main therapy.
After the end of therapy, disinsection of bed linen, household items, shoes is carried out.
Anti-scabies preparations are applied by rubbing, especially in areas of favorite localization of ticks. Each hand wash should be followed by a re-treatment with an anti-scabies agent. When complications are attached, treatment is carried out by lubricating the affected areas, but not by rubbing. To loosen the epidermis before applying the funds, you must take a hot shower with a washcloth. For the treatment of scabies, preparations based on sulfur, benzyl benzoate, permethrin, pyrethrin, Peruvian balsam can be prescribed. The chosen therapy approach depends on the form of scabies, its symptoms, complications, and is selected by the doctor individually, taking into account laboratory data and the clinical picture.
[Video] SUPER REMEDY FOR SCABIES:
Диспансерное наблюдение и лечение пациентов, у которых обнаружена чесотка;
Изучение окружения пациента и всех бытовых контактов;
Ликвидация очагов чесотки, с применением дезинсекции – обеззараживание постельного белья и бытовых предметов;
Профилактический осмотр детского населения, ограничение заболевших на период до полного восстановления.









